Sewerage legend. Projects: legend on drawings for water supply and sewage
WATER SUPPLY AND SANITATION
(lecture course)
WATER SUPPLY AND SANITATION
(Engineering networks and equipment of buildings and structures)
1. PURPOSE AND OBJECTIVES OF DISCIPLINE
The purpose of this discipline is to study the plumbing and sewage system as part of the engineering equipment and networks of buildings and structures in the field of civil and industrial construction.
The objectives of this discipline are:
a) to study the structure of the internal water supply and sewerage of buildings and structures;
b) to study the structure of external networks and water supply and sewage structures.
2. BASIC COMPONENTS OF DISCIPLINE
a) Federal component: Water supply and sanitation: water supply systems and schemes of populated areas; internal water supply of buildings and structures; internal sewerage of residential and public buildings; outdoor sewer networks and structures.
b) Regional component: the study of the device part of the sewer systems - drainage to protect against flooding of Siberian cities.
in) Institutional component: study of the plumbing and sewage system of a large city using the example of Omsk.
Tema I. Internal water supply to buildings
Internal water supply of cold (B1, B2, B3) and hot (T3) water.
Domestic and drinking water supply B1. Water quality requirements. Elements of the internal water supply: input, water meter unit, booster pump installation, distributing network of pipelines, water risers, floor pipelines, pipelines, water fittings. Calculation of the internal water supply: water consumption, economical speeds when selecting the diameters of pipelines, pressure losses in the water supply network, selection of water meters and pumps.
Fire water supply B2. B2 systems with fire hydrants. Automatic fire extinguishing systems: deluge and sprinkler systems.
Industrial water supply B3. Areas of water use in production. Water supply to construction sites. Water users at a construction site.
Water pipes hot water T3 Water quality requirements. Classification of hot water by location of the heat source. Elements of a centralized hot water system. Hot water circulation. Open (from the heating system) and closed (from water heaters) hot water supply systems.
Design, installation, testing and operation of internal water supply systems.
Theme II. Internal sewage of buildings
Internal sewage systems: separate (K1, K2, K3) and combined K1 + K3.
Domestic sewage K1. Elements of the internal sewerage: sanitary appliances and receivers wastewater, siphons and hydraulic locks, floor drain pipes, sewer risers, collectors in the technical underground, sewer outlets. Sewer pipes and fittings. Devices for cleaning the network. Ventilation of sewer networks. Construction of networks of internal sewerage. Calculation of the sewer network, restrictions on the flow rate, filling and slope of the pipes. Diameters of pipelines of the internal sewerage.
Rainwater drainage of buildings K2: internal gutters. Elements of internal drains. Design and calculation of internal drains.
Industrial sewage K3. Local installations for wastewater treatment and pumping.
Sewerage of solid waste: garbage chutes.
Design, installation, testing and operation of domestic sewage systems.
Theme III. Water supply: external networks and facilities
Water supply systems. Water consumers. Water supply schemes for populated areas and industrial zones (for example, Omsk). Norms and regimes of water consumption. Estimated costs and free water heads. Sources of water supply. Water intake facilities. Pumping stations. Water conduits. Water treatment plants: processes (cleaning and disinfection) and structures (sedimentation tanks, filters, reagent and chlorine facilities). Water towers and reservoirs. External water supply networks and structures on them. Water supply for industrial enterprises: direct-flow, with reuse of water and reverse water supply.
Theme IV. Sewerage: external networks and facilities
Purpose of the sewerage. Classification of sewage systems by wastewater composition. Sewerage schemes (for example, Omsk). Urban sewer networks and facilities on them: courtyard networks, street and district collectors, pumping stations, the main city collector.
Sewage treatment plants: types of wastewater treatment and applied technological schemes. Facilities for mechanical, biological treatment, wastewater disinfection and sludge treatment. The principle of operation of sedimentation tanks, aeration tanks, digesters.
Rain (storm) sewerage of cities. Drainage in industrial and civil engineering to lower the groundwater level: protection against flooding of Siberian cities. Connection of drainage systems to rain sewers.
