Afroasian family of languages. Major language families Notable Afro-Asiatic families
As you know, there are 4 large races in the world: Caucasoid, Mongoloid, Negroid and Australoid (for example, the natives of Australia belong to it). The descendants of interracial marriages are called mestizos, but, as a rule, mestizos are understood to be the descendants of Caucasians and Mongoloids. The descendants of Negroids and Caucasians are called mulattoes. As for the Australoids, for example, the Polynesians (Maori, etc.) or the Filipinos are a mixture of three races: Australoid, Mongoloid and Caucasoid (see and rating).
Negroids practically did not mix with the Mongoloid and Australoid races. This is due to the fact that that part of Africa, which is inhabited by Negroids, from the north and east borders on territories inhabited by Caucasian peoples. The only region where a mixture of Negroids and Mongoloids occurred is the island of Madagascar off the southeast coast of Africa. In the first millennium of our era, immigrants from Indonesia penetrated Madagascar by sea, where they mixed with the Negroid representatives of the Bantu tribes. The inhabitants of Madagascar are called Malagasy, there are about 20 million of them.
The second wave of mixing of Mongoloids and Negroids occurred in America by mixing people from Africa and Indians. The descendants of such marriages in Latin America are called sambos, and in the USA they are called black Indians.
Another small proportion of mixed Negroid-Mongoloid marriages are the offspring of marriages between African Americans and Asians. The offspring of such marriages are called Afroasiatics (Malagasy also fit the definition of "Afroasiatics").
This rating contains the most beautiful, in my opinion, Afro-Asian and black Indian women. There is also a representative of the Malagasy. The rating includes only those girls who do not have Caucasian roots. What an Afro-Asian woman with European roots looks like can be seen in the example of Noemie Lenoir, who is included in.
12th place. Radmilla Cody- singer and model from the second largest Indian people in the United States - the Navajo. In 1997, she won the Miss Navajo title, which evaluates not so much beauty as knowledge of the Navajo language and traditions. Radmilla's father is an African American, his mother is from the Navajo people.
11th place. Nataly Andria(born February 3, 1985, Madagascar) is a French singer of Malagasy origin. Her real last name is Andrianaivoson.
.jpg)
10th place. Thelma Aoyama(born October 27, 1987, Japan) is a Japanese singer. Her male grandfather is from Trinidad and Tobago.

9th place. Natasha Shanta Reid(born May 31, 1981, USA), better known as Yoon Mi-rae, is a South Korean singer. Her father is African American and her mother is Korean.

8th place. Ananda Lewis(born March 21, 1973, USA) is an American TV presenter and model. She has African-American and Native American roots (her ancestors from among the Indian peoples are Creeks and Blackfoot).

7th place. Anya Ayoung Chee(born October 17, 1981, USA) - Trinidadian fashion designer, TV presenter, model, Miss Trinidad and Tobago 2008. Has Chinese roots.

6th place. Leona Mitchell(born October 13, 1949, USA) is an American opera singer. Has African American and Indian (Chickasaw people) roots.

5th place. Crystal Kay(born February 26, 1986, Japan) is a Japanese singer and actress. However, she has no Japanese roots. Her father is African American and her mother is Korean.

4th place. Ariana Miyamoto- Miss Japan 2015, the representative of Japan at the Miss Universe 2015 pageant, where she entered the top 10. Ariana was born in Nagasaki, Japan on May 12, 1994. Her father was an African American who served at that time at the US Navy base in Japan, and her mother was Japanese. After winning the Miss Japan contest, the girl was criticized for her non-Japanese appearance. This is due to the fact that Miyamoto became the first mestizo to win the national beauty contest, although this has long become the norm in Europe, the USA and Canada.
3rd place. Julia Jones /Julia Jones(b. January 23, 1981, USA) is an American actress who became famous after playing the role of Lea Clearwater in The Twilight Saga: Eclipse (2010). Has African American and Native American (Chickasaw and Choctaw) roots.

2nd place. Chanel Iman / Chanel Iman(born December 1, 1990, USA) is an American top model who took part in the Victoria's Secret Fashion Show three times. Vogue Paris magazine included her in the top 30 best models of the 2000s. Chanel Iman's father is African American, her mother is half Korean, half African American.
1st place. Naomi Campbell / Naomi Campbell(born May 22, 1970, UK) is a British supermodel. For the most part, Naomi Campbell's ancestors are Afro-Jamaican, also has Chinese roots (her male grandmother was Chinese).
