Why is the water dirty. Why did the water in the well become dirty and smell or disappear altogether
Often in summer cottages where water is supplied by a well or a well, the water becomes muddy for no apparent reason. Usually the water becomes cloudy in shallow wells. If the well is dirty water, you need to do something urgently. You can defend it, filter it, but it is better to find the cause of the pollution and try to solve the problem faster.
Turbid water is a fairly common nuisance faced by summer residents, but you can cope with the problem on your own
Causes of water pollution in a well or well
- If the sealing of joints, joints, walls of the mine is broken, particles of sand and soil fall into the water, making it cloudy.
- There may be dirty water in a well in a country house or in a private house if the well is located in “floating” soil and liquefied sand falls into the water under pressure.
- If the aquifer is contaminated, water can be drunk only after installing additional filtration systems.
- A pollution source can also be found inside the mine, in this case the water changes color - it becomes brownish, green, black. Well cleaning will help.

A well that needs to be cleaned
- Water can turn green from an excess of microorganisms. To prevent contamination of the source, a sealed cover must be installed on the head. When stagnating, regular cleaning and disinfection will help.
- Often the water in the well acquires a metallic taste and a rusty color. This means that the aquifer contains a large amount of iron. In this case, there is no point in cleaning, you need to install a filtration system in the house.
- People living outside the city noticed that water often becomes turbid in wells in the spring. This is due to abundant snow melting and spring rains. Moisture remaining in the upper layers of the soil seeps into shallow wells. Unheated earth prevents its penetration into the deep layers of the soil.
Methods for cleaning dirty water in a well
To take action, you need to establish the cause of the pollution. If the overhead runs between well rings, at the joints, it is necessary to block its penetration. You can check whether you have done the job correctly after the first heavy rain - if the water remains clean, everything is done correctly.
The following set of works will help to purify water for any type of pollution.
Required:
- Pump all water out of the shaft using a pump.
- Go down to the well on a cable and brush to clean the walls of dirt and silt.

Descent into the well using a mine cleaning cable
- Disinfect surfaces from bacteria.
- Scrape silt and debris from the bottom.
- Seal all joints and cracks.
- To protect a well or a well from precipitation from the outside, make a clay castle.
With proper arrangement of the well, a clay castle is made during digging, but it can be done later.
How to make a clay castle
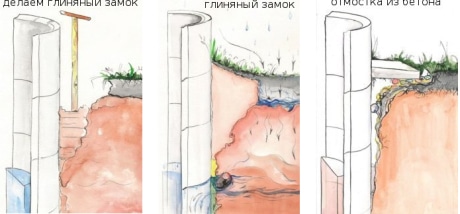
The diagram shows how a clay lock protects a well from moisture from outside.
The upper well ring needs to be dug out, in a circle around the upper ring we make a trench about 50 cm wide and 1.5-2 m deep. We clog the resulting space tightly with a layer of clay, and make a bias on the surface from the well.

Clay lock - reliable protection against moisture penetration from the outside
Disinfection as a cleaning method
Disinfection is a necessary measure to maintain clean water. The procedure is carried out after general cleaning.
It is necessary to determine the volume of water in the well. If it is built from concrete rings diameter and height of about 1 m, the volume of water per ring is about 700 liters. By the number of rings it is easy to determine the total volume of liquid.
If there is a lot of water, it is pumped out before disinfection begins. The walls are treated with a solution of bleach. 20 mg of dry matter are taken per 1 liter of water. For processing, you can use a long stick or a mop by wrapping a rag on it. The solution can also be sprayed.

Chlorine lime - an effective tool for cleaning wells from siltation and bacteria
When the well is filled again, a solution is poured into it: 200 mg of bleach are taken per liter of water. Use clean dishes and cold water. Lime should be infused in water for some time, then the solution is poured into the well, mixed. It is convenient to use a bucket for mixing. Everything needs to be processed: both the inside of the house and dry well rings. Wear a respirator or mask.
After mixing, cover the head with plywood or a metal sheet, otherwise the chlorine will evaporate and leave the well for a day. After a day, the procedure is repeated, after which the water is pumped out of the mine until the smell of chlorine disappears. Usually you have to pump out several times.