4. Work plan for training sessions for the 5th or 6th semester
5. Practical classes (5 or 6 semester)
Get full text|
Lesson topic |
number |
|
|
Choosing a system and developing an internal water supply scheme | ||
|
Construction of a axonometric diagram of a water supply system | ||
|
Hydraulic calculation of water supply | ||
|
Selection of water meters and pumps | ||
|
Choosing a system and developing a sewage system for a building | ||
|
Construction of a axonometric scheme of sewerage | ||
|
Hydraulic calculation of sewer network | ||
|
Building a longitudinal profile of the yard sewer | ||
|
TOTAL hours |
6. LITERATURE
BASIC:
2. Guidelines for the implementation of coursework on the water supply and sewerage of a residential building / Compiled. –Omsk: SibADI, 19s. - (1st edition).
3. Guidelines for the implementation of coursework on the water supply and sewerage of a residential building / Compiled. –Omsk: SibADI, 20s. - (2nd edition).
4. Hydraulics, water supply and sewerage: a textbook for high schools / and others. –M.: Stroyizdat, 1980. –359 p.
5. Internal sanitary facilities. Part 2. Water supply and sewerage. - M .: Stroyizdat, 19s. - (Designer reference).
6. SNiP 2.04.01-85. Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings. –M .: TsITP Gosstroy of the USSR, 1986. –56 p.
7. SNiP 2.04.02-84. Water supply. External networks and facilities. –M .: Stroyizdat, 1985. –136 p.
8. SNiP 2.04.03-85. Sewerage. External networks and facilities. –M.: TsITP Gosstroy of the USSR, 1986. –72 p.
9. SNiP 3.05.01-85. Internal sanitary systems. –M .: TsITP Gosstroy of the USSR, 1986. –40 p.
10. GOST 21.601-79. Water supply and sewerage. - M .: Publishing house of standards, 19s.
11. GOST 21.604-82. Water supply and sewerage. Outdoor networks. - M .: Publishing house of standards, 19s.
ADDITIONAL:
1. SNiP 2.06.15-85. Engineering protection of the territory from flooding and flooding. –M.: TsITP Gosstroy of the USSR, 1986. –20 p.
2. Flood forecasts and calculation of drainage systems in built-up and built-up areas / VNII VODGEO: et al. –M.: Stroyizdat, 1991. –272 p. (Reference manual to SNiP).
3. Degtyarev in industrial and civil engineering. –M .: Stroyizdat, 1990. –238 p.
4. Sologaev from flooding in urban construction. Device and work. Omsk: Publishing house of SibADI, 19c.
Term paper on water supply and sewerage of a residential building consists of calculations and a graphic part in the amount of 1 sheet in A1 format (594x841 mm). On a sheet of whatman paper (or graph paper) are drawn and made out:
1) technical underground plan with drawing and designation of all pipelines and risers of the building's water supply and sewage systems, including water supply and sewage outlets - scale 1: 100 or 1: 200;
2) axonometric diagram of the internal cold water supply system with the application of stop and water fittings and designation of the input of the water supply, risers, pipe diameters and characteristic elevations - scale 1: 100 or 1: 200;
3) axonometric diagram of the sewer riser with the release to the first inspection well with the application of sanitary equipment and designation of the riser, discharge, pipe diameters, their slopes and marks of pipe trays - scale 1: 100 or 1: 200;
4) the longitudinal profile of the courtyard sewerage to the inspection well of the external network - horizontal scale 1: 500, vertical 1: 100;
Literature (minimum set from the library):
1. Water and Sewerage Program / Compiled. –Omsk: SibADI, 1991. –4 p.
2. Guidelines for the implementation of coursework on the water supply and sewerage of a residential building / Compiled. –Omsk: SibADI, 19s.
3. Hydraulics, water supply and sewerage: a textbook for high schools / and others. –M.: Stroyizdat, 1980. –359 p.
4. SNiP 2.04.01-85. Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings. –M .: TsITP Gosstroy of the USSR, 1986. –56 p.
NOTE:
A complete set of literature is listed in the WORK PROGRAM. A full set of literature is in electronic form in the program Lotus Notes (WATER SUPPLY) in the computer classroom of the auditorium on the 3rd floor of the 4th building of SibADI (at the Drama Theater).
ACCEPTED ABBREVIATIONS
B1 - domestic water supply.
B2 - fire water supply.
B3 - industrial water supply.
K1 - domestic sewage.
K2 - rain sewage.
K3 - industrial sewage.
St B1-1 - riser B1 in the order of numbering of the 1st.