.jpg)
Bak language (one)
Altai family of languages
The Altaic family of languages includes Turkic (Turkish, Azerbaijani, Turkmen, Tatar, Bashkir, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Uzbek, Chuvash, Yakut, Tuvan, Khakass languages), Mongolian (Mongolian, Buryat, Kalmyk languages), Tungus-Manchu (Siberian, Manchu and Amur language groups) and Japanese-Ryukyuan (Japanese, Ainu, Ryukyuan languages) language branches, as well as Korean language isolate. These languages are spoken in Northeast Asia, Central Asia and of Eastern Europe(Buryatia, Kalmykia, etc.).
The Basque language (self-name Euskara) is the language of the Basques, the people inhabiting the Basque Country (Navarre) - the northern regions of Spain and the adjacent southern regions of France. Basque, unlike the other languages of Europe, does not belong to any of the Indo-European or any of the other known families of languages, and is a so-called isolated language. The genetic connections of the language have not been established, however, Basque is traditionally included by scientists in the so-called Paleo-Spanish languages, and in a broader sense, in an unclassified and probably heterogeneous group of Mediterranean languages.
The total number of carriers is about 800,000 people, most of whom (700 thousand) live in the territory of the Basque Country, of which more than 500 thousand are in its Spanish part. A small number of carriers live in other regions of Europe, in America and Australia.
The Basque language is divided into a number of dialects that are very different from each other. A unified literary Basque language was created in the 1960s. linguist Koldo Michelena.
The Basque language is not related to any known language family. There is an assumption about its connection with the Aquitanian language (see references in the article Iberian script). According to another hypothesis, the Basque language reveals an ancient relationship with the Sino-Caucasian macro-family.
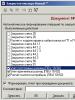
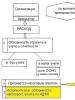
Afroasian languages (sometimes also Afroasiatic; the name ʼʼSemitic-Hamiticʼʼ is also very common today) is a family of languages that includes six branches of languages that have signs of a common origin (the presence of related root and grammatical morphemes). Sometimes it is included in a more general formation - the Nostratic macro-family of languages (combining the Indo-European, Kartvelian, Uralic, Dravidian and Altaic families). At the same time, recently the Afro-Asian macro-family has been excluded from the Nostratic one and is considered along with the latter as a separate and independent macro-family, but closely related to the Nostratic one.
The Afroasian languages include both living and dead languages. The former are currently distributed over a vast area, occupying the territory of Western Asia (from Mesopotamia to the coast of the Mediterranean and Red Seas) and vast territories of East and North Africa - up to the Atlantic coast. Separate groups of representatives of the Afroasian languages are also found outside the main territory of their distribution. The total number of speakers currently fluctuates between 270 million and 300 million people, according to various estimates.
The Afroasian family includes the following language branches:
· Berber-Libyan languages. The living languages of this family are distributed in North Africa west from Egypt and Libya to Mauritania, as well as in the oases of the Sahara, as far as Nigeria and Senegal. In Morocco, Berber speakers make up about 40% of the total population of the country, in Algeria - about 25%. In Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Mauritania, the Berber-speaking population is smaller. All living languages are unwritten. The Berber tribes of the Tuareg (Sahara) use their own script in everyday life, called tifinagh and dating back to the ancient Libyan script. The Libyan script is represented by brief rock inscriptions found in the Sahara and the Libyan desert; the earliest of them date back to the 2nd century BC. e. The inscriptions are partially deciphered; they are divided into three groups of monuments: fezsansko-Tripolitan, western Numidian and eastern Numidian. The languages of these inscriptions represent a group of dead languages of the Berber-Libyan family.
· Ancient Egyptian language. With its later descendant - the Coptic language - it is a dead language. It was distributed in the valley of the middle and lower Nile (modern Egypt). The first written monuments of ancient Egyptian date back to the end of the 4th - the beginning of the 3rd millennium BC. e. It existed as a living and colloquial language until the 5th century AD. e. Monuments of the Coptic language have been known since the 3rd century AD. e.; to XIV century it falls into disuse, remaining as a cult language of the Coptic Christian Church. In everyday life, the Copts, who, according to the end of 2010, there are about 8 million people, use Arabic and are now considered an ethno-confessional group of Egyptian Arabs.
· Cushitic languages. Of these, only living ones are known, distributed in Northeast Africa: in the northeast of Sudan, in Ethiopia, Djibouti, Somalia, in northern Kenya and in western Tanzania. The number of speakers is about 25.7 million people.
