Heat pump from the compressor of the refrigerator. Homemade heat pumps for heating
Since ancient times, mankind has “become accustomed” to using accessible natural energy carriers that simply burned to generate heat or to convert into other forms of energy. People also learned to use the hidden potential of water flows - they started from water mills and reached powerful hydroelectric power stations. However, what seemed quite sufficient a hundred years ago, today can no longer satisfy the needs of the growing population of the Earth.
Firstly, natural “storerooms” are still not bottomless, and energy production is becoming more and more difficult every year, moving to inaccessible regions or even offshore. Secondly, the burning of natural raw materials is always associated with emissions of combustion products into the atmosphere, which, with the current enormous volumes of such emissions, has already put the planet on the brink of ecological disaster. The energy of hydroelectric power plants is not enough, and violation of the hydrological balance of rivers also entails a lot of negative consequences. Nuclear power, which was once looked at as a "panacea", after a number of resonant technological disasters raises a lot of questions, and in many regions of the world the construction of nuclear power plants is simply prohibited by law.
However, there are other, almost inexhaustible sources of energy that have become widely used relatively recently. Modern technologies have made it possible to very effectively use wind, sunlight, ocean tides, etc. to produce electricity or heat. One of the alternative sources is the thermal energy of the earth's interior, water bodies, and the atmosphere. The use of heat pumps is based on the use of such sources. For us, such equipment is still included in the category of “exotic new products”, and at the same time, very many European residents heat their homes in this way - for example, in Switzerland or the countries of Scandinavia the number of houses with similar systems has exceeded 50%. Gradually, this type of heat generation is beginning to be practiced in Russian open spaces, although the prices for acquiring a high-tech set of equipment still look very frightening. But, as always, there are master enthusiasts who show their creative abilities and assemble heat pumps with their own hands.
The publication is aimed at enabling the reader to take a closer look at the principle of operation and the basic design of heat pumps, and learn about the advantages and disadvantages. In addition, the successful experiences of creating existing facilities on their own will be described.
Not everyone thought about this, but around us there are a lot of heat sources that “work” year-round and around the clock. For example, even in the most severe colds, the temperature under the ice of a frozen pond still remains positive. The same picture and when deepening into the thickness of the soil - below the freezing boundary, the temperature is almost always stable and approximately equal to the average annual characteristic for this region. A considerable thermal potential carries in itself air.
Perhaps someone will be completely embarrassed by the seemingly low temperatures of water, soil or air. Yes, they belong to low-potential energy sources, but their main “trump card” is stability, and modern technologies based on the laws of thermophysics make it possible to convert even insignificant differences into the necessary heating. Yes, and you must admit, when the frost in the winter stands at 20 degrees, and below the freezing level the soil has 5–7 degrees, then this amplitude difference is already quite decent.
It is this property of continuity of supply of low potential energy that is embedded in the heat pump circuit. In fact, this unit is a device that "pumps" and "gigs" the heat taken from an inexhaustible source.
You can draw a certain analogy with all the familiar refrigerator. Products that are placed in it for cooling and storage, and air entering the chamber when the door is opened, also do not have a very high temperature. But if you touch the heat exchanger lattice of the condenser on the back of the refrigerator, then it is either very warm or even hot.
The prototype of the heat pump is a refrigerator familiar to everyone, the condenser grate of which heats up during operation.
So why not use this principle for heating the coolant? Of course, the analogy with the refrigerator is not a direct one - there is no stable external heat source, and electricity is consumed to a large extent. But in the case of a heat pump, such a source can be found (organized), and then it turns out “the refrigerator is the other way around” - the main focus of the unit will be precisely on receiving heat.
What is the principle of the heat pump?
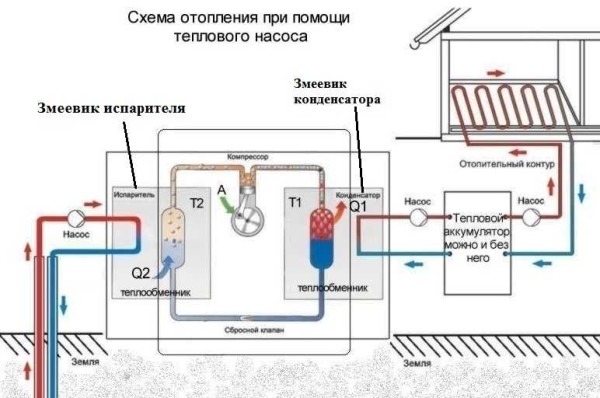
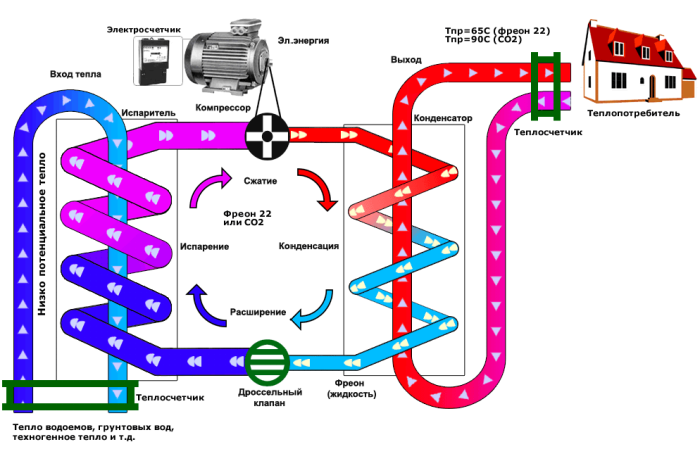
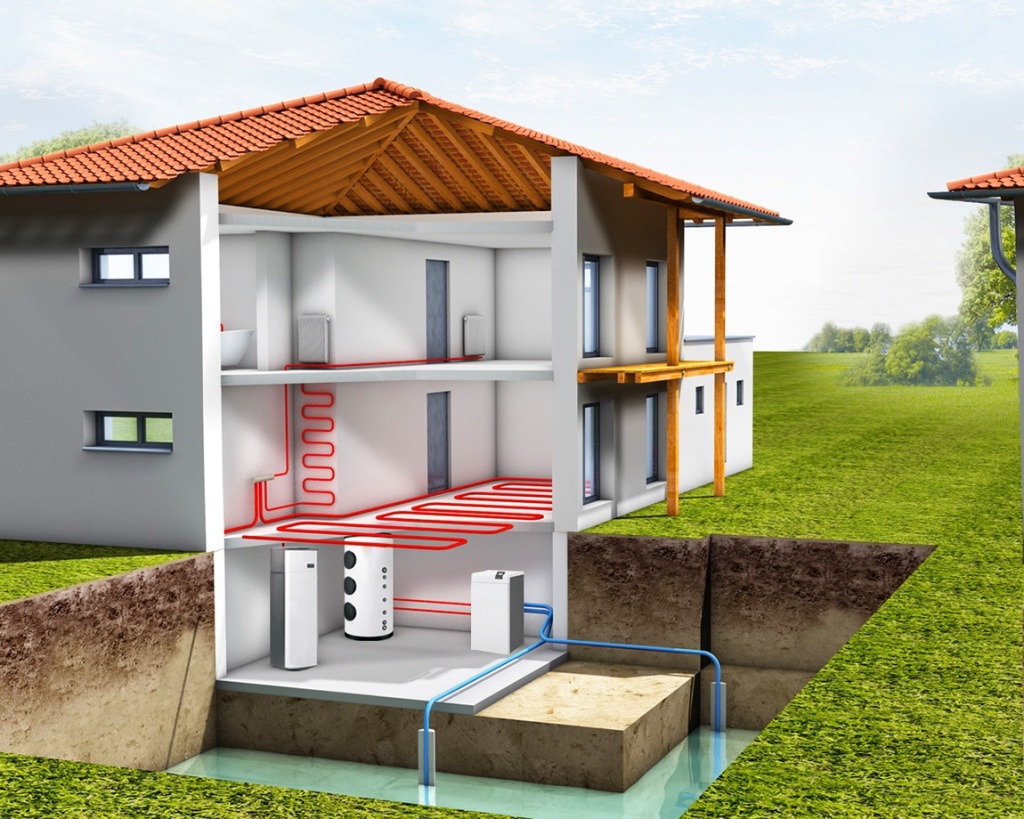
It is a system of three circuits with coolants circulating through them.
- In the heat pump housing (pos. 1), two heat exchangers (pos. 4 and 8), a compressor (pos. 7), a refrigerant circuit (pos. 5), and control and regulation devices are located.
- The first circuit (pos. 1) with its own circulation pump (pos. 2) is located (immersed) in the source of low-grade heat (we will discuss their design below). Receiving thermal energy from an external uninterrupted source (shown by a wide pink arrow), heating only a few degrees (usually, when using probes or collectors in the ground or in water - up to 4 ÷ 6 ° FROM), the circulating coolant gets into heat exchanger-evaporator (item 4). Here is the primary transfer of heat received from the outside.
- The refrigerant used in the internal circuit of the pump (key 5) has an extremely low boiling point. Usually one of the most modern, environmentally friendly freons, or carbon dioxide (in fact, liquefied carbon dioxide) is used here. At the entrance to the evaporator (pos. 6) it is suitable in a liquid state, at reduced pressure - this provides an adjustable throttle (pos. 10). The special shape of the capillary type inlet and the shape of the evaporator contribute to an almost instantaneous transition of the refrigerant into a gaseous state. According to the laws of physics, evaporation is always accompanied by sharp cooling and absorption of ambient heat. Since this part of the inner circuit is located in the same heat exchanger as the first circuit, the freon takes the thermal energy from the coolant, while cooling it (wide orange arrow). The cooled coolant continues to circulate, and again gains thermal energy from an external source.
- The refrigerant is already in a gaseous state, transferring the heat transferred to it, enters the compressor (pos. 7), where under the influence of compression its temperature rises sharply. Further, it enters the next heat exchanger (item 8), in which the condenser and pipes of the third circuit of the heat pump are located. (Pos. 11).
- Here the completely opposite process takes place - the refrigerant condenses, turning into a liquid state, while giving its heating to the coolant of the third circuit. Further, in the liquid state at high pressure, it passes through the throttle, where the pressure decreases, and the cycle of physical transformations of the state of aggregation of the refrigerant is repeated again and again.
- Now it proceeds to the third circuit (pos. 11) of the heat pump. Through the heat exchanger (pos. 8), heat energy is transferred from the refrigerant heated by compression (wide red arrow). This circuit has its own circulation pump (item 12), which ensures the movement of the coolant through the heating pipes. However, it is much more reasonable to use an accumulating, carefully insulated buffer tank (key 13), in which the transferred heat will accumulate. The accumulated supply of thermal energy is already consumed for the needs of heating and hot water, diverging gradually, as needed. Such a measure allows you to insure yourself in case of power outages or use a cheaper nightly rate for electricity needed for the heat pump to work.
If a buffer storage tank is installed, then a heating circuit (pos. 14) with its own circulation pump (pos. 15) is already connected to it, which ensures the movement of the coolant through the system pipes (pos. 16). As already mentioned, there may be a second circuit, which provides a feed hot water for domestic needs.
The heat pump cannot work without power - it is required for the compressor to function (wide green arrow), and the circulation pumps in the external circuits also consume electricity. However, as the developers and manufacturers of heat pumps assure, the consumption of electricity is not comparable with the received "volume" of thermal energy. So, with proper assembly and optimal operating conditions, there is often a conversation about 300 or more percent of efficiency, that is, with one kilowatt of electricity spent, the heat pump can produce 4 kilowatts of thermal energy.
In fact, such a statement about efficiency is somewhat incorrect. The laws of physics have not been canceled, and the efficiency above 100% is the same utopia as " perpetummobile"- the perpetual motion machine. In this case, we are talking about the rational use of electricity in order to "pump" and convert energy from an inexhaustible external source. It is more appropriate to use the concept of COP (from English "Coefficient of performance"), which in Russian is often called the "heat conversion coefficient". In this case, in fact, values \u200b\u200bthat exceed one can be obtained:
CO R = Qn / awhere:
CO R Is the heat conversion coefficient;
Qp - the amount of thermal energy received by the consumer;
A - work performed by the compressor unit.
There is another nuance that is often simply forgotten - a certain energy consumption for the normal functioning of the pump requires not only a compressor, but also circulation pumps in external circuits. Their power consumption, of course, is much less, but, nevertheless, it can also be taken into account, and this is often not done for marketing purposes.
The resulting total amount of thermal energy can be consumed:
1 - The optimal solution is a system of warm water floors. As a rule, heat pumps give rise to a temperature of about 50 ÷ 60 ° FROM - This is enough for underfloor heating.
2 - hot water supply at home. Typically, in hot water systems, the temperature is maintained at this level - about 45 ÷ 55 ° C.
3 - but for conventional radiators, such heating will be clearly not enough. The way out is to increase the number of sections or use special low-temperature radiators. Convection-type heating appliances will help to solve the issue.
4 - One of the most important advantages of heat pumps is the ability to switch to the "opposite" mode of operation. In the summer, such a unit can perform the function of air conditioning - taking heat from the premises and transferring it to the ground or pond.
Low Potential Energy Sources
What sources of low potential energy are able to use heat pumps? Rocks, soil at various depths, water from natural reservoirs, wells or underground aquifers, atmospheric can play this role. air or warm air currents discharged from buildings or from industrial technological complexes.
A. Use of thermal energy soil
As already mentioned, below the level of soil freezing characteristic of this region, the temperature of the soil is stable throughout the year. This is used for the operation of heat pumps according to the "soil - water" scheme.
Schematic diagram of energy extraction "soil - water"
To create such a system, special surface thermal fields are prepared, on which the upper soil layers are removed to a depth of about 1.2 ÷ 1, 5 meters. Circuits made of plastic or metal-plastic pipes with a diameter of, as a rule, 40 mm are laid in them. The efficiency of removal of thermal energy depends on local climatic conditions and on the total length of the created circuit.
Tentatively, for the middle zone of Russia, it is possible to operate with the following relationships:
- Dry sandy soil - 10 watts of energy per meter of pipe.
- Dry clay soils - 20 W / m.
- Wet clay soils - 25 W / m.
- Clay rock with a high location of groundwater - 35 W / m.