Attention! When disinfecting, do not drink water!
Manganese can also be used as a disinfectant. Proportions: teaspoon per bucket of water. The solution also sprayed the walls and shaft of the well.
In what cases is disinfection carried out?
- With a constant intake of water. The soil sags during intensive watering in spring and summer. This leads to an increase in humidity, the growth of bacteria and fungi.
- If you are infrequent guests in the country, for example, come only on the weekend. Water with rare use of the well stagnates, which leads to the accumulation of sludge and bacteria.
Complete cleaning is required for any well at least once every five years, and sanitation - as necessary.
Keeping the well clean is a guarantee of the safety of well water. Specialists of specialized companies will help to avoid hassle and mistakes, who will perform the work as soon as possible in compliance with all the rules.
A rare summer resident was not bothered by the question of why dirty water comes from the well - unfortunately, this problem is widespread. Often the point here is not only the mistakes made during drilling, and not the poor-quality filters, but also the natural factors independent of you, related to the nature of the soil and the quality of groundwater.
What to do if the water from the well is dirty, and what measures to take to avoid this? How to clean a well with your own hands and minimize the risk of its further contamination? About everything in detail - on this page.
Causes of siltation of wells in the country
The main reason for the contamination of wells in the country is siltation, which leads to a decrease in the rate of flow of water instead of pumped out. Depending on the structure of the well, siltation can occur for various reasons. Wells come with a straight hole and with a filter.

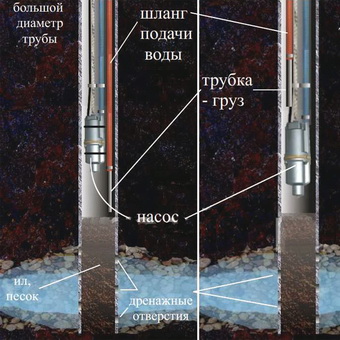
Wells with a straight hole are simpler to build, and therefore more common. In such wells, you can lower it to the bottom, because "then the wellbore is long and consists of several pipes of the same diameter. Pipes should be connected by welding or threaded connection.
One of the reasons why dirty water is in the well is its rare use. With low water consumption, the well can quickly silt. What to do when silting a well in this case? It is easy to clean using the same pump that is installed in it. To do this, first raise the pump to the surface, and then lower it in several steps to the bottom.
Other wells have in their lower part in the aquifer a filter made of two pipes of different diameters connected together with holes drilled in them. There should be a tightly wound wire spiral between the pipes. With such a device of the well, it is impossible to lower the pump to the very bottom, which causes its siltation. The same circumstance makes it difficult to clean the bottom.
The reasons for silting a well can be different - low water consumption, improper installation of the pipe while drilling a well, use of a self-priming (vacuum) pump, or vibration pump with an upper water intake, the presence of a filter with a diameter less than that of the main pipe.
At low water consumption, siltation occurs due to subsidence of clay, sludge and rust from the pipe at the bottom of the well, which leads to a decrease in the rate of water intake. With frequent water intake and high water consumption, the risk of siltation is significantly reduced.
However, if water is often not pumped out of the well, it is recommended that more water be pumped out in the summer. Sometimes you just need to turn on the pump for a while just to clean the system. This allows clay, silt and rust to settle to the bottom along with water. Sand in this case (especially clean, without impurities of clay, silt or rust) does not affect the quality of the well.
If the pipe was initially installed incorrectly when drilling a well (not in an aquifer or in a weakly aquifer), the pump will silt very quickly. Such a well is considered an open marriage, which cannot be corrected in any way, and it remains only to drill a new well or to deepen an existing one, which is as difficult as drilling anew.


When using self-priming (vacuum) pumps for water supply, which are used in wells up to 10 m deep, water is taken only from a depth of 8 m. Because of this, small particles gradually settle and accumulate on the bottom, and the bottom also becomes silted. To clean the blockages, you can use the same pump, which is located in the well. First you need to raise it up, and then gradually lower it to a depth, pumping sludge and other garbage with water.
When using a vibration pump with an upper water intake, siltation occurs for the same reason.