· Omot languages. Living unwritten languages, common in southwestern Ethiopia. The number of speakers is about 1.6 million people. As an independent branch of the Afroasian macro-family, they began to stand out only recently (G. Fleming, M. Bender, I. M. Dyakonov). Some scientists attribute the Omot languages to the Western Cushitic group, which separated from Proto-Kushit earlier than the rest.
· Semitic languages. The most numerous of the Afroasian language families; represented by modern living languages (Arabic, Maltese, New Aramaic dialects, Hebrew, Ethio-Semitic - Amharic, Tigre, Tigrinya, etc.), common in the Arab East, Israel, Ethiopia and North Africa, islands - in other countries of Asia and Africa . According to different sources, the number of speakers fluctuates, amounting to approximately 200 million. Ancient languages also belong to the Semitic - Akkadian, Ugaritic, Eblaite, Phoenician, Hebrew, Old Aramaic, epigraphic South Arabian, ancient Ethiopian - Geez.
· Chadic languages. More than 150 belong to this branch. modern languages and dialect groups. Distributed in Central and Western Sudan, in the region of Lake Chad, Nigeria, Cameroon. The Hausa speakers are the most numerous, numbering about 30-40 million people; for most of them, Hausa is not their native language, but the language of interethnic communication.
Semitic branch - divided into subgroups: Akkadian, or northeastern (Akkadian); Canaan-Aramaic, or northwestern (Amarean, Hebrew or Canaanite, Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Assyrian); Arabic, or Central (Arabic and Maltese); Abyssinian, or southern (Minean, Sabaean, Ethiopian);
Egyptian (Ancient Egyptian, Coptic languages); Berber; Chadic; cushitic.
5. The Caucasian family of languages combines three branches of languages:
West Caucasian (Abkhazian, Adyghe and Kabardino-Circassian);
East Caucasian (Circassian, Ingush, Avar, Lezgin languages);
South Caucasian (Georgian, Zan, Laz, Svaneti).
6. Altaic language family:
Turkic branch (Chuvash, Tatar, Bashkir, Kyrgyz, Uzbek, Kumyk, Kazakh, Yakut, Turkmen, Turkish, Azerbaijani; dead Pecheneg, Polovtsian and Khazar);
Mongolian (Mongolian, Buryat, Kalmyk);
Tungus-Manchu (Nanai, Udege, Evenk).
7. The Sino-Tibetan family is divided into two branches:
eastern(Chinese, Dungan and Karen); western(Burmese, Tibetan, Kachin).
47. Typological classification of languages.
CLASSIFY (from the Greek “rank” + “do”) - distribute any objects into classes (departments, detachments) depending on their common features and regular connections between them. CL-CIA OF LANGUAGES is the determination of the place of each language among the languages of the world.
TYPOLOGICAL (MORPHOLOGICAL) CLASSIFICATION OF LANGUAGES - a classification of languages based on similarities and differences in morphological and grammatical structure, i.e. in the ways of forming the forms of individual words. regardless of genetic or territorial proximity.
According to these differences, languages are usually divided into the following classes:
1. Root or isolating languages most languages of the Southeast. Asia (China, Vietnam) They are characterized by: no word forms. The words don't change. The root word consists only of the root. Order and intonation play an important role (languages of West Africa). Mao ra doi, doi vi ra tao (cats are afraid of dogs, dogs are not afraid of cats); grammatical the significance of the word order in the sentence (Chinese word "hao" m/b different parts of speech and have different meanings "hao zhen" a good person, "zhen hao" a person loves me)
2. Affixing languages affixes play an important role in the grammatical structure, the connection between words is more grammatical, affixes have morphogenesis
1) agglutinative languages, the formation of grammatical forms and derivative words in languages by attaching affixes to the root or to the base of the word, having grammatical meanings. Affixes are unambiguous, that is, each of them expresses only one grammatical meaning, and the same affix always serves for a given meaning. Affixes follow each other, do not merge with roots or other affixes, and their boundaries are distinct. The vowels of affixes may undergo phonetic changes depending on the sound composition of the stem (see vowel harmony), consonants at the junctions of morphemes may also change, but all these changes are subject to purely phonetic patterns characteristic of a given language. This is observed, for example, in most Altaic and Finno-Ugric languages: ish- business, work -chi- derivational affix ( ishchi- "worker"), -ler, -imiz, -den- (plural), accessories (1st person plural) and case (original case). Features: each morpheme almost always has one meaning. Morphemes can be used in all parts of speech.
Example: bash - head. I.p., units h.