St K1-1 - riser K1 in the numbering order of the 1st.
KV1-1 - water supply well B1 according to the numbering order 1.
KK1-1 - sewage well K1 in the order of numbering 1st.
l - the length of the pipeline in the design section, m.
N - the number of devices serviced by the settlement site.
U - the number of water consumers (residents).
P - the probability of the combined action of devices.
qC is the estimated flow rate of cold water in the area, l / s.
q0C - standard consumption of cold water by the device, l / s.
d - the inner diameter of the pipeline, mm.
V is the velocity of water in the pipeline, m / s.
i - hydraulic slope.
kL - coefficient of accounting for local pressure losses.
D H - pressure loss in the design section of the pipeline, m.
Legend
- the visible section of the pipeline B1 (open gasket).
- invisible section of the pipeline K1 (hidden gasket).
- intersection of pipes.
- The crane is folding.
- watering tap.
- float valve flush toilet bowl.
- mixer for washing or washbasin.
- faucet with shower mesh.
- a common mixer for bathtubs and washbasins.
- shut-off valve (diameter 15, 20, 25, 32, 40 mm).
- gate valve (with a diameter of 50 mm and more).
- Check Valve.
- water meter (water flow meter).
- pressure gauge.
- centrifugal pump type.
- vibration insert (reinforced rubber hose).
- kitchen sink.
- washbasin.
- bathtub.
- a toilet with an oblique release.
- floor drain with siphon (water lock).
- a drain funnel hood (for non-operating roofs).
- flat drain funnel (for exploited roofs).
- Sewer pipe.
- transitional branch pipe (usually for transition from Æ 50 mm to Æ 100 mm).
- elbow (for turning sewage pipelines 90 °).
- tap (for turning sewage pipelines by 135 °).
- straight tee (for risers).
- oblique tee (mainly for horizontal sections).
- straight cross (for risers).
- oblique cross (mainly for horizontal sections).
- elbow type siphon (under washbasins and sinks).
- bottle type siphon (under washbasins and sinks).
- siphon for a bathtub.
- revision.
Section 1
Internal water supply of buildings
The internal water supply of buildings is a system of pipelines and devices that supply water inside buildings, including the inlet of the water supply that is located outside.
The composition of the internal water supply includes:
1) pipelines and connecting fittings (fittings);
2) fittings (taps, mixers, valves, gate valves, etc.);
3) instruments (manometers, water meters);
4) equipment (pumps).
Symbols for internal water supply see above.
Classification of domestic water supply
The classification of domestic water pipes is shown in Fig. 1.

Thus, the internal water supply is divided primarily into cold (B) and hot (T) water supply. In the diagrams and drawings in the domestic documentation, cold water pipes are indicated by the letter of the Russian alphabet B, and hot ones are indicated by the letter of the Russian alphabet T.
Cold water pipes have the following varieties:
B1 - domestic drinking water supply;
B2 - fire water supply;
B3 - industrial water supply (general designation).
A modern hot water supply system must have two pipes in the building: T3 - supply, T4 - circulation. Along the way, we note that T1-T2 are designated heating systems (heating systems), which are not directly related to the water supply, but are associated with it, which we will consider later.
b) not lower than + 50 ° С ¾ for centralized hot water supply systems connected to closedheat supply systems;
c) not higher than + 75 ° С ¾ for all systems specified in subparagraphs "a" and "b".
3) In the premises of kindergartens, the temperature of the hot water supplied for showers and washbasins should not exceed +37 ° C.
Classification T3-T4 by location of heat source
The classification of the hot water supply T3-T4 by the location of the heat source is shown in Fig. 7.

Fig. 7
It should be noted that external hot water supply networks are usually not laid, that is, hot water T3-T4 ¾ this is typically an internal water supply. The classification shown in fig. 7 reflects the fact that the location of the heat source is centrally or locally decided. In large and medium-sized cities, the external water heating networks T1-T2 carry heat and bring heat into the buildings with separate T1-T2 inlets. These are centralized heat supply systems. In small towns and cities, the heat source is in a house or apartment ¾ this is a boiler house or hot water boiler that runs on gas, fuel oil, oil, coal, firewood or electricity. This is a local system.