Despite the apparent simplicity of such heat transfer, the method is by no means always the optimal solution. The fact is that it involves a very significant amount of earthwork. What looks simple in the diagram is much more difficult in practical execution. Judge for yourselves - in order to “remove” even only 10 kWt of thermal energy from clay underground on clay soil, about 400 meters of pipe will be required. If you still take into account the mandatory rule that between the turns of the contour there must be an interval of at least 1, 2 meters, then for laying will be necessary a plot of 4 acres (20 × 20 meters).
Laying a field for taking heat from the soil is an extremely large-scale and labor-intensive task
Firstly, not everyone has the opportunity to highlight such a territory. Secondly, on this site any buildings are completely excluded, since the contour is likely to be damaged. And thirdly, the selection of heat from the soil, especially with poorly performed calculations, may not pass without a trace. The effect of supercooling of the site is not ruled out when summer heat cannot fully restore the temperature balance at the depth of the contour. This may adversely affect the biological balance in the surface layers of the soil, and as a result, some plants simply will not grow in a supercooled area - such a peculiar local effect of the “ice age”.
B. Thermal energy from wells
Even the small size of the site will not be an obstacle to organizing the care of thermal energy from a drilled well.
As a source of low potential heat - a deep well
Soil temperature with increasing depth becomes only more stable, and at depths above 15 — 20 meters stands firmly at the 10-degree mark, increasing by two to three degrees for every 100 meters of diving. Moreover, this value is absolutely independent of the time of year or the vagaries of the weather, which makes the well the most stable and predictable source of heat.
A probe, which is a U-shaped loop of plastic (metal-plastic) pipes with a coolant circulating through them, is lowered into the wells. Most often, several wells are made with depths from 40 ÷ 50 and up to 150 meters, no closer than 6 m from one another, which are connected either in series or with connection to a common collector. The heat transfer of the soil with this arrangement of pipes is much higher:
- With dry sedimentary rocks - 20 W / m.
- Stony ground layers or sedimentary rocks saturated with water - 50 W / m.
- Hard rocks with high thermal conductivity - 70 W / m.
- If you are lucky, an underground aquifer is caught - about 80 W / m.
In case of insufficient space or difficulties in deep drilling due to soil characteristics, several inclined wells can be run with rays from one point.
By the way, in the event that the well falls on an aquifer with a stable debit, sometimes an open primary heat exchange circuit is used. At the same time, water is pumped from a depth by a pump, participates in heat transfer, and then, cooled, is discharged into a second well of the same horizon, located oncertain distance from the first (this is calculated when designing the system). At the same time, water intake for domestic needs can be organized.
The main disadvantage of the downhole method of heat extraction is the high cost of drilling operations, which are carried out on their own without having the appropriate equipment, is very difficult or simply impossible. In addition, well drilling often requires permits from environmental authorities. By the way, the use of direct heat exchange with the reverse discharge of water into the well may also be prohibited.
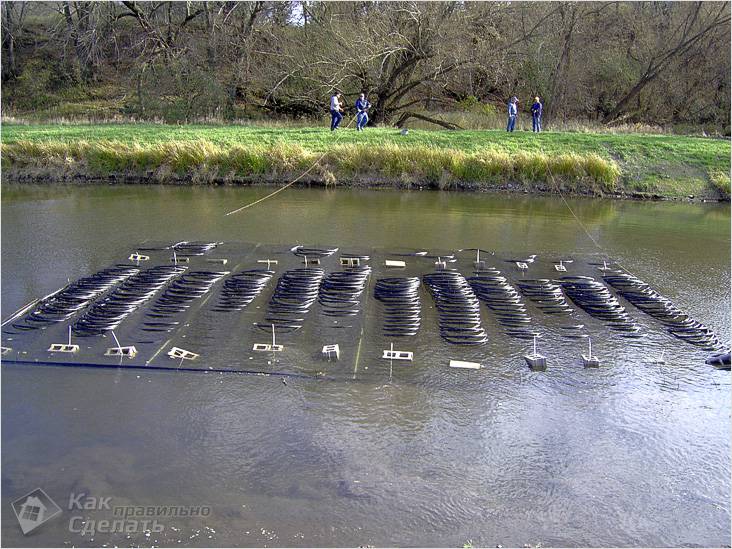
Estimated heat transfer from a circuit immersed in water is 30 kW / m. So, to get a return of 10 kW, you need a circuit of about 350 m.
Such collector circuits are mounted on land from plastic pipes. Then they move into the pond and plunge to the bottom, to the depth at least 2 meters, for which cargo is tied at the rate of 5 kg per 1 linear meter tr loss.
Then executed thermally insulated laying pipes to the house and connecting them to heat exchanger pump.
However, one should not think that any body of water is fully suitable for such purposes - again, very complicated thermotechnical calculations will be needed. For example, a small and not deep enough pond or a shallow quiet rivulet can not only cope with the task of uninterrupted supply of low potential energy - they can simply be frozen completely to the bottom, thereby killing all the inhabitants of the reservoir.
Advantages of water sources of heat - there is no need for drilling work, earthworks are reduced to a minimum - only digging trenches to the house for laying pipes. And as a disadvantage, low accessibility for most homeowners can be noted simply because of the lack of ponds in a reasonable proximity to housing.
By the way, sewer drains are often used for heat exchange - even in the cold they have a fairly stable positive temperature.
D. The intake of heat from the air
Heat for heating homes or for hot water can be taken literally from the air. On this principle, heat pumps "air - water" or " air – air».
By and large - this is the same air conditioner, only switched to the "winter" mode. The effectiveness of such a heating system very much depends on the climatic conditions of the region, and on the vagaries of the weather. Although modern units are designed to operate even at very low temperatures (up to - 25, and some - even up to - 40 ° FROM), but the energy conversion coefficient drops sharply, the profitability and feasibility of such an approach immediately begin to raise a bunch of questions.
But on the other hand, such a heat pump does not require any labor-intensive operations at all - most often its primary heat-exchange unit is installed either on the wall (roof) of the building, or in close proximity to it. By the way, it can hardly be distinguished from the external unit of the split air conditioning system.
Such heat pumps are often used as additional sources of thermal energy for heating, and in the summer, as a heat generator for hot water supply.
The use of such heat pumps is fully justified for the recovery - the use of secondary heat, for example, at the outputs of ventilation shafts (channels). So the installation receives a fairly stable and high-temperature energy source - this is widely used in industrial enterprises, where there are constantly sources of secondary heat for its utilization.
In the systems “air-air” and “air-water” there is no primary heat exchange circuit. Fans create an air stream that directly blows the evaporator tubes with the refrigerant circulating through them.
By the way, there is a whole line of DX heat pumps - type (from the English "direct exchange", which means "direct exchange"). In them, too, in fact, there is no primary circuit. Heat exchange with a source of low potential heat (in wells or in a layer of soil) passes immediately in copper pipes filled with x lead agent. On the one hand, this is more expensive and more difficult to implement, but it can significantly reduce both the depth of the wells (just one 30-meter vertical or several slanted up to 15 m) and the total area of \u200b\u200bthe horizontal heat-exchange field, if it is located under the upper soil layer. Accordingly, we can talk about a larger conversion coefficient, and in general - the efficiency of the heat pump. But copper copper heat exchangers are only much more expensive than plastic pipes and more difficult to install, and the cost of the refrigerant is much higher than that of a conventional coolant-antifreeze.
A reasonable solution is to create a combined heating system (bivalent). While the power of the VT is enough, it acts as the main source of heat, with insufficient power atoffensive of real cold weather - electric heating, a liquid or solid fuel boiler, a solar collector, etc. come to the rescue. Gas equipment is not considered in this case - if it is possible to use network gas for heating, then the need for a heat pump looks very doubtful, at least at the current level of energy prices.
IN. A heating system with a heat pump does not require a chimney. It works almost silently.
Indeed, the owners will not have difficulties with arranging the chimney. As for the silence of the work, like any other household appliances with various drives, the noise background is still present - from the compressor circulation pumps. Another question is that in modern models this noise level with proper debugging of the unit is very small and does not cause concern to residents. In addition, probably, few people would think of installing such equipment in living rooms.
G. Full environmental friendliness of the system - there are completely no emissions into the atmosphere, there is no threat to the residents of the house.
Everything is true, especially with regard to models in which a modern, ozone-friendly freon (for example, R-410A) is used as a refrigerant.
You can also immediately note the fire - and explosion safety such a system - there are no flammable or combustible substances, the accumulation of their explosive concentrations is excluded.
D. Modern heat pumps are universal climate systems that can work for heating and air conditioning in the summer.
This is a very important advantage, which, indeed, gives the owners a lot of additional amenities.
E.The operation of the heat pump is fully controlled by automation, and does not require user intervention. Such a system, unlike others, does not require regular maintenance and maintenance.
One can completely agree with the first statement, however, without forgetting to mention the fact that most modern heating gas or electric installations are also fully automated, that is, not only heat pumps have this advantage.
But on the second question, you can enter into a discussion. Probably, none of the industrial or domestic heating units can do without regular inspections and preventive maintenance. Even if it is fair to assume that you should not climb into the internal circuit with refrigerant and automation yourself, external circuits with antifreeze or other coolant will still require some participation. Here, regular cleaning of the filters (especially in air systems), and monitoring the composition and level of the coolant, and revising the operation of circulation pumps, and checking the condition of the pipes for integrity and the presence of leaks on the fittings, and much more - in a word, something that can not do without no heating system. In a word, the statement that service is completely unnecessary seems at least unfounded.
G. Quick payback of a heating system with a heat pump.
This question is so controversial that it should be highlighted.
Some companies involved in the sale of such equipment promise their potential customers a very quick return on investment in the project. They give calculations in the tables, according to which, in fact, one can create the opinion that the heat pump is the only acceptable solution if there is no way to extend the gas main to the house.
Here is one such sample:
Types of fuel Natural gas (methane) Firewood chopped birch Email energy at a single rate Diesel fuel Heat pump (nightly rate) Units fuel supply m ³ 3 m ³ kW × h liter kW × h Fuel cost. with delivery, rub 5.95 6000 3.61 36.75 0.98 Fuel calorie content 38.2 4050 1 36 1 Units calorie measurement MJ / m³ kW × h kW × h MJ / liter kW × h Boiler efficiency,% or COP 92 65 99 85 450 Fuel cost, rub / MJ 0.17 0.41 1.01 1.19 0,06 Fuel cost, rub / kW * h 0.61 1.48 3.65 4.29 0.22 Fuel cost, rub / Gcal 708 1722 4238 4989 253 Fuel cost per year, rub 24350 59257 145859 171721 8711 Equipment service life, years 10 10 10 10 15 Estimated cost of equipment, rubles 50000 70000 40000 100000 320000 Installation cost, rub 70000 30000 30000 30000 80000 The cost of connecting networks (technical specifications, equipment and installation), rubles 120000 0 650 0 0 Initial investment, rub (approximately) 240000 100000 70650 130000 400000 Operating costs, rub / year 1000 1000 0 5000 0 Types of operational work maintenance, cleaning the camera cleaning chimneys Replacement of heating elements cleaning the chamber, nozzles, replacing filters not Total expenses for the entire period of operation (with fuel costs), rubles 493502 702572 1529236 1897201 530667 Total relative cost of 1 year of operation (fuel, depreciation, maintenance, etc.) 49350 70257 152924 189720 35378 Yes, the final line is really impressive, but is everything “smooth” here?
The first thing that catches the eye of an attentive reader is that the tariff for electricity for electric heating was taken as the general one, and for the heat pump, for some reason, it was preferential at night. Apparently, in order to make the final difference more visual.