Turkish bashlar - head, pl., im.p.
Bashtyn - r.p., singular
Bashlartyn - r.p., pl.
2) inflectional(from lat. flectivus"flexible") - a device of a synthetic type of language, in which inflection dominates with the help of inflections - formants that combine several meanings at once. The inflectional structure is the opposite of the agglutinative one, in which each formant carries only one meaning. Classical examples of inflectional languages are Latin, German, Russian. with help endings including zero ones (home - at home, walked - walked); with help internal inflection- grammatically significant change in the phonemic composition of the root (English) foot - feet "foot - feet"; mouse - mice mouse - mice").
3. Incorporating, or polysynthetic, e.g. Chukchi-Kamchatka, pl. languages of the Indians. America. Many languages of the peoples of the North (Chukchi, Koryak, Kamchadal, etc.), American Indians. A sign of the morphological structure of the word in these languages is its incompleteness, "incompleteness": the word acquires a peculiar structure only as part of a sentence. You/mine/yvalya/mna/rkyn (I sharpen a big knife).
There is not a single language that would purely belong to one type of classification, for example, Russian. Refers to inflectional, but there are elements of agglutination (read, read-a, read-and in which suf –l- conveys the meaning of the past tense, and gender and number are expressed by inflections)
Typological classification criterion- the structure of the language is analytical and synthetic ACCORDING TO SCHLEICHER. Analytical structure involves a wider use of service words, phonetic means and word order to form word forms, phrases and sentences. The languages of the analytical system are English, French, Italian, Spanish, Persian, Bulgarian and some other Indo-European languages. Synthetic tuning characterized by the fact that along with the use of service words, word order and intonation, a large role belongs to the forms of words formed with the help of affixes - inflections and formative suffixes and prefixes. The languages of the synthetic system are Russian, Polish, Lithuanian and most other Indo-European languages; all ancient written Indo-European languages were synthetic, for example, Latin, Greek, Gothic.
In its pure form, analyticism and synthetism are not represented in more than one language of the world, each has elements of both.
H. Steinthal divided all languages into languages with a form and languages without a form, and the form should be understood as both the form of the word and the form of the sentence. Steinthal called languages with no inflection as joining languages: without a form - the languages of Indochina, with a form - Chinese. Steinthal defined languages with the presence of inflection as modifying, without form: 1) through repetition and prefixes - Polynesian, 2) through suffixes - Turkic, Mongolian, Finno-Ugric, 3) through incorporation - Indian; and modifying, with the form: 1) through the addition of elements - the Egyptian language, 2) through internal inflection - Semitic languages and 3) through "true suffixes" - Indo-European languages.
F.N. Fink (1909) based his classification on the principle of constructing a sentence and the nature of the links between the members of the sentence. As a result, Fink shows eight types: 1) Chinese, 2) Greenlandic, 3) Subiya, 4) Turkish, 5) Samoan (and other Polynesian languages), 6) Arabic (and other Semitic languages), 7) Greek (and other Indo-European languages). languages) and 8) Georgian.
In a typological study, two tasks must be distinguished: 1) the creation of a general typology of the languages of the world, united in certain groups, for which one descriptive method is not enough, but the use of a comparative historical method is also necessary; 2) a typological description of individual languages, including their individual features, distinguishing regular and irregular phenomena, which, of course, must also be structural.
Language families
Indo-European family
The Indo-European family is the most studied family of languages with the largest number of speakers of these languages. This family includes English, Spanish, Portuguese, French, Italian, Russian, Greek, Hindi, Bengali; and classical languages: Latin, Sanskrit, Persian.
Ural family
The languages of this family are located in Europe ( Hungarian, Finnish) and Russia ( Mordovian). These languages have enough complex structure nouns.
Altai family
The language family extends from Europe ( Turkish) through Central Asia ( Uzbek), Mongolia ( Mongolian) before Far East (Korean, Japanese). The main distinguishing feature of these languages is the harmony of vowels.
Sino-Tibetan family
An important family of Asian languages, which includes the most widely spoken language on Earth - Chinese (Putonghua). These languages have features of monosyllables and tonality.
Malayo-Polynesian family
The family includes more than 1000 languages that are common on the Indian islands. Pacific Oceans as well as in Southeast Asia. Among these languages Malay, Indonesian, Maori And Hawaiian.
Afro-Asian family
Languages in this family North Africa and the Middle East. The main languages are Arab And Hebrew.
caucasian family
The family is located in the Caucasus Mountains region between the Black and Caspian Seas. Georgian And Chechen - main languages. They are known for having a large number of consonant sounds.