Openthe hot water supply system (see Fig. 7) takes water from the return pipe of the T2 heating system directly, directly, and then the water flows through the T3 pipe to the mixers in the apartments. Such a hot water supply solution is not the best from the point of view of ensuring the drinking quality of hot water, since the water actually comes from the water heating system. However, this solution is very inexpensive. In this way, for example, most of the buildings on the right bank of Omsk are supplied.
Closedthe hot water supply system (see Fig. 7) draws water from the cold water supply B1. Water is heated with the help of water heaters-heat exchangers (boilers or high-speed) and flows through the T3 pipe to the mixers in the apartment. Part of the unused hot water circulates inside the building through the T4 pipeline, which maintains a constant required water temperature. The heat source for water heaters is the supply pipe of the heating network T1. Such a hot water supply solution is already better in terms of ensuring the drinking quality of hot water, since water is taken from the drinking water supply system B1. In this way, for example, most of the buildings on the left bank of Omsk are supplied.
Elements T3-T4
We will consider the elements of the hot water supply T3-T4 using the example of Fig. eight.

1 ¾ heating system input in the technical underground of the building. This is not an element of hot water.
2 ¾ thermal unit. Here the scheme ( open or closed) hot water supply.
Get full text3 ¾ a water meter on a supply pipe of a hot water pipe T3 at a heating unit.
4 ¾ distributing network of supply pipelines T3 of hot water supply.
5 ¾ supply riser T3 hot water. A shut-off valve is installed at its base.
6 ¾ heated towel rails on the supply risers T3.
7 ¾ residential hot water meters on floor T3 connections.
8 Т floor-level connections of hot water T3 (usually Æ 15 mm).
9 ¾ mixing fittings (Fig. 8 shows a faucet common to the washbasin and bathtub with shower net and swivel spout).
10 ¾ circulation riser T4 hot water. A shut-off valve is also installed at its base.
11 ¾ discharge network of circulation pipes T4 of hot water supply.
12 ¾ a water meter on the circulation pipe of the hot water pipe T4 at the heating unit.
INSTALLATION, TEST AND OPERATION OF INTERNAL WATER PIPES
INSTALLATION OF INTERNAL PIPES
Installation of internal water supply to buildings is usually carried out by specialized installation organizations, which are subcontracting organizations in relation to purely construction organizations (general contractors), for example, some installation company in relation to a construction trust.
Installation is carried out in accordance with the provisions of SNiP 3.05.01-85 “Internal sanitary-technical systems”. Before starting the installation, before the installers come to the construction site, builders must do:
3. Sanitary cabins. It is used in large-panel housing construction. The main pipelines and fittings are installed in the cab at the factory, and in the conditions of construction of the cab you only need to carefully join along the axes.
As soon as the installation of the water supply system is completed, the next stage begins: testing.
TESTING THE INTERNAL PIPE
Testing of the installed internal water supply system is carried out in the presence of a commission composed of representatives:
a) customer;
b) general contractor (construction organization);
c) subcontractor (installation organization).
The following system indicators are checked:
1) Costs. For example, the normal flow rate of cold water from a tap or mixer should be at least 0.2 l / s.
2) Pressures. The minimum free pressure at the most distant and highest tapping device on the top floor should not be less than 2-3 meters of water column.
3) The system must comply with the project in terms of dimensions, elevations, pipe diameters, their material, including water quality indicators.
4) There should not be any leaks and leaks on the pipelines.
The test of the internal water supply is carried out for 10 minutes at a pressure one and a half times higher than the maximum allowable excess (gauge) pressure for this system. For example, for a domestic drinking water supply, the maximum allowable excess (gauge) pressure is 0.45 MPa or 45 meters of water. Then the pressure during the test will be 0.675 MPa or 67.5 m water. Art. If the system successfully passed the pressure test, that is, it did not leak, then the act of a manometric leak test is finally drawn up in the form of Appendix 3 of SNiPa 3.05.01-85, which is signed by the representatives of the aforementioned commission.
After the test, the internal water supply system is ready for transfer to its operation.