Further. The cost of heat pump equipment is not shown correctly. If you carefully look at the offers on the Internet, then prices for installations with a capacity of about 7 ÷ 10 kW, which can be used for heating, start from 300 - 350 thousand rubles (air heat pumps and low-power installations, used only for hot water supply, are slightly smaller).
It would seem that everything is correct, but “the devil is in the details” This is just the cost of the hardware unit itself, which is without peripheral devices, circuits, probes, etc. - useless. The price of only one collector (without pipes) will give at least 12 ÷ 15 thousand, the downhole probe is no less. And if we add the cost of pipes, fittings, shut-off and reinforcing elements, a sufficiently large amount of coolant - the total amount is growing rapidly.
Pipes, collectors, shutoff valves - also quite a "weighty" item of total costs
But that is not all. It has already been mentioned that a heating system based on a heat pump, like probably no other, needs complex specialized calculations. When designing, a lot of factors are taken into account: the total area and volume of the building itself, the degree of its insulation and calculation of heat losses, the availability of a sufficient source of power supply, the availability of the necessary area (nearby reservoir) to accommodate horizontal heat exchange circuits or drilling wells, the type and condition of soils , the location of aquifers and much more. Of course, both survey and design work will also require time and appropriate payment to specialists.
Installing the equipment at random, without proper design, is fraught with a sharp decrease in the efficiency of the system, and sometimes even with local "environmental disasters" in the form of unacceptable overcooling of soil, wells or wells, water bodies.
The next is the installation of equipment and the creation of heat transfer fields or wells. The extent of earthworks, the depth of drilling has already been mentioned. To fill the wells after installing the probes, a special concrete solution with a high degree of thermal conductivity is required. Plus, switching circuits, laying highways to the house, etc. - all this is another considerable "layer" of material costs. This also includes the acquisition and installation of storage tanks with the necessary control automation, the alteration of the heating system for underfloor heating, or the installation of special heat-exchange devices.
In a word, the costs are very impressive, and probably this is what keeps heating systems from heat pumps so far in the category of “exotic”, inaccessible to the vast majority of owners of private houses.
But what about their highest popularity and mass application in other countries? The fact is that there are government programs to stimulate the population to use alternative sources of energy supply. Consumers who have expressed a desire to switch to such types of heating have the right to receive government subsidies, which largely cover the initial costs for the design and installation of equipment. And the income level of working citizens, to be honest, there slightly higherthan in our area.
For European cities and towns this is a fairly familiar picture - a heat pump heat exchanger near the house
Summary - statements about the quick payback of such a project should be treated with some caution. Before undertaking such a large-scale and responsible set of measures, it is necessary to carefully calculate and weigh all the “bookkeeping” to the smallest detail, assess the degree of risk, your financial capabilities, the planned profitability, etc. Perhaps there are more rational, acceptable options - gas laying, installation of modern solid fuel long-burning boilers, the use of new developments in the field of electric heating, etc.
It should not be taken as written as a “negative” to heat pumps. Of course, this is an extremely progressive direction, and it has enormous prospects. It is only a matter of the fact that in such matters one should not show rash voluntarism - decisions should be based on carefully thought out and comprehensively carried out calculations.
Is it possible to assemble a heat pump with my own hands?
The general prospect of using “gratuitous” sources of thermal energy, together with the continuing high price of equipment, unwittingly lead many home craftsmen to the issues of creating such heating systems on their own. Is it possible to make a heat pump with your own forces?
Of course, it is quite possible to assemble such a heat engine using some ready-made units and the necessary materials. On the Internet you can find videos and articles with successful examples. True, it is unlikely that it will be possible to find the exact drawings, everything is usually limited to recommendations on the possibility of manufacturing certain parts and assemblies. However, there is a rational “grain” in this: as already mentioned, a heat pump is such an individual system that requires calculations in relation to specific conditions, that it would hardly be advisable to blindly copy other people's developments.
Nevertheless, those who nevertheless decide to do their own production should heed some technological recommendations.
So, we “take out the brackets” the creation of external circuits - heating and primary heat transfer. The main task in this case becomes the manufacture of two heat exchangers, an evaporator and a condenser, connected by a copper tube circuit with a refrigerant circulating through it. This circuit, as can be seen from the circuit diagram, is connected to the compressor.
It is not difficult to find a compressor - new or from dismantled equipment
It is not so difficult to get the compressor itself - you can buy it new in a specialized store. You can search the economic market - they often sell units from old refrigerators or air conditioners disassembled for spare parts. It is possible that the compressor will be found in its own reserves - many prudent owners even do not throw such things away when buying new household appliances.
Now - the issue of heat exchangers. There are several different options here:
A. If you can purchase prefabricated plate heat exchangers , sealed in a sealed enclosure, then this will immediately solve a lot of problems. Such devices have excellent heat transfer efficiency from one circuit to another - it is not without reason that they are used in heating systems when connecting an autonomous intra-apartment wiring to the pipes of the central network.
Convenience is also that such heat exchangers are compact, have ready-made pipes, fittings or threaded connections for connecting to both circuits.
Video: making a heat pump using off-the-shelf heat exchangers
B. Variant of a heat pump with heat exchangers made of copper tubes and closed containers.
Both heat exchangers, in principle, are similar in design, but different capacities can be used for them.
A stainless steel cylindrical tank with a capacity of about 100 liters is suitable for a condenser. It is necessary to place a copper coil in it, leading its ends from above and from below to the outside and hermetically sealing the passage at the end of assembly. The inlet should be located below, the outlet, respectively - in the upper part of the heat exchanger.
The coil itself is wound from a copper tube, which can be purchased in the store with a meter (wall thickness - at least 1 mm). As a template, you can take a pipe of large diameter. The coils of the coil should be slightly spaced among themselves, attaching, for example, to an aluminum perforated profile.
The water heating circuit can be connected by means of ordinary water pipes mounted (welded, soldered or on a threaded connection with a seal) in opposite edges of the heat exchange tank. The internal space of the heat exchanger is used for water circulation. As a result, you should get something like this design:
For the evaporator, such difficulties are not needed - there are no high temperatures or overpressure, so there will be enough bulk plastic container. The coil coils in approximately the same way, its ends are brought out. For the circulation of water from the primary circuit, conventional plumbing connections are also sufficient.
The evaporator is also mounted on the brackets next to the condenser, and a platform is being prepared near them for mounting the compressor with its subsequent connection to the circuit.
Recommendations for compressor piping, installation of a throttle control valve, the diameter and length of the capillary tube, the need for a regenerative heat exchanger, and etc., will not be given - it should be calculated and installed only by a specialist in refrigeration units.
It should be remembered that it requires high skills of hermetic soldering of copper pipelines, the ability to properly pump refrigerant - freon, carry out checks and carry out a test run. In addition, this work is quite dangerous, requiring the observance of very specific precautionary rules.
IN. Heat pump with pipe heat exchangers
Another option for the manufacture of heat exchangers. For this, metal-plastic and copper pipes will be needed.
Copper tubes are selected in two diameters - about 8 mm for the condenser, and about 5 ÷ 6 for the evaporator. Their length is 12 and 10 meters, respectively.
Plastic pipes are designed to circulate water through them from the primary heat transfer and heating circuits, and copper tubes of the internal circuit of the heat pump will be located in their cavity. Accordingly, the diameter mp can be taken 20 and 16 mm.
The metal-plastic pipes are stretched in length, so that they can easily insert copper pipes, which should protrude on each side by about 200 mm.
A tee is put on and “packed” on each end of the pipe, so that the copper pipe passes straight through it. The space between it and the body of the tee is securely sealed with heat-resistant sealant. The remaining perpendicular outlet of the tee will serve to connect the heat exchanger to the water circuit.
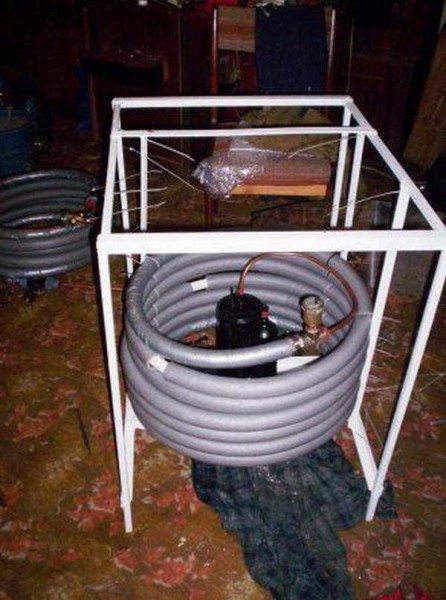
Frame with first heat exchanger and compressor installed
You can place them one above the other in an impromptu frame-type case. On the same frame, a platform for installing a compressor is also provided. And in order to reduce the transmission of vibration from it to the general design, it is possible to mount the compressor, for example, through automobile silent blocks.
In order to tie the compressor and fill the resulting circuit with freon, again, you will need to invite a refrigeration specialist.
You can install such a heat pump in its intended place and connect the tee fittings on the heat exchangers each to its own circuit. All that remains is to supply power and start the unit.
All the considered home-made heat pumps are fully functional designs. However, one should not assume that it is just that you can completely solve the problem of cheap heating at home. Here we are talking more about the creation of existing models that require further refinement, modernization. Even experienced craftsmen in this matter, who have already made more than one such apparatus, are constantly looking for ways to improve, creating new “versions”.
Video: how a master perfects a heat pump with his own hand
In addition, only the heat pump itself was considered, and for normal operation, it requires control, monitoring, adjustment equipment associated with the home heating system. Here one can not do without certain knowledge in the field of electrical engineering and electronics.
Again, we can return to the problems of calculations - will the home-made heat pump “pull” the heating system so as to become a real alternative to other sources of heat? Often, homemasters have to "make their way to the touch" in these matters. However, if the basic principle is learned, and the first model has successfully worked, this is already a big victory. You can temporarily adapt your test sample to provide hot water for domestic purposes at home, and you can begin to design a more advanced unit yourself, taking into account already gained experience and correcting mistakes.
Heat pumps allow you to take the scattered energy from the surrounding nature: air, water and earth, accumulate and direct it to the heating of the house. Energy is also used to heat water for washing or to condition indoor air. This makes it possible to save money by reducing the consumption of traditional heat sources: electricity, gas, firewood. In the article we will tell you how to make a heat pump with your own hands.
What is a geothermal pump