If a filter with a smaller diameter than the main pipe is installed at the bottom of the well, it will not be possible to lower the pump to the bottom of the well. As the well operates, such a filter will be filled with various deposits and will pass water poorly. This flaw is best eliminated immediately, even before the construction of the well by making adjustments to its plan.
How to clean a well from sludge with your own hands
There are several ways to clean a well and prevent further siltation. There are also special mechanisms and substances for cleaning.


You can use a water compressor, and with it, deposits from sand and silt can be easily removed with a stream of water under pressure. There is an air compressor that is used to remove soft particles, such as sludge. Another way to clean the well from sludge is to blow the pipe along its entire length using a vacuum plug. To clean the well, a so-called explosion is used - an artificially caused short circuit, as a result of which a bottle of gunpowder is lowered to the bottom of the well. As a result, the blast wave breaks up the blockage at the bottom of the well, and it is easy to pump it out with the pump along with water.
You can remove the blockage with acid, but use it with caution, since it can damage the filter or even the pipe itself. Therefore, you must strictly adhere to the instructions and observe the proportions of the solution that are indicated in it. Acid must be injected into the borehole at one time and left in the borehole for 2 days, and then pump water to completely clean the bottom.
It is found in water in the following forms:
Divalent - dissolved as Fe ions
Trivalent (although chlorides and sulfates are highly soluble in water, Fe ions
completely hydrolyzed into insoluble hydroxide Fe (OH) 3, which is in the form of a suspension or precipitate)
Organic iron (found in the form of various soluble complexes with natural organic acids (humates), having, as a rule, a colloidal structure)
Bacterial iron is a vital product of iron bacteria (iron is in their shell).
In underground waters, mainly dissolved ferrous iron is present in the form of Fe2 + ions. Ferric ferric iron appears after the contact of such water with air and in worn water distribution systems upon contact of water with the pipe surface. In surface waters, iron is already oxidized to a trivalent state and, in addition, is part of organic complexes and iron bacteria.
Of course, it does not matter to the consumer of the water in what form the iron is in the water, because it is faced with the consequences of a high iron content in any form. So, for example, the standard iron content in drinking water - no more than 0.3 mg / l.The iron content in water above the norm contributes to the accumulation of sediment in the water supply system, intensive painting of plumbing equipment.
Iron gives the water an unpleasant red-brown color, worsens its taste, causes the development of iron bacteria, sedimentation in the pipes and their clogging. A high iron content in water leads to adverse effects on the skin, can affect the morphological composition of the blood, and contributes to allergic reactions.
If, as a result of the analysis of water, the total iron content is found to be higher than 0.3 mg / l, such water needs to be adjusted by iron removal. The process of removing iron from water is based on iron oxidation reactions (2+). When underground water comes into contact with air, ferrous iron is oxidized by atmospheric oxygen to ferric, which hydrolyzes at a pH of more than 3.5. The colloid of iron hydroxide at pH 6.5-6.8 coagulates with the formation of a brown flocculent precipitate. With an increase in the pH of water, both the rate of oxidation of iron oxide to the base and the rate of hydrolysis and coagulation of iron hydroxide increase. Therefore, the liberation of water from iron is carried out at a pH greater than 7. For this purpose, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide are removed from the water by aeration.
Hardness of water
(total content of calcium and magnesium salts)
According to WHO standards, optimum stiffness drinking water makes up 1.0-2.0 mEq / L.
As a rule, the hardness level of natural waters is much higher than these values. In everyday conditions, an excess of hardness salts leads to overgrowing of heated surfaces in boilers, kettles, pipes, the deposition of salts on plumbing fixtures and their failure, and also leaves a deposit on the hair and skin of a person, creating a feeling of their “hardness”. When washing, interacting with surfactants of soap or laundry detergents, hardness salts bind them and require a higher consumption. In the food industry, hard water degrades the quality of products, causing salt to precipitate during storage.
In the energy sector, accidental short-term hard water entering the system very quickly destroys heat-exchange equipment and pipelines. Even a small layer of salt deposits on the surface of heat exchange equipment leads to a sharp decrease in the heat transfer coefficient and an increase in fuel consumption. Therefore, the water hardness for these purposes is limited by very small values \u200b\u200bof 0.03-0.05 mEq / L.