OPERATION OF THE INTERNAL WATER PIPE
The operation of internal water pipelines is managed by PZHREU (industrial housing and repair and maintenance sites) or by the department of the chief power engineer or the mechanics of enterprises - this depends on the building's affiliation (municipal or departmental) and on the type of system (B1, B2, B3, T3-T4 )
The work performed is as follows:
Current repairs at the request of residents (changing gaskets for cranes, replacing faulty fittings, equipment, eliminating leaks in pipes, installing clamps, replacing pipe sections with a high degree of corrosion damage, etc.);
Get full textRain sewer cities
Rainwater drainage systems in K2 cities are designed according to the requirements of SNiP 2.04.03-85 “Sewerage: external networks and structures”. Its old name: storm sewer, stormwater.
The K2 rain sewer collects rain and melt surface water on the territory of the city, discharges them by gravity through the K2 network and, through its regional collectors, discharges conditionally clean drains into the reservoir in the city, If necessary, build additional treatment facilities, mainly mechanical cleaning, and in conditions of a flat, flat relief, pumping stations are arranged.
Elements of external rainwater drainage:
1 ¾ grate storm water inlets are arranged along the roads in increments of 50-80 meters;
2 ¾ discharge underground pipeline with a diameter of at least Æ 200 mm;
3 ¾ street collectors with a diameter of Æ mm;
4 ¾ district collectors with a diameter of Æ mm.
From the territories of industrial enterprises, K2 effluents are cleaned, mainly at mechanical structures.
Groundwater drainage
Drainage is an engineering system of drains (pipes with holes), filtering dusting, layers and other elements, designed to lower the water discharge rate by at least the drainage rate or at least 0.5 meters below the basement floor, the base of the structure with drainage water discharge:
In the rain sewer K2;
Nearby body of water or stream;
The underlying underground layer.
Drainage is most often associated with the K2 rainwater drainage system, but unlike it, it does not divert surface water, but underground water.
We list the main elements of drainage:
1) water intake device (drain, well);
2) filtering dust and layers (protection against siltation);
3) inspection wells (for ease of maintenance and repair);
4) drain pipe (drainage collector);
5) pumping station for pumping drainage water (not always);
6) drainage water discharge pipe (in K2, a reservoir or reservoir).

Fig. 18. Elements of drainage (for example, ring drainage)
We consider the drainage elements using the example of ring drainage (Fig. 17). It protects the basement of the house from groundwater flooding. Drains 1 are laid around the building at such a depth that the UHW depression curve is at least 0.5 meters lower relative to the basement floor. Drains are sprinkled with layers of gravel (in the immediate vicinity) and sand (between gravel and surrounding soil) to protect the interior of the drains from siltation by soil particles. Ground water passes through filtering dust 2 and, quite clean, enters drain 1 through water inlets or cuts. Groundwater entering the drain is called drainage, which is drained by gravity and drains through one of the manholes 3 through the drainage collector 4 into the reservoir pumping station pumping 5. From there, drainage water is pumped from time to time to the K2 rainwater collector. Element 5 is not always needed.
Drainages for industrial and civil construction are considered in another course: “Protection against flooding in urban construction” (Author:, SibADI, Omsk, 2000). The normative document is SNiP 2.06.15-85 "Engineering protection of the territory from flooding and flooding".
END OF LECTURE COURSE
During the construction of sewer wells, utility workers try to leave certain information about them on the walls or using special signs.
Inscriptions can be seen on almost every home. They have become so ordinary that no one notices them. The designation of sewer wells in the area has several options.

An example of a designation on the facade of a building
Designations of sewer wells are made on walls or special plates. Marking is done so that utilities can easily find the hatch in all weather conditions.
Safety marking
The designation of sewer wells on the plates has its own characteristics. The color of the indicator indicates hazard types of the container.
The safest are blue and white backgrounds of inscriptions. They show that the sewer and water supply are very close.
Red labels indicate dangerous devices. In addition, fire hydrants are also indicated on red plates. By standards, numbers on light plates should be in black. The hue of the letters does not matter. The upper digits indicate the distance from the wall along the axis back. The lower numbers indicate the distance the sunroof is offset from the main axis.

See decoding below
If you decipher the picture above, you can understand that you need to move 5.5 meters from the wall and immediately turn right 0.5 meters. The distance to the hatch is indicated by numbers near the letter "T".
On the walls you can find green signs. They mean gas hatches or “covers”. The numbers on the pointers are indicated in centimeters.
Consider the lettering of sewer wells
The types of sewer wells on the plates have certain abbreviations:
- linear well - “KL”;
- viewing - "C";
- cumulative - “KN”;
- storm water well - “D”;
- rotary well - "KP";
- control - "K";
- typical differential - "TPK";
- mine - "Sh";
- borehole - "BS";
- cable inspection well - "KSK".