First you need to understand what a geothermal pump is, and by what principle it works, because it is he who is the heart of the whole device we describe.
It's no secret that in the thickness of the earth is always maintained plus temperature. In the same condition is water under the ice. In this relatively warm environment, a closed pipeline with liquid is placed.
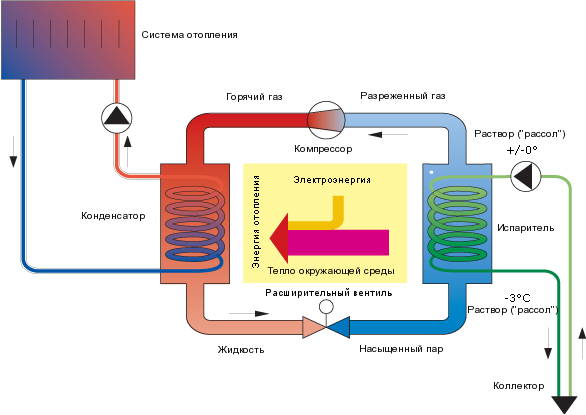
The operation scheme of heat pumps is quite simple and based on the inverse Carnot principle:
- The coolant, moving along the external circuit, is heated from the selected source and enters the evaporator.
- There he exchanges energy with a refrigerant (usually it's freon).
- Freon boils, goes into a gaseous state and is compressed by a compressor.
- Hot gas (it is heated within 35–65 o C) enters another heat exchanger, in which it transfers its heat to the heating system or hot water supply of the house.
- The cooled refrigerant again becomes liquid and returns to a new circle.
Fridge pump
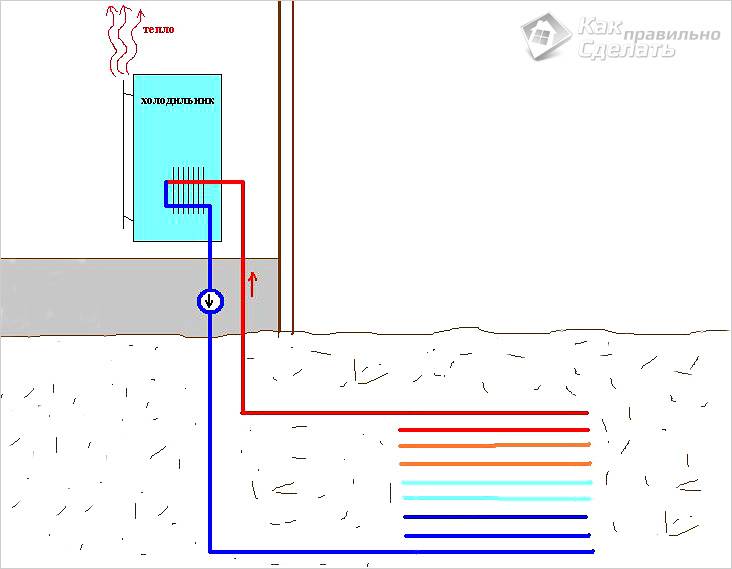
The main part of the system is the compressor. It is better to buy it ready-made at the store or use one available from the refrigerator or air conditioning. All other components - the evaporator, condenser, pipeline - can be assembled by yourself. Such an apparatus will consume energy only for compression and heat transfer, while generating 5 times more.
Using an old compressor, you need to rely on the fact that its service life can be short-lived, and the system power will decrease. In addition, the power of a worn compressor may not be enough for the full operation of the system.
Some craftsmen went further and made a heat pump from the refrigerator, placing radiators inside it, heated by the heat of the earth. Inside, the positive temperature is constantly maintained, which makes the refrigerator work constantly, heating the radiator located behind it. Using a native radiator, they make a heat exchanger from it (or make a homemade one), and the heat released by it is taken.
The efficiency of such a heat pump is more suitable for demonstrating the operation of the device, since its efficiency is very low. In addition, the refrigerator is not designed for this mode of operation and can quickly fail.
Types of Heat Pumps
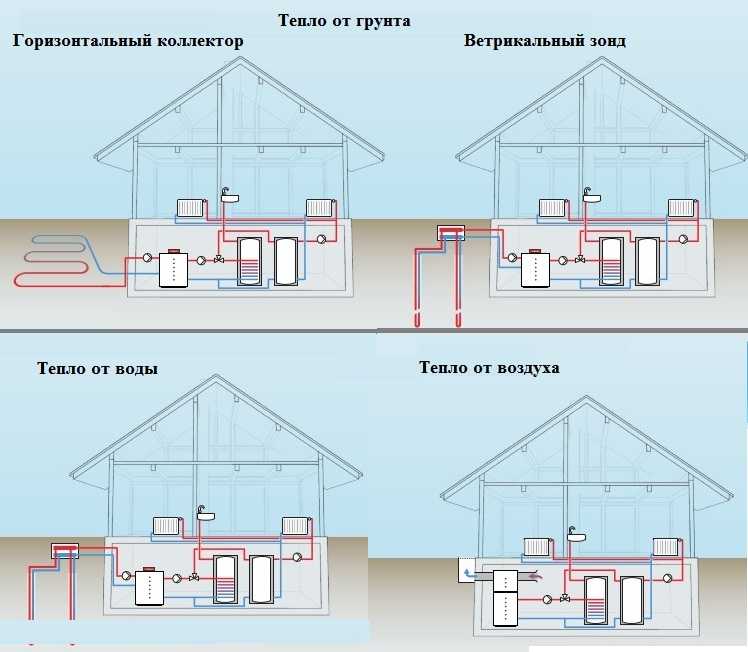
There are three types of pumps, depending on the source of heat:
Soil-water