The processes of extracting calcium and magnesium salts from water in water treatment are called softening. Relatively selective removal of hardness salts is carried out by reagent softening(liming and soda liming), ion exchange(contact of water with strongly acidic cation exchanger in sodium form, as a result of which calcium and magnesium cations are extracted from the water, and replaced by sodium ion) and nanofiltration (membranes with a certain pore size are used that retain hardness salts).
Copper
Copper and its compounds are widespread in the environment, so they are often found in natural waters. Concentrations of copper in natural waters usually amount to tenths of mg / l, in drinking water they can increase due to leaching from pipes and fittings from materials. Copper gives water an unpleasant astringent taste in low concentrations, which limits its content in drinking water. This circumstance must be taken into account when choosing a source of water supply for the production of bottled drinking water. In case of detection of copper in drinking water in quantity more than 1.0 mg / ladjust the composition of water using cation exchange resins.
Organic compounds
Several thousand organic substances of various chemical classes and groups were found in the water of water supply sources.
Organic compounds of natural origin (humic substances, various amines) and technogenic origin (surfactants) are able to change the organoleptic properties of water (smell, taste, color, turbidity, foaming ability, film formation). which allows them to identify and limit the content in drinking water. At the same time, a huge number of organic compounds are very unstable and prone to continuous transformation, therefore, direct determination of the concentration of organic substances in drinking water is difficult, therefore, their content is usually characterized indirectly in mgOg / L, determining, for example, permanganate oxidation of drinking water.
The value of permanganate oxidation above 2 mgOg / l indicates the content in the water of easily oxidized organic compounds, many of which adversely affect the liver, kidneys, reproductive function of the body. When disinfecting such water by chlorination, chlorohydrocarbons are formed, which are much more harmful to public health.
If during the analysis of a water sample it was found that the value of permanganate oxidation is higher than 5, and even more so 2 mgOg / L, such water requires purification from organic contaminants.
Cleaning in this case is carried out in two ways:
1. extraction by sorption, coagulation and using membranes
2. oxidation (destruction) to carbon dioxide and water using chlorine, oxygen, ozone and hard ultraviolet radiation.
Nitrates
Nitrogen compounds in the form of nitrates and nitrites are present in surface and underground water sources. Currently, there is a constant increase in their concentration due to the widespread use of nitrate fertilizers, the excess of which with groundwater enters water sources. According to sanitary rules and regulations, in the centralized water supply, the nitrate content should not exceed 45 mg / l, nitrites - 3 mg / l.
Nitrates in a concentration of more than 20 mg / l have a toxic effect on the human body. The constant use of water with a high content of nitrates leads to diseases of the blood, cardiovascular system.
If nitrates are detected in the water sample in an amount higher than the norm, they resort to water purification using reverse osmosis or ion exchange.
Water that has deviations from the standards for the content of certain chemical elements and substances, as a rule, has a smell and aftertaste. Among the substances that affect the organoleptic characteristics, one can distinguish iron, manganese, sulfates, chlorides, residual chlorine, hydrogen sulfide, as well as most organic compounds.
Experienced specialists who have undergone special training in tasting water analysis will identify the smell and taste, and with the help of a quantitative chemical analysis, they will determine the components that can cause a taste and smell.
Dirty water in a well is a purely visual perception. The general. It’s almost impossible to determine what’s wrong with the water - it’s an analysis of it, but you can see that the water turned yellow, cloudy, green, covered with a film, cast with all the colors of the rainbow, and we say that the water in the well is dirty. It can be really banal dirty, because an improperly installed pump raises all the dregs from the bottom or melt water calmly penetrates a well when there is no lock. But it could be otherwise.
Turbid water in the well
Turbidity is one of the indicators regulated by SanPiN. It is measured in mg or EM (depending on the suspension for photometry). The permissible maximum is 2.6-3.5 EM / dm 3.