In addition, there are letters on the plates and hatches that describe the type of sewage system. The letter "B" means water supply, "K" indicates a sewer, and "D" means a hatch from rain sewers.

Examples of other markings
The designation of sewer wells in the area is a very useful and necessary measure. In any case, it allows you to quickly find the sewer manhole.
Unfortunately, homeowners often paint over the plaques, which impedes the quality of utilities. Do not do that.
We hope the article was useful to you. We will be grateful if you share the link to it with your friends, share it on social networks. Let everyone who needs it learn about the nuances of marking sewer manholes from an article on our portal.
Have a nice day.
Read also:
 Pumping of sewer wells - do it yourself or order from professionals?
Filtration well - types and nuances of use
Pumping of sewer wells - do it yourself or order from professionals?
Filtration well - types and nuances of use
Symbols on the drawings of water supply and sewage are mandatory indicated not only in the construction of multi-storey buildings, but also in the construction of small houses. Regardless of the type of structure, special conventions are always used. They are regulated by GOST, and they are used in any programs that allow you to create drawings of the sewage system and water supply, including in AutoCAD.
Most modern buildings are equipped with systems that are responsible for the implementation of sanitary standards. As a rule, this is a whole complex of engineering communications, which includes a hot and cold water supply system, sewage system, gas supply, garbage chute, drains, heating. All this is necessary for a comfortable stay in a residential building. But in order for all systems to work correctly, the risks of malfunctions must be minimized. And so that with any breakdowns you can immediately fix the problem, everything is carefully planned. The most important systems, including the sewage system with water supply, should be thought out as qualitatively as possible, put on the drawing, and then executed in accordance with a pre-compiled plan. Only in the case of the correct drawing up of the drawing and the fulfillment of all its requirements can it be possible to build a building that will meet all the standards of landscaping and comfort.
Sewerage and water supply design
These systems play a very large role in people's lives. The comfort of the residents of the house, as well as the improvement of the premises, depend on how correctly the drawing of the sewage system and water supply is drawn up. Drainage systems play a special role. Some believe that there is nothing complicated in installing a sewer system, but, in fact, drafting its project is a very large, laborious and demanding job. If you make even the slightest mistake, then it will certainly show itself. Sometimes it comes to the point that design inaccuracies lead to the fact that the house is unsuitable for living.
A sewer system is needed in order to remove waste liquids and some solid waste from each apartment. Most often they have very unpleasant odors, so the design of the sewage system is made taking into account all the norms, rules of hygiene and the improvement of residential premises. Solid elements, fats, and a large amount of storm water pass through the sewer. This suggests that the system must be reliable in order to fulfill its main purpose efficiently throughout the entire specified period of operation.
But no one is protected from force majeure situations. Therefore, the sewer project should be designed in such a way that in case of unforeseen circumstances and any breakdowns, everything could be quickly fixed.
The drainage system is very important for any home - both multi-story and private. Its task is the removal of wastewater into special reservoirs. It is very important to design the system so that contaminated liquids do not enter the soil. Otherwise, there may be a threat of sanitary and epidemiological danger throughout the surrounding area.
 Designing a water supply system is no less difficult and very responsible task. There also have their own rules and regulations. Most often, the water supply and sewerage system is designed at the stage of the start of construction of the building. But it also happens that it is necessary to bring in water and make a drain in a ready-made house. Most often, this is found in the old fund and in the private sector. In the preparation of such drawings, there are peculiarities. For each case, decisions are made individually.
Designing a water supply system is no less difficult and very responsible task. There also have their own rules and regulations. Most often, the water supply and sewerage system is designed at the stage of the start of construction of the building. But it also happens that it is necessary to bring in water and make a drain in a ready-made house. Most often, this is found in the old fund and in the private sector. In the preparation of such drawings, there are peculiarities. For each case, decisions are made individually.
It is worth noting that even in the simplest case at first glance, there are a lot of nuances that must be taken into account. Therefore, when drawing up a drawing and a project for water supply and sewage for a residential building, it is worth contacting professionals. Specialists know exactly how to properly and safely provide a house with water and remove waste water from the room.