Water-to-water

Air-to-water

A soil-water installation uses the heat of the bowels. The temperature of the earth at horizons of more than 20 m always remains unchanged, and therefore the pump can generate the required energy all year round. There are two mounting options:
- vertical shaft;
- horizontal collector.
In the first case, a well with a depth of about 50–100 m is drilled and pipes with a circulating coolant, a special non-freezing fluid, are placed in it.
At a depth of 5 m, collectors are laid along which the coolant also moves. To heat a house with an area of \u200b\u200b150 m 2, a plot of at least 250 m 2 is required, and it cannot be used for agricultural planting. Only a decorative lawn and flowerbed is permissible.
The water-to-water pump uses the energy of water from lakes, wells, or boreholes. Some manage to extract heat even from drains. The main thing is that the filter is not clogged and the metal is not destroyed.
This type usually shows the highest efficiency, but it is not possible to establish it in every suburban area, and groundwater exploitation must be obtained. Such devices are more typical for industrial production.
The air-to-water design is less efficient than the first two, since winter production is significantly reduced. On the other hand, when installing it, you do not need to drill or dig anything. The installation is simply mounted on the roof of the house.
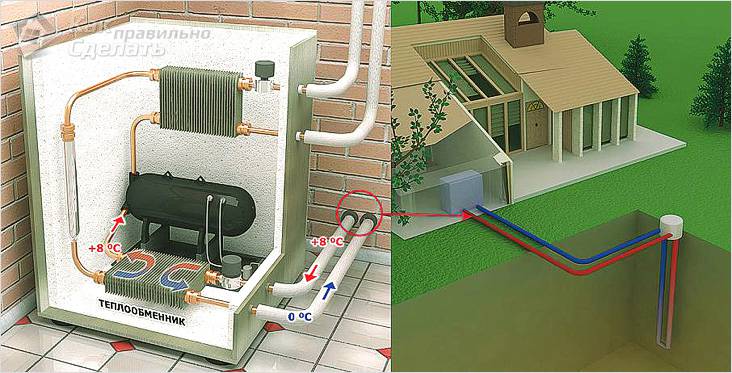
As already mentioned, it is preferable to buy a compressor ready. Any model used in air conditioners is suitable.
We collect all other components on our own:
- A stainless tank with a capacity of about 100 liters is taken as the case of the condenser. It is cut in half and inside mounted a coil from a copper tube with a wall thickness of at least 1 mm. Threaded connections are soldered into the shell for connection to the circuit. After this, parts of the tank can be welded.
- For an evaporator, a polyethylene bottle with a volume of 80 l or a pipe section is perfect. A coil is also inserted into it and water inlets and outlets are brought in. Heat carriers are isolated from the external environment with a foam rubber “fur coat”.
- Now you need to put the whole system, solder the pipes and fill in the refrigerant. The amount of freon is very important for the proper operation of the pump, it is better to entrust this calculation to the heating engineer. He will be able to finally connect the installation and configure the compressor.
- It remains only to connect the external circuit. Its assembly will depend on the type of pump.
A vertical soil-water installation requires a well; a geothermal probe is lowered into it.
For a horizontal apparatus, a collector is collected and buried in the ground at a depth that excludes freezing.
In the "water-water" system, the circuit consists of a network of plastic pipes through which the coolant will flow. Then all this must be fixed in a reservoir at the required depth.
The air-water pump manifold is also installed and mounted on or near the roof of the house.
For stable operation and protection against breakage, it is advisable to supplement the machine with the ability to manually start the compressor in case of a sudden outage. The cost of such an installation is quite high. The factory pump is even more expensive. However, practice shows that the acquisition pays off in several years of operation.
Video
Homemade heat pump from compressor
A heat pump is an interesting but expensive thing. The approximate cost of equipment + external circuit devices is from $ 300 to $ 1,000 per 1 kW of power. Knowing the “sleekness” of Russian people, it is easy to assume that more than one do-it-yourself heat pump is already working in the vast expanses of our vast and diverse climatic homeland. And indeed it is. Most often, there are home-made devices made by “refrigerators”. And this is understandable, because the heat pump and the freezer work on the same principle, just the thermal installation system is focused on collecting heat, and not on its removal, and the compressor uses more power.
Read about the principle of work here.
What can become a heat source for a heat pump
Heat for heating the premises can be taken from the air on the street. But here difficulties will inevitably arise during operation: the temperature fluctuations are too large, even the average daily, not to mention the fact that the heat pump shows normal efficiency at temperatures above 0oC. And how many regions do we have in winter such a picture? In the spring, and even then not early, and not throughout, and not always.
Any environment can become a source of heat for your home with heating from a heat pump.
A heat source located in water looks much more acceptable. If there is a river nearby, a lake or a decent pond depth - this is just great: you can simply drown the pipeline. It is only important that fishermen with donks not fish there.
Another good option is a well. But here, as with a well: there is a chance that the water level will drop and you have to look for another source. But for now, everything is fine, it will work well: the average water temperature in the underground horizons is 5-7oC. This is more than enough for the operation of the heat pump.
You may be surprised, but you can use the sewer. And it’s nice to use it: temperatures are higher there than in wells. The pipeline can be placed in a sewage pit or well, but provided that all of it will be covered with water permanently. And the pipe will need to choose chemically resistant.
A horizontal underground collector is extremely time-consuming: you will have to remove the soil from several hundred parts to a depth below the freezing point. These are very large volumes that cannot be mastered alone or even with an assistant. And, as practice has shown, in our climatic conditions such systems are ineffective: winters are too harsh.
With vertical collectors, the situation is no better: it is unlikely to manage without drilling equipment. The number and depth of wells depend on the soil: the spread of possible heat removal from a meter of the well is very large. From 25 W / m in dry gravelly and sandy soil, up to 80-85 W / m in moist gravelly and sandy soils or in granite. Accordingly, the difference in the length of the wells is 3 times or more.
Here is a diagram of home heating with a heat pump. When using, as in the described example, two wells and in the absence of a closed loop, the distance between the two wells should be at least 20 meters. And you need to take into account the flow direction so that cold water from the pump does not reduce the temperature in the "donor" well
In the described example of a home-made heat pump, the heat source is a well with a good rate of water intake. Water arrives so quickly that it covers domestic consumption and is enough to transfer the right amount of heat (the required water flow rate was calculated, and the pump was selected accordingly). But the heat source for this modification can be any of the above, except for air. Having decided on a heat source, it will be possible to make a heat pump for heating a house with your own hands.
Do-it-yourself water-to-water heat pump from an air conditioning compressor
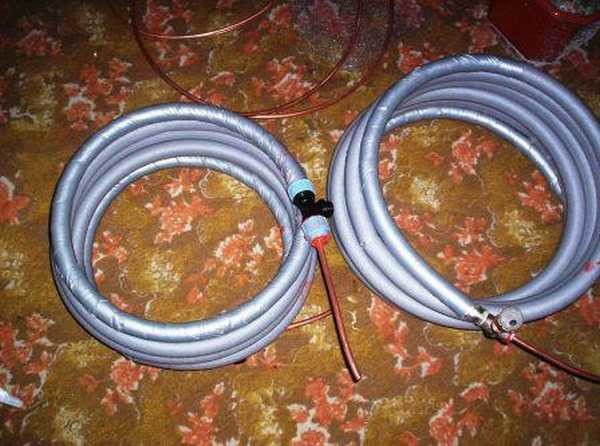
This heat pump from an air conditioner is easy to make with your own hands, but you need the help of a good master in repairing a refrigeration technician. To make you need to purchase:

All these components with a fee for the work of the refrigerator (for assembly and soldering, pouring freon) amounted to approximately $ 600. Plus, the cost of personal time for arranging the input circuit and assembly.
Now we begin to manufacture the heat pump itself.

These are ready-made heat exchangers with installed fittings
Pay more attention to vibration isolation and sound absorption: if the device is installed in a house, they decently get on the nerves without additional measures to neutralize them.