Turbidity appears due to the presence in the water of various suspensions of organic / inorganic origin. Seasonal floods, showers, melting ice / snow erode clay, sand, silt, and their small particles mix with water. These particles form a favorable environment for the development of bacterial colonies, the growth of algae. Reasons for the penetration of melt and flood waters into the well:
- waterproofing violation,
- lack of waterproofing,
- castle violation
- lack of lock.
In addition to plant and animal microorganisms (phytoplankton, zooplankton), turbidity is caused by:
- carbonates
- aluminum hydroxides,
- humic impurities
- oxides of iron and manganese.
Turbidity in itself only makes it clear that there are impurities in the water. The nature and composition of impurities is determined by analysis.
What to do if muddy water in the well
First of all, it is necessary to find out what caused the turbidity, that is, to conduct an analysis (you can do without analysis in 2 cases: a seasonal change in the state of water, improperly installed equipment). Based on the results of the study, take action.
If the water becomes cloudy during periods of floods, melting snow, rain showers, most likely, the problem is in a clay castle or waterproofing. They either do not exist at all, or everything is done incorrectly: melt or storm waters penetrate the clay (or freely pass through the soil, cracks in well rings) and mixed with well water - blurry particles of soil and create turbidity (the water is simply dirty).
For the device of a clay castle it is necessary (according to SanPiN 2.1.4.1175-02):
- dig around the head of the foundation pit 2 m deep, 1 m wide;
- thoroughly rinse and compact clay (or oily loam);
- fill the foundation pit with clay or loam;
- tamp clay / loam;
- make a blind area of \u200b\u200ba 2-meter radius with a slope of 10 cm from the well.
The blind area can be made of asphalt, concrete, stone, brick. SanPiN require source fencing.

Water color
Color depends on the content of ferric iron and humic substances in the water, whose concentration depends on:
- nature of soil
- the proximity of swamps and peat bogs,
- aquifers
- geological conditions
- other natural aspects.
It is not always possible to determine the color of the eye. The parameter is measured in degrees. The maximum permissible value for drinking water is 30 ०. The indicator does not indicate the nature of the pollution - it indicates only the presence of impurities.
What to do if there is yellow water in the well
The exact composition of the impurities will show the analysis, but the water turns yellow most often due to the high iron content. It is not the color of water that arises, but turbidity. It is desirable to clean the well shaft, an iron-absorbing filter must be introduced into the water supply system (often a regular paper filter is enough). It is necessary to periodically check the equipment - iron particles settle on the parts and disable the pump.

Green water in the well
If the water is green, then again, this is not color, but turbidity - phytoplankton. Wells without covers are at risk - the sun's rays contribute to the flowering of water. But phytoplankton is not the only reason for the green color: in addition to almost harmless algae, chromium gives the green tint to the water, which is already not so harmless. Analysis is needed. If the problem is in living organisms, disinfection will help. If it’s about chrome, the only true recommendation is to dig another source, onto another layer.
Costly water treatment does not always help. Masters do not dig wells if the MPC is exceeded - geological studies are carried out in order not to open a layer with a high content of chromium (and other harmful impurities). If you managed to dig a well with your own hands and get it right on a chromed formation, enter the cost of effort and time in the “loss” column and dig a new source, or rather, turn to specialists (so as not to make a colander out of an unfortunate formation, but still find a normal one water).
Why does the water smell in the well?
The smell appears for many reasons. Here, both organic matter and anthropogenic pollution:
- mold mushrooms
- sulfur bacteria (smells like hydrogen sulfide),
- glandular bacteria
- rotting plants
- pesticides
- chlorine,
- industrial drains.
What to do if the well smells of water:
- establish the cause of the smell (make an analysis),
- select the appropriate filter,
- to install a water treatment system.
Multi-filter water treatment system
Important! If you detect odor, discoloration, turbidity or any other changes in the state of water, you need to analyze it: chemical, microbiological, according to organoleptic indicators. Based on the results, disinfect, disinfect, install a filtration system.
Disinfection
SanPiN disinfection preparations are not regulated, any suitable ones (approved by the Ministry of Health) can be used, but chlorine lime or DTSGK (the two-base calcium hypochlorite salt - 3Ca (OCl) 2 x2Ca (OH) 2) is most often used
If the disinfection of the well is carried out according to indications, then it includes:
- pre-disinfection
- cleaning
- re-disinfection.