Features of the legend on the diagram
In order to properly place the water supply and sewage system, it is necessary to draw up a preliminary drawing. For each type of room, it will be different. Moreover, specialists always take into account the features of the house, and the geographical location, and the number of rooms where it will be supplied, and where the water will come from. There are many nuances in this matter, but always before the start of work a scheme is created, on the basis of which further work will be carried out.
When carrying out the drawings, generally accepted designations should be used. These are conditional symbols according to which any master will be able to easily read one or another scheme, even the most complex.
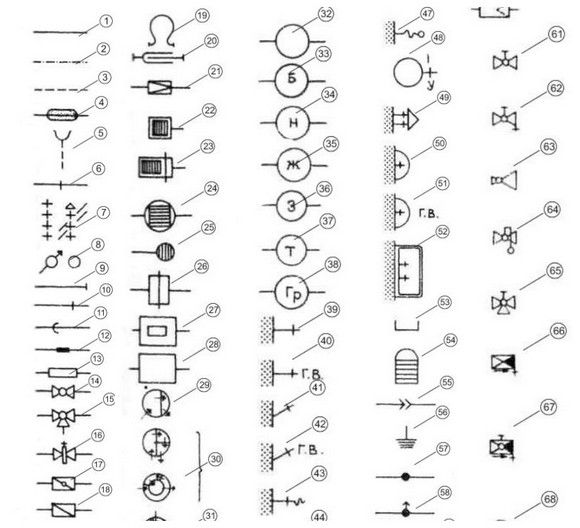 The designations that are used to make drawings of the water supply and sewage systems are regulated by the SNiP and GOST documents. Other conditional images are not allowed. There is a whole list of valid characters with which you can make detailed diagram of how water will enter and out of the house.
The designations that are used to make drawings of the water supply and sewage systems are regulated by the SNiP and GOST documents. Other conditional images are not allowed. There is a whole list of valid characters with which you can make detailed diagram of how water will enter and out of the house.
Each specialist knows how to correctly draw drawings using symbols. There are special programs for this, for example, AutoCAD. Here, the use of all elements that are approved by GOST is allowed. But keep in mind that creating quality and correct scheme systems for supplying and removing water from a house is a rather complicated task. No errors are permissible here, therefore, if there is no work experience in such a matter, it is worth entrusting the creation of the drawing to professionals.
When planning a project with the help of symbols, the master indicates the points of entry of hot, cold water, the location of plumbing fixtures and the withdrawal of sewage. Depending on the type of building, a compact or stretched design can be used. Here, a large role is played by the possibilities of the living quarters. If a water supply and sewage project is prepared before the start of the construction of the building, then it is possible to arrange all the facilities nearby, which will simplify further work. When it comes to conducting water and introducing sewage in an already finished building, there may be obstacles due to which plumbing fixtures will have to be located in different places. This must be indicated in the design documents.
Drawing legend
When designing a hot and cold water supply and sewage system, it is customary to use special notation. They can be different, but GOST regulates all standards, so you cannot change them at your discretion. The scheme should contain only those signs that are used by all specialists in this field.
 Special symbols and alphanumeric elements can be used to designate a water supply and sewage system. In addition, lines are always used in the drawing. Conventional signs are used without any further explanation. The only exceptions are those elements that are regulated by industry standards. In this case, it is recommended to indicate a link to them.
Special symbols and alphanumeric elements can be used to designate a water supply and sewage system. In addition, lines are always used in the drawing. Conventional signs are used without any further explanation. The only exceptions are those elements that are regulated by industry standards. In this case, it is recommended to indicate a link to them.
In total, more than 70 elements are used to create a water supply and sewage scheme. Not all of them are common, but some are necessarily present when drawing up a standard drawing.
On the diagram, you can often see straight and dashed lines and dotted lines with a dot. This is a line of wastewater, storm and mixed sewers. On the diagrams there are elements with lines of different lengths, which are complemented by all kinds of elements, such as rectangles, circles, triangles and simply perpendicular segments. They have different meanings and indicate the presence of runoff, the completion of a pipe segment, the presence of a damper, etc. A circular mark with one or another letter indicates the presence of a gas trap, grease trap, fuel damper, dirt trap, etc. on this section. By the letter in the center of the circle it is easy to understand what is at stake. If, on the diagram, a circle is simply indicated without a letter, then a drawing tank is provided for here.