Dravidian family
The languages of southern India (as opposed to the Indo-European languages of northern India). Tamil is the best known of these languages.
Austro-Asian family
This is a group of languages located in Asia. They are found in the territory from eastern India to Vietnam. Among these languages are Vietnamese And Khmer.
Niger-Congo family
This family includes many languages of southern Africa and the Sahara. Common languages include: Swahili, khosa, Shona And Zulu.
Present and future of languages
In 2003 in the world there were a total of approximately 6,809
languages.
90% of these languages are spoken by less than 100,000 people. Over a million people speak 200-150 languages. There are languages, their approximate number is about 357, which are spoken by less than 50 people. On the tongue kambap(Central Cameroon) spoken by 30 people; in the language easy(in the Andes mountains in Bolivia) speaks about 20 people. Language Mati ke(in northern Australia) in 2003 was known by four people. About 46 languages have one native speaker.
Unfortunately, with the development mass communications(high-speed air travel, radio, television, telephones, the Internet), many small languages began to be under the threat of extinction. With their disappearance, the exceptional cultural way of perceiving the world around us will also disappear. Linguist Edwardsapir, wrote:
“There are no two such languages that could adequately convey the same social reality in the same way. Words in which they clothe different cultures reflect separate worlds, not the same world with different labels."
Over the past 500 years, about 4.5% of the described languages have disappeared from the face of the Earth. IN North America 52 out of 176 languages have disappeared since 1600. In Australia, 31 out of 235 languages have become extinct.
But even with all this, in some countries and regions one can observe a rich linguistic diversity. There are 52 languages in Mexico. Within the territory of former USSR- about 100. There are over 400 languages in Nigeria. There are over 700 different languages on the island of Papua New Guinea: in fact, every village has its own language. There are more than 800 languages in India belonging to different families (Indo-European, Dravidian, Sino-Tibetan, Austro-Asiatic).
Children from mixed marriages (mestizos) always turn out to be amazingly beautiful, or at least incredibly cute. This is an indisputable fact. In Korea, if one of the parents is Korean, they call them "chagubya" and they are perceived as their own Koreans, but with the appearance of Europeans. Chagubya, as a rule, are very beautiful, and therefore they are not deprived of the attention of others. Well, more to the topic… below we will present to your attention the 16 most charming celebrities who are half Korean.
Christina Kay Williams, singer, actress and host, was born in Yokohama, Japan in 1986. Her mother is Korean and her father is American. Both her parents were talented musicians. Mom was a professional singer, and dad played musical instruments.
American actor, born in Los Angeles (one of the largest Korean diasporas lives there). Half Korean, half German-Scottish.
Half Korean and half Japanese. Simon is considered one of the sexiest idols in the K-POP industry.
French actor and model. Julien's father is Korean and her mother is French. He rose to prominence through his role in the sitcom High Kick Through the Roof and his appearances on Korean television.
His main profession is a model, but he also took part in the filming of Korean films. Popular in both America and Korea. His mother is Korean and his father is American.
Professional American and Korean actor and model. He starred in the film "X-Men" in the role of Zero. Daniel's dad is Irish-American and his mom is Korean (adopted by an American family after the Korean War).
Yun Mire (Tasha) is known as the queen of Korean hip hop. She was born in Texas in 1981. Yoon Mire's mother is Korean and her father is African-American.
British idol singer. At the age of 7, she took part in the musical 'Les Miserables', and in 2010, she performed on the popular Korean show 'Star King', where she impressed everyone with her vocal skills. Shannon is a former member of the Five Dolls and currently has a solo career. Her father is Welsh and her mother is Korean.
Sin Richard Duleik was born in Los Angeles in 1984. His mother is Korean and his father is British. Known for his role in Athena: Goddess of War.
Gained popularity thanks to the show "Law of the Jungle". Born and raised in Hawaii. Mom is Korean and dad is American. Many fans were disappointed when they found out that he is already married and has two children.
11. Mizuhara Kiko / Audrey Kiko Daniel
Professional Japanese model and actress. Mom is a Japanese citizen of Korean origin, and dad is American. Is the exclusive model of the Japanese fashion magazine "ViVi"
Gained popularity due to participation in the first season of "K-Pop Star". She signed a contract with YG Entertainment and became a member of the group SuPearls, but after two years of preparation, the group was disbanded and the contract with YG was canceled. Currently under LOEN Entertainment.
13. Gangnam (M.I.B)