Pre-disinfection
First of all, the volume of water is determined - they multiply the height of the water column by the sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe well. Then a solution is prepared: bleach - 5 percent, DTSGK - 3 percent. This solution from the hydraulic console irrigate the walls of the mine (0.5 l per sq. M surface). The drug is added to water at the rate of 100–150 mg of chlorine (active! See contents on the package) per liter. Mix thoroughly and leave for a couple of hours, after closing the well with a lid.
Water is pumped out of the well, foreign objects are removed, silt. The walls are cleaned mechanically (they simply tear off everything that has grown) and, if necessary, repair (close the seams). After that, they are irrigated from the control panel with a solution (0.5 l per cubic meter of mine) for disinfection.
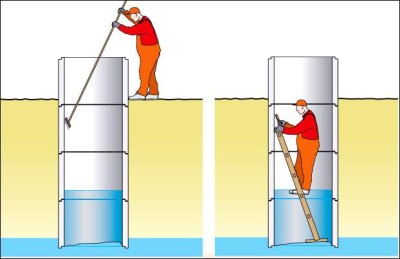
Wall cleaning
Re-disinfection
After cleaning, wait until the mine is full. Again measure the water column. Introduce a solution for disinfection into water (the norm is 100-150 mg of active chlorine per liter of water) and mix it for 10 minutes. Leave for 6 hours, after closing the well with a lid. After 6 hours, the well is opened and the water is checked for residual chlorine (by nose or using the iodometry method). If there is no residual chlorine, the solution is again introduced into the water, but less - about a third of the volume. Again close the well, leave for 3-4 hours. And so on until after the next check for residual chlorine the result is positive (that is, the chlorine remains, there is nothing more to fight with it). Water is pumped out to eliminate the chlorine odor.
If disinfection is carried out for the purpose of prevention, the well is cleaned and treated, bypassing the preliminary stage.
Well water disinfection
Disinfection is carried out when the microbiological analysis of water showed that it does not meet the requirements for sources of decentralized water supply (found bacteria, germs), and for preventive purposes (in foci of infections).
Water disinfection is carried out after disinfection of the well. Water is disinfected with a dosing cartridge (the simplest and most effective method) containing a preparation with chlorine. The amount of residual chlorine should be 0.5 mg per liter.
![]()
Dosing Cartridge Scheme
To calculate the required amount of the drug, the following parameters are needed:
- water volume,
- flow rate
- water intake
- chlorine absorption.
First, consider how much the drug will need, then select the cartridge (or several) of the desired capacity. The amount of DTSGK will be \u003d 0.07 volume of water + 0.08 flow rate + 0.02 volume of water intake + 0.14 chlorine absorption. The amount of bleach is twice as much. The calculation is valid for 52% (active chlorine content) DTSGK and 25% bleach. If the purchased product has a different content of active chlorine, it is necessary to recalculate based on the ratio of parameters.
The drug is placed in a cartridge, water is added and mixed until a homogeneous slurry is formed. Then a rope is attached to the cartridge, placed in a well at a level of 20-50 cm from the bottom, tying the rope to the tip.
The effectiveness of disinfection is determined by the residual chlorine of 0.5 mg / L. Then do a microbiological analysis of water - determine the number of colimorphic bacteria. Within a month, analysis is done at least weekly. After a month, they check the level of residual chlorine - if it has decreased or disappeared, you need to get a cartridge, wash it, fill it with a preparation and lower it into a well. Disinfection can be considered successful when after a month the level of residual chlorine will be equal to 0.5 mg / l.
Film on the water in the well
A film on water is the result of oil pollution. Oil products enter the well in three ways (the first and second are clearly preferable to the third):
- oil leaked from a depressurized pump - one of the elements (protection against dry running, for example) of some models is filled with oil, when for one reason or another the pump fails, the oil can get into water;
- accident - Annushka splashed oil in the wrong place (and not vegetable);
- petroleum contamination of the aquifer - sewage from gas stations, industrial effluents containing petroleum products, mixed with flood, storm or melt water and entered the reservoir by infiltration.