You need to install a compressor on the frame, then assemble the entire circuit
In the described example, water is pumped from the well. The aquifer is located at a depth of 4 meters. One pump lifts it and delivers it to the heat pump, water is discharged into the second well. But you can organize a closed loop, then you will need to calculate the power of the circulation pump.
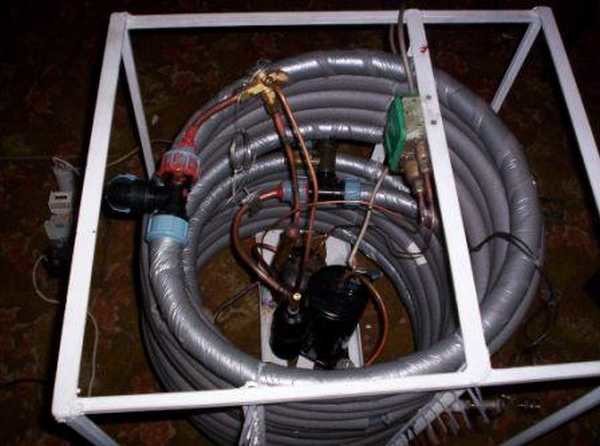

This is after the work of the "refrigerator"
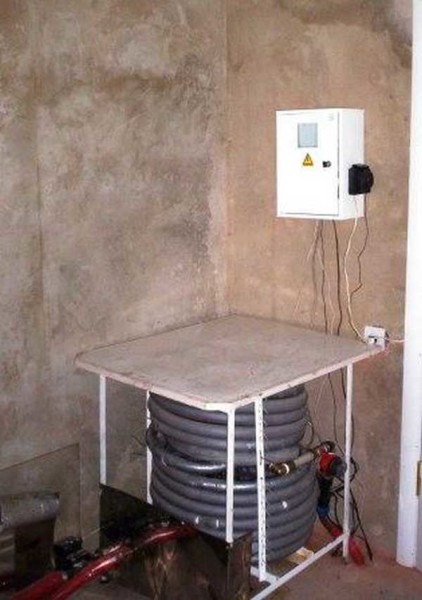

Not the most presentable look, but it works
From the operating experience of a DIY heat pump
As practice shows, the performance of the presented option is not too high: 2.6-2.8. There is no need to talk about the super efficiency of this heat pump: on an area of \u200b\u200b60 m2 at -5oC on the street, it itself supports + 17oC. But the system was considered and mounted under the boiler, radiators for the incoming temperature + 45oC simply can not give out more. The system in the house was working old and the number of radiators was not increased. But while in the cold they warmed up by the stove.
If a regenerative heat exchanger is added to the design, this will increase the efficiency by 10-15%. Given that small costs can be made. You will need two copper pipes of 1.5 meters each. One with a diameter of 22 mm, the second - 10 mm. A 4-wire conductor (3-4 meters long, 4 mm in diameter) is wound onto a thinner one to increase the heat transfer area, its ends are soldered to the tube so that they do not unwind. A tube with wound wire is carefully inserted into a tube of a larger diameter. It must be installed between the compressor and the evaporator. The refinement is insignificant, but it significantly increases efficiency. True, under certain conditions, it is unsafe: warm freon can get into the compressor, which will lead to its failure.
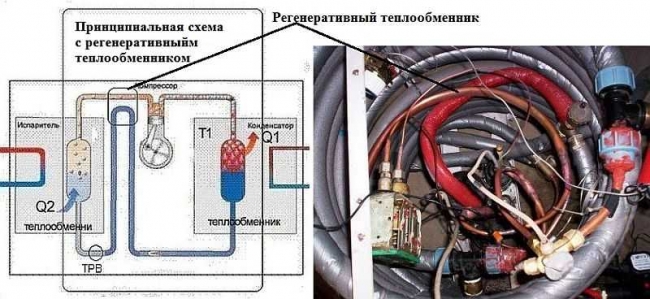
Refinement of the scheme: you can add a regenerative heat exchanger, which will increase productivity by about 15-20%
The second option to increase efficiency, safer and no less effective is to install an additional heat exchanger for heating water or glycol.
What to look for if you decide to make a heat pump yourself. There are several things that can only be learned from experience:
- Starting currents of this particular installation were very decent. Not always the network resources were enough to start the installation. Therefore, if you make a serious installation, it is better to take a three-phase compressor, and let, respectively, a three-phase input. Yes, it’s not cheap, but for a stable start of a single-phase compressor, a decentralized electronic stabilizer is required, which also cannot be called cheap
- A heat pump on a finished radiator system will not give a normal room temperature. They are designed for a different temperature of coolants, which these installations, especially home-made ones, are extremely rarely able to give. Therefore, either upgrade the system (adding at least as many sections of radiators), or install water floors.
- If there are three rings of water in the well, this does not mean that he has a large debit. You need to know how much he is able to give water with its constant selection.
Summary
Undoubtedly, the cost of this heat pump from an air conditioner is several times lower than ready-made factory options, even Chinese ones. But there are a lot of nuances here: you need to take care of the heat source, and the supplied heat should be enough, correctly calculate the length of the heat exchangers (coils), set the automation, provide guaranteed power, etc. But if you are able to take care of all this, then this is undoubtedly beneficial. Let us give you advice: in the first year it is very desirable to have backup heating, and it is better to carry out tests and the first start in the summer so that there is time to finalize the unit and bring it to mind.
Photo Gallery (9 photos):
- An innovative device related to alternative energy sources. Removing heat from the natural resources around, the device is an economical device with a high degree of autonomy.
Specifications
On heating and water supply of a private house, I want to save most of the zealous owners. A heat pump is suitable for such purposes.
It is quite possible to build it yourself, while saving a lot - a factory device is very expensive.
Properties and device
The device has an external and internal circuit along which the coolant moves. The components of a standard appliance are a heat pump, an intake device and a heat distribution device. The inside circuit consists of a mains powered compressor, an evaporator, a butterfly valve, and a condenser. Also used in the device are fans, a pipe system, geothermal probes.
Advantages of a heat pump:
- does not emit any harmful substances, absolutely eco-friendly;
- no costs for the purchase and delivery of fuel (electricity is spent only on moving freon);
- no need for additional communications;
- absolutely fire and explosion proof;
- full heating in winter and air conditioning in summer;
- a self-built heat pump is an autonomous construction that requires a minimum of control effort.
Application
A self-assembled heat pump is suitable for such cases:
![]()
- if you want to save on fuel for heating a house;
- if it is impossible to bring gas to the house or make it too troublesome when buying bottled gas is not a way out;
- there is no desire and ability to heat coal, wood, electricity, other fuel;
- if the landlord is committed to using clean alternative energy. The device is quite practical, even along with the availability of opportunities to use other energy sources.
Do-it-yourself heat pump is made for the home, based on the technology of heat removal from the earth, water, air. It is used for heating, water heating and even air conditioning indoors.
Principle of operation
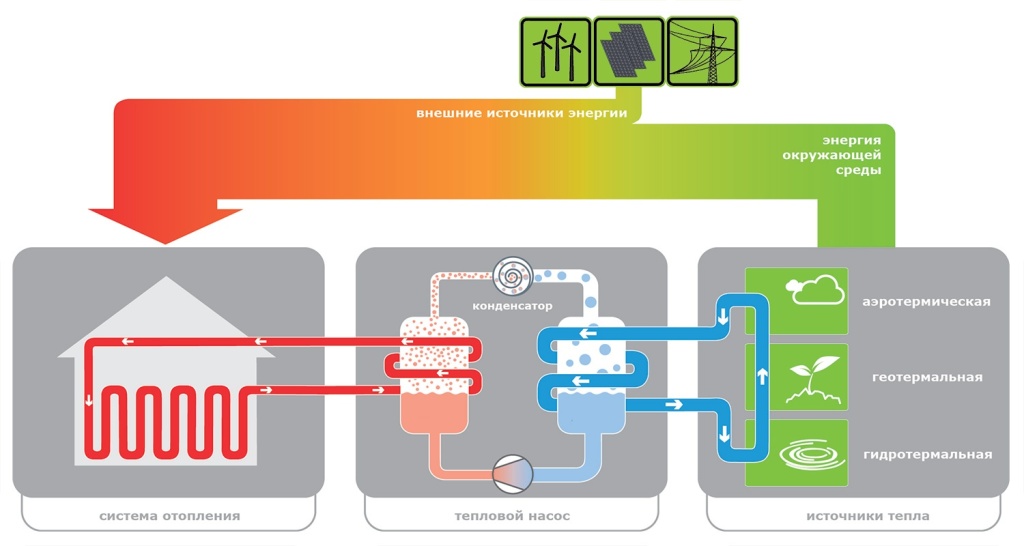
All the space around us is energy - you only need to be able to use it. For a heat pump, it is necessary that the ambient temperature be more than 1 ° C. It should be said that even the earth in winter under the snow or at some depth retains heat. The work of a geothermal or any other heat pump is based on the transportation of heat from its source using a heat carrier to the heating circuit of the house.
The scheme of the device operation by items:
- a heat carrier (water, soil, air) fills the pipeline under the ground and heats it;
- then the heat carrier is transported to the heat exchanger (evaporator) with the subsequent transfer of heat to the internal circuit;
- in the external circuit there is a refrigerant - a liquid with a low boiling point under low pressure. For example, freon, water with alcohol, glycol mixture. Inside the evaporator, this substance heats up and becomes gas;
- refrigerant gas is sent to the compressor, compressed under high pressure and heats up;
- hot gas enters the condenser and there its thermal energy goes to the house;
- the cycle ends with the conversion of the refrigerant into a liquid, and it, due to heat loss, returns back to the system.