Special designations are also provided in order to apply plumbing to the drawing. GOST provides for the designation on the diagram and a shower with a flexible hose for water, and sinks with faucets, and bathtubs, and toilets with different types of flushing. Each element has its own element. They are displayed in the form of conditional drawings, by which it is easy to determine what type of plumbing is involved in the drawing.
What does the water supply and sewerage scheme contain?
When designing a project, you need to consider a lot of different points. Here, as a rule, not only layouts of various nodes, pipes, valves and catchers are indicated, but also a considerable amount of other important information for performers. It is necessary to make it easier and more convenient for craftsmen to read drawings. Symbols are used here, but mainly in the alphanumeric version.
The design documentation should contain a plan for the layout of communications, namely, the hot and cold water supply and sewage supply systems. The data of the well table, the specification of the project and many other information that may be useful during the execution of the planned work are indicated. Only with the correct preparation of all documents can you be sure that the system will function correctly and will not cause inconvenience to people who will live in the designed building. It will be impossible to cope with this task without certain knowledge and experience, therefore, if you have doubts about your own strengths, it is worth entrusting this work to professionals.
Information about the designation of the sewer system and water supply is usually made in the design documents using alphanumeric symbols. They are common to all schemes and drawings of plumbing pipelines.
The general designation of the water supply system is marked as B0, pipes for household drinking water will be registered as B1. If the water supply for the fire protection system is marked on the diagram, B2 is indicated, and water for industrial needs is supplied through the B4 pipe.
Thus, everything that has the mark “B” refers to the water supply system. The sewer sign is marked with the letter "K". If the scheme needs to designate a domestic drainage system, K1 will be indicated. For rain sewage, the symbol K2 is used. To create a drainage system in an industrial building, the K3 mark will be used.
 All numeric, alphabetic, and graphic characters must be applied correctly. It is not allowed to use in the drawings of water supply and sewerage those elements that are not regulated by GOST and SNiP. It must be remembered that with the help of appropriate signs a formula is created, according to which the performers further work. If you spell the diagram and draw the drawing incorrectly, this can lead to excessively fast wear of the network, frequent breakdowns or even make the building unsuitable for human life. Correct symbols and symbols ensure that the contractor will read the document as it should, and the quality of construction and installation works depends on this in many respects. If all the requirements of GOST are observed, an effective sewage system and a water supply system can be developed, which will guarantee their long and uninterrupted operation.
All numeric, alphabetic, and graphic characters must be applied correctly. It is not allowed to use in the drawings of water supply and sewerage those elements that are not regulated by GOST and SNiP. It must be remembered that with the help of appropriate signs a formula is created, according to which the performers further work. If you spell the diagram and draw the drawing incorrectly, this can lead to excessively fast wear of the network, frequent breakdowns or even make the building unsuitable for human life. Correct symbols and symbols ensure that the contractor will read the document as it should, and the quality of construction and installation works depends on this in many respects. If all the requirements of GOST are observed, an effective sewage system and a water supply system can be developed, which will guarantee their long and uninterrupted operation.
Creating a drawing in AutoCAD
This program is one of the main assistants in the design, as it allows you to create drawings quickly and conveniently. In the AutoCAD system, you can also develop a water supply and sewage project. But this will require certain knowledge, since the program has its own characteristics.
Even in order to develop the simplest drawing in AutoCAD, you need to spend several hours studying the program. The worldwide network offers a lot of free lessons, which will be enough to learn the basics. This is enough to create a simple drawing of a water supply and sewage system.
The program is convenient in that you can draw any diagram here. To create a system for withdrawing and discharging water from a residential building in AutoCAD, the same conventions are used as in ordinary drawings.
The AutoCAD program has a huge number of advantages that will be useful for those who create projects for water supply and sewage systems. Here you can make a scanned drawing, and then make corrections on it, but already on the computer. The program features do not allow to draw all the elements, but mark only half, and then use the reflection function of the drawing. This saves time and effort when it comes to a symmetrical image.
The AutoCAD program will be useful for those involved in the design of various systems. But it needs to be thoroughly studied so that the work is simple and convenient. In addition to AutoCAD, there are other special programs. But in any case, their development will require a lot of time, so it is much easier to entrust the work of creating drawings of water supply and sewage system to professionals.