If the water in the well smells of kerosene, you need to understand that there is nowhere to take it from, and most likely the aquifer is polluted.

Film on the water in the well
Sorbents are used to clean the well from oil products. It is strictly forbidden to use detergents (this will simply replace one pollutant with another). Water from the well must be pumped out, the walls of the mine must be washed, the bottom must be cleaned of sediment, consisting of the remains of a large fraction of the petroleum product and the sorbent. Please note that when mixed with water, petroleum products form light, medium and heavy fractions, which makes it difficult to visually evaluate the cleaning efficiency: the film will disappear from the surface and the pollution will remain. We need a chemical analysis of water.
These measures will help get rid of accidental contamination, including those that have occurred due to a pump malfunction. If the aquifer is contaminated, a single cleaning will not help - you will need a water purification system or you will have to close the source (analysis will show the degree of pollution) and find an alternative. Naturally, aquifers clear for a very long time.
If an oil film is detected on the surface of the water, it is necessary (without delay):
- establish the cause of pollution;
- if the problem is in the pump, replace the equipment;
- limit water consumption to the maximum, without lowering the water level in the well prior to cleaning activities;
- clean the well;
- pump the well several times and flush the entire water treatment / water supply system.
Why did the water disappear in the well
Water disappears for several reasons:
- neighbors dug a deep source or drilled a well, revealing the same layer;
- banal drought, the reservoir was left without recharge;
- the mine is out of order (seams have spread, rings have shifted);
- siltation of a well.
If the pump worked correctly, sand and silt from the bottom did not pump out, but suddenly it started, most likely, a siltation of the well also occurred, but so far not so powerful as to completely block the water.

Empty mine
Well siltation
Digging a well is either possible or impossible.
You can dig out if:
- clay / sand got into the mine through the seams (the problem of wells made of concrete rings - diverging seams; a sure sign of the diverged seams - soil dips around the well);
- sand / sludge enters the mine through an unfinished hole for connecting the pipeline;
- seams are not closed (through the joints of rings without locks sand / silt penetrate into the well and settle at the bottom);
- water flows through the side seams, not through the bottom.
For the last item in more detail. There are two types of wells - in the first (full) water flows through the seams, in the second (incomplete) - through the bottom. In the wells of the first type, filters are installed on the seams (it is strictly forbidden to use rotting materials!) So that sand does not enter the mine. If this was not done on time, gradually the bottom level will rise (the speed of the process depends on water), and it will have to be lowered.
A rapid rise in the bottom indicates that the aquifer lies above it - at the level of the seam. In this case, you should immediately contact the specialists: they either dig a well, or raise the bottom by laying drainage. It will not be possible to determine what exactly should be done, whether it is possible to do anything at all without specific knowledge. Remotely, this is also unrealistic. If you come across a know-it-all, gang-banging on the phone, contact other masters.
![]()
Scheme of structures: complete, incomplete, with a sump
What wells can not be dug up
If the well is incomplete (water enters through the bottom), digging it out is useless: at first everything goes fine, but then liquid sand begins to flow into the mine - not water, just sand. This means that the well is on a quicksand. In this case, you can dig to graying, but not to victory - the reservoir equalizes hydraulic pressure and will equalize. Performing such a number is not only inefficient, but sometimes dangerous.
It is likewise futile to try to dig out a well when voids form around it. The sand is removed from the well, and it enters again (pressure is equalized) until the lower ring is displaced. Sand will joyfully pour into the torn seam, fill the ring, and this will end. Or the rings will sag, the seams, of course, will open, opening the way to the water tank, sand, clay. Occasionally, having spent a huge amount of effort, it is possible to dig a well, but after a couple of months the situation repeats.
Of course, you can use any of the above recommendations, bypassing the analysis of water, but in this case you must be prepared for the fact that the measures taken will be ineffective due to an incorrect interpretation of what happened. This happens often. Almost everything done by one’s own hands ignores probability theory, because it relies on Murphy’s law: if a well can, in principle, be silty and water is rotten and stink, this will certainly happen. If, digging blindly, they run the risk of running into a quicksand, it will run into him.