The same principle is used for refrigerators, so heat pumps for the home can be used as air conditioners to cool a room. Simply put, a heat pump is such a refrigerator with the opposite effect: heat is generated instead of cold.
Kinds
Do-it-yourself heat pumps can be constructed on the basis of three principles - according to the energy source, heat carrier and their combination. The source of energy can be water (reservoir, river), soil, air. All types of pumps are based on one operating principle.
Classification
There are three groups of devices:
- water-water;
- groundwater (geothermal heat pumps);
- use water and air.
Thermal collector "soil-water"
A do-it-yourself heat pump is the most common and efficient way to extract energy. At a depth of several meters, the soil has one constant temperature and is little susceptible to weather conditions. On the external circuit of such a special environmentally friendly liquid is used, popularly called "brine".
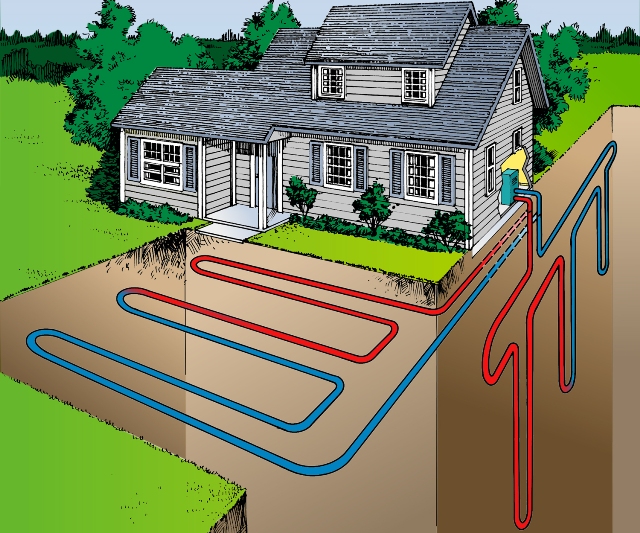
The outer contour of the geothermal pump is created from plastic pipes. They are dug into the ground vertically or horizontally. In the first case, one kilowatt may require a fairly significant area of \u200b\u200bwork - 25-50 m2. The area cannot be used for planting work - here only planting of annual flowering plants is allowed.
A vertical energy collector requires several wells at 50–150 m. Such a device is more efficient, special depth probes transmit heat.
At great depths, the water temperature is constant and stable. The source of low potential energy can be an open reservoir, groundwater (well, well), wastewater. There are no fundamental differences in the design for heating of this type with different coolants.

The water-to-water device is the least labor-intensive: it is enough to equip the pipes with a heat carrier with a load and place them in water if it is a body of water. Groundwater will require a more complex structure and there may be a need to construct a well to discharge water passing through the heat exchanger.
"Air-water"
Such a pump is slightly inferior to the first two and in cold weather its power decreases. But it is more universal: for it there is no need to dig the earth, to create wells. It is only necessary to install the necessary equipment, for example, on the roof of the house. This does not require complex installation work.

The main advantage is the ability to reuse the heat leaving the room. In winter, it is recommended to have another source of heat, since the power of such a heater can be significantly reduced.
Installation steps
Do-it-yourself heat pump can be made entirely from old parts, taken, for example, from a non-working air conditioner.
Costs, payback, capacity
A factory appliance costs about 4,000 euros and more. A home-made pump for heating 100 m² of space will pay off after about 2 years. For houses with not very good thermal insulation, the power should be 75 W / m²., With good thermal insulation, 50 W / m² is enough, and when using modern thermal insulation materials, 30 W / m² is enough.

The ideal option is when the pump is included in the project for heating a house with a heated floor and tiled flooring.
Process of creation
First you need to get the compressor from a non-working air conditioner, not necessarily a new one. It will be cheaper to purchase it in workshops for repairing refrigerators. The compressor is attached to the wall with brackets (L-300 is suitable).

For the manufacture of a capacitor, a stainless steel tank of 100-120 liters is suitable. It is cut in half, a coil is installed inside. You can make the coil yourself from the plumbing or from the refrigerator. Here you need thick walls - from 1 mm or more. The tube is wound on a regular cylinder (gas, oxygen) with a uniform distance between the turns and is fixed in this position by a perforated aluminum corner (they form the corners under the putty). He wraps himself around the coil so that each coil is positioned against a hole in the corner.
As a result, there will be an even pitch of turns and structural strength. After creating the coil, half the tanks are welded. Threaded connections are also welded. Then an evaporator is created. For him, an ordinary plastic container of 60–80 liters can come up. with a ¾-inch pipe coil mounted inside. Simple water pipes are used to transport water.
The evaporator is mounted on the wall with an L-bracket. But the specialist in refrigeration equipment should do the freon injection: he will weld the tubes and pump the freon into them. After that, the structure is connected to the heating system inside the house, and then to the external circuit.
Features for every kind
A vertical pump for heating "ground-water" requires the creation of a well 50-150 m. Geothermal probes are placed in it and connected to the pump. The probes take heat from the soil, which is transferred with non-freezing water to the pump, and from there to the heating system. Probes are suitable for small areas, and a horizontal collector for large areas.
For a horizontal apparatus such as "soil-water" you need to create a collector from a pipe system. It is located below the freezing level (1–1.5 m) and it looks like a kind of coil under the ground. The soil layer is removed, pipes are laid and the soil is poured back. You can lay the pipes in separate trenches.
For the unit of the type "water-water" is collected from HDPE pipes, which are filled with a heat carrier and then transferred to the reservoir. The pipes look like a large coil at the bottom of a reservoir. It is advisable to place them in its center.
The air-to-water apparatus does not require laborious earthworks. A place is chosen near the house or on its roof, where a home-made heat pump is connected to the internal heating. Heat is extracted by fans and evaporator.
Improving the efficiency of the home heating system is one of the main tasks of its owner, since the costs of this article in Russian climatic conditions are very significant. Therefore, the task of using the energy of the surrounding space for heating is very interesting, constantly evolving and remains a subject of attention, especially in the community of "homemade". It is quite possible for a trained person to assemble the heat pump with his own hands, since this work does not present any special difficulties, and there is no need to manufacture parts of complex configuration.
The principle of operation of the device
It is based on the collection of heat from the surrounding space and its use for a home heating system in order to reduce the cost of this function. Devices of this type are available in many houses, these are refrigerators, split - systems and air conditioners. Some of them have a dual purpose, performing at the user's choice either heating or cooling the premises, depending on the need.
The theoretical basis of such machines is the reverse Carnot cycle. But, without going into details, we simply describe the operation of such a device.
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the operation of the heat pump in the heating network
The working fluid in such devices, as in refrigerators, is freon or ammonia, which is injected by the compressor into the heating circuit. In this case, the pressure inside the system rises sharply, since the coolant outlet is blocked by a throttle. The resulting heat warms up the coolant in the home heating system, as a rule, the temperature reaches a level of 64 ° C. The hot stream complements the circulation in the main heating network, reducing fuel consumption. At a certain pressure, the throttle opens, and the working fluid enters the chamber of the evaporator. At the same time, its temperature decreases. Additional heat is obtained from the heat collection register. Next, the cycle repeats, as in the device of the refrigerator.
Calculation of system parameters
The power that a homemade heat pump will require can be calculated from the ratio:
R = ( k * v * T )/860, where
R – power required for space heating
k – coefficient for accounting for heat losses by the building (1 - a qualitatively insulated room, 4 - a wooden hut);
v - the total volume of the room to be heated;
T – the largest temperature difference in the outside world and inside the house;
860 – conversion factor of the calculation result to kw of kcal.
As an example, we give a calculation for a house of 200 square meters with a ceiling height of 2.8 meters:
R \u003d 1 * 200 * 2.8 * (22 - -25) / 860 \u003d 560 * 47/860 \u003d 30.6 kW.
It is advisable to use a heat pump with a power reserve of 10 - 12%, that is, about 35 kW.
It is necessary to pay attention to such an indicator as the difference between the external and internal temperatures. If we take heated air from the surrounding space with a temperature of about 7 ° C, the difference indicator will be (22 - 7) 15 degrees, and the heat pump's power will be 9.8 kW. Compare these two indicators and feel the difference when using the heat of the surrounding space.
Part of the equipment
External circuit
For the external circuit of the home heating unit, you need pipes. Metal products (but not stainless steel) have the highest thermal conductivity, therefore it is better to use them for a heat collection system.

Fig. 2. Heat collection in the ground using a well for a homemade heat pump
Figure 2 shows a do-it-yourself geothermal heat pump using parts from an old air conditioner and refrigerator. The depth of the well for collecting heat from geothermal waters is about 60 - 120 meters. The casing is not shown in the above diagram, but its use is necessary, since the casing protects the walls of the well from destruction. External heat collection register must be inside the casing.
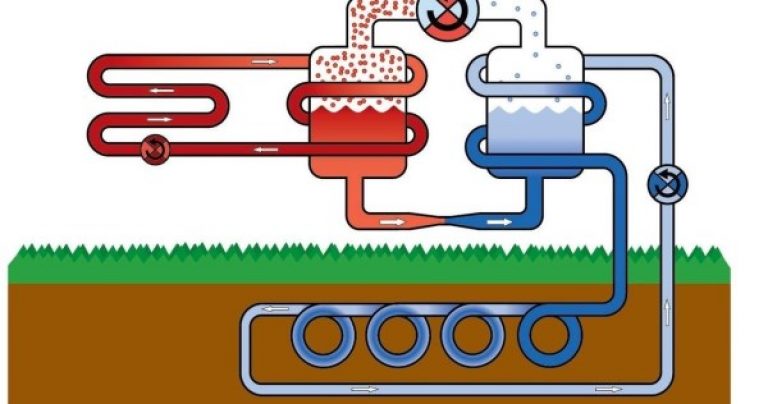
Fig. 3. Surface heat collection
The collection of spatial energy for heating a house can be carried out not only through deep well, but also using a horizontal pipe system buried no less than the amount of freezing of the soil.
A sufficient result is given by the collection of heat from the reservoir, since at the bottom the water temperature is always 4 degrees heat, since it is in this state that it has the highest density. An attractive aspect is the significantly smaller amount of excavation work.
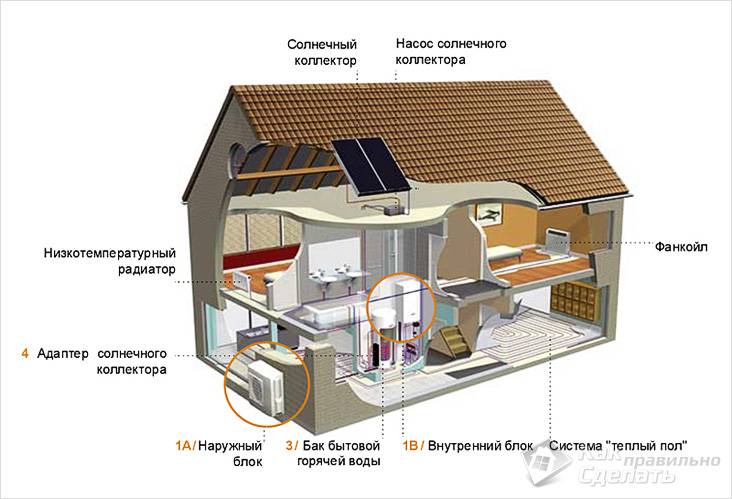
Used to collect heat and systems that are heated by exposure to the sun. Such blocks are most often installed on the roof of the house and are intended for heating water or air. They significantly increase the temperature in the evaporator of the heat pump, increasing the efficiency of the home heating system.
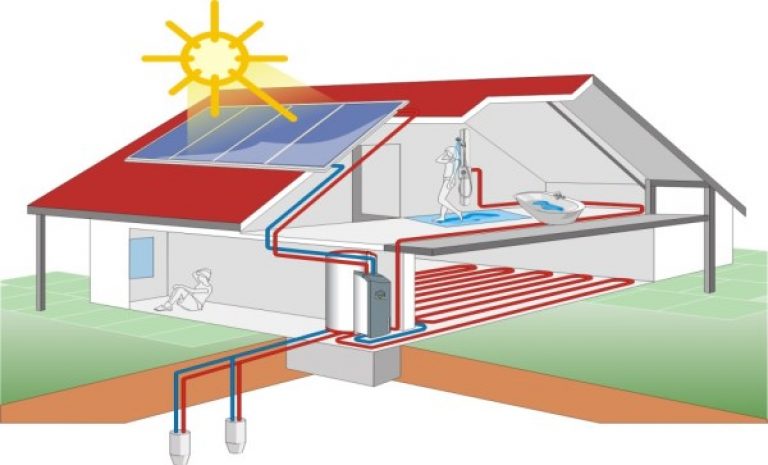
Fig. 4. Use of a solar collector in a building heating system with a heat pump
Evaporator
This unit is a container in which a heat exchanger is located, carrying a carrier of heat collected by the external circuit. The constructive solution to this part may be different, but most often it is made of copper pipes.
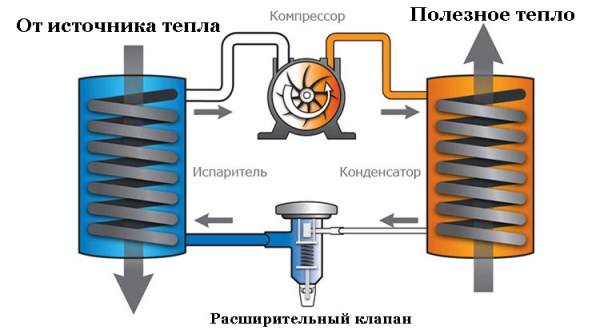
Fig. 5. The shape of the heat element of the evaporator should provide maximum contact with the refrigerant
Making a heat pump with their own hands, they often use units and parts suitable for use from an old refrigerator or air conditioner, as well as a broken split system.
Compressor
On home-made heat pumps, compressors from existing old equipment are most often used. When the unit system is assembled and tested, you can think about replacing the compressor from the old refrigerator to another, more or less powerful. When choosing a compressor, it is best to pay attention to the nodes of split systems, which are characterized by increased power and reliability. Modern units, as a rule, are equipped with automatic control and adjustment units, which greatly simplifies the management of these units.
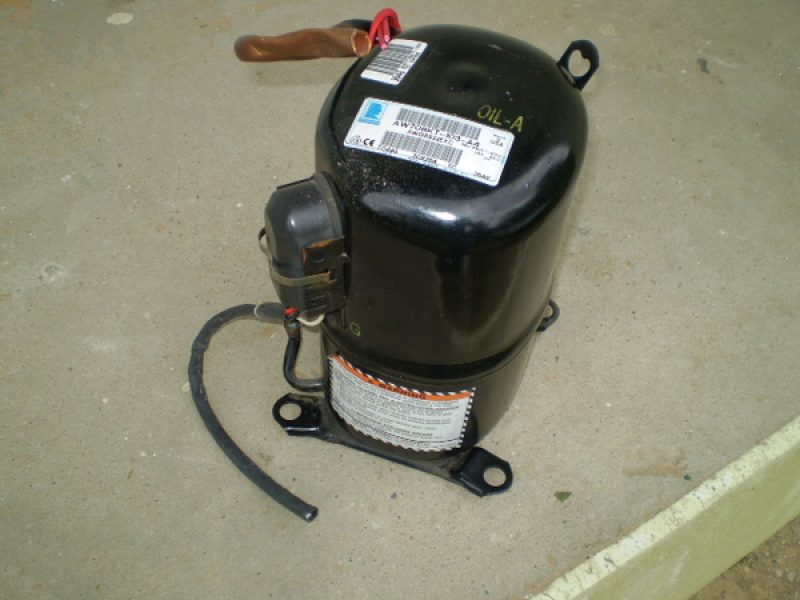

Fig. 6. Heat pump compressor
Capacitor
The choice of this element of the system must be approached with particular care, since it is a pressure vessel. It is preferable to use an old gas cylinder. It will have to be cut to place the heat exchanger there, and then welded again.
Chokes
In heat pumps, these are devices for relieving pressure from the condenser to the evaporator. The item is easy to find in shops or workshops for the repair of rubble equipment, since they are very durable in operation.

Fig. 7. Choke for heat pump
Frenett Heat Pumps
These devices are extremely simple and efficient. However, for their manufacture, the accuracy of each part and the careful balancing of the entire rotor system are important.
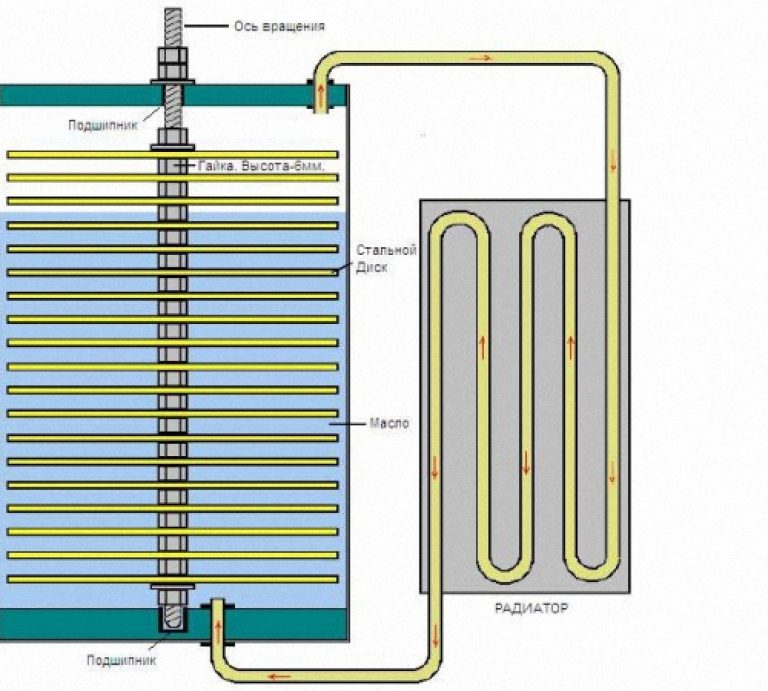
Fig. 8. Frenett Heat Pump Diagram
During the operation of such a heat pump, oil is heated, and heat is transferred to the heating system of the house through a radiator. Vertical and horizontal schemes of the device are possible.
Do-it-yourself fresnett heat pump for heating a house can be made only with access to metalworking equipment and good metalwork training.
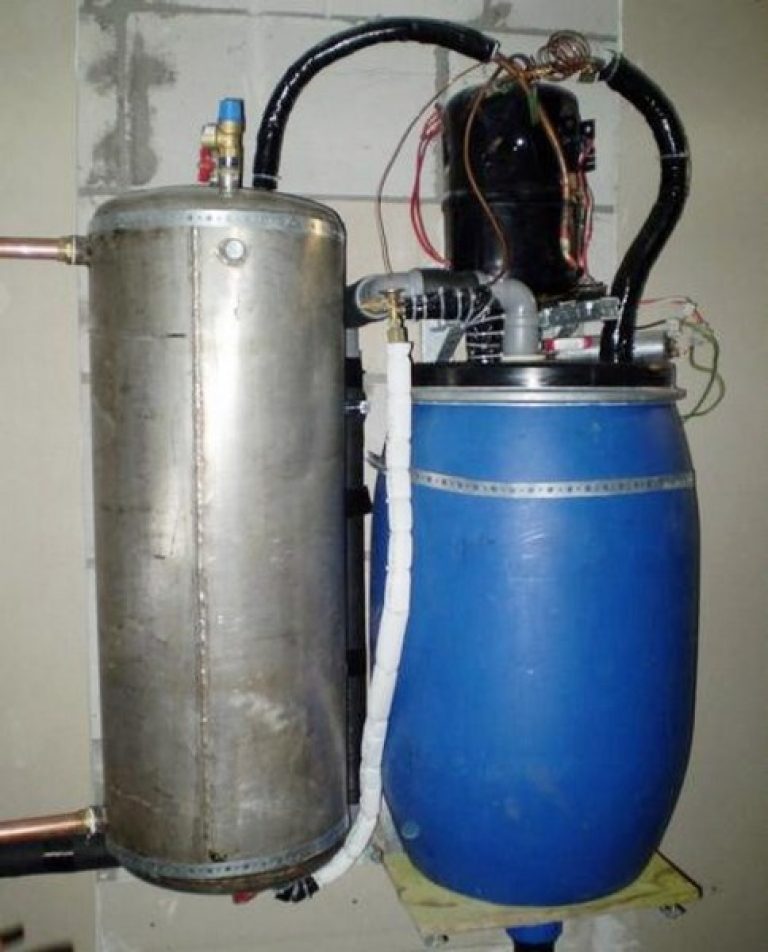

Fig. 9. Homemade heat pump embodiment
Conclusion
The use of the energy of the surrounding space is noteworthy, allowing you to reduce the cost of heating the house. When using the heat of geothermal water or ground air heating, it does not quickly pay off due to the large labor and financial costs, but the efficiency of the process is not in doubt.
In addition, it is possible to use heat pumps as split systems, increasing the comfort of living, and the use of an automatic control unit will facilitate the management of the device.