Deferred tax liability is formed from income. Deferred tax liability - what is it
The procedure for accounting for income and expenses for accounting and for calculating income tax is different. This leads to the fact that calculated from accounting profit does not coincide with the income tax reflected in the tax return.
To reflect differences in the amount of tax, RAS 18/02 “Accounting for income tax settlements” was put into effect.
Divides differences in the tax base into permanent (if any income/expense is reflected in accounting and is never taken into account when calculating the tax base, or vice versa, is taken into account when calculating the tax base and is not subject to accounting) and temporary (when income/expense is the expense is reflected in accounting in one reporting period, and is accepted for taxation in another reporting period). Permanent differences give rise to permanent tax liabilities (assets), give rise to deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities;
It provides for the reflection of income tax in the following order:
Notional income/expense for income tax (equal to the product of accounting profit and the income tax rate) is adjusted for the amount of deferred tax assets, deferred tax liabilities, permanent tax liabilities (assets). The result is the amount of income tax reflected in the tax return.
Definition of the term "deferred tax liability
Under deferred tax liability (IT) refers to that portion of deferred income tax that is expected to result in an increase in income tax in subsequent reporting periods.
In other words, a deferred tax liability arises if the profit before tax in accounting is greater than in tax, and this difference is temporary.
Deferred tax liability = temporary difference * income tax rate.
In accounting, deferred tax liabilities are reflected in the account of the same name. In the financial statements, deferred tax liabilities are reflected in line 1420 of the balance sheet, in line 2430 of the income statement.
Example
Company A leased equipment worth RUB 1.5 million with a useful life of 15 years. Depreciation of this equipment in accounting amounted to 100 thousand rubles, and in tax accounting 300 thousand rubles. as a result of applying a special coefficient of 3. There are no other differences between accounting and tax accounting. Profit before tax, according to accounting data, amounted to 800 thousand rubles, according to income tax, respectively, 600 thousand rubles. Income tax rate = 20%.
The difference between depreciation in accounting and tax accounting amounted to 200 thousand rubles. (= 300 thousand rubles -100 thousand rubles).
This temporary difference, because - in 15 years, the equipment will be fully depreciated in both accounting and tax accounting;
This difference gives rise to a deferred tax liability because the tax base is less than profit before tax in accounting.
The amount of deferred tax liability = 40 thousand rubles. (temporary difference of 200 thousand rubles * income tax rate of 20%).
If the calculation is correct, the amount of income tax calculated in accordance with the rules of PBU 18/02 will be equal to the amount of tax reflected in the tax return.
Current income tax (PBU18/02) =
Conditional income tax expense 160 thousand rubles. (profit before taxation according to accounting data 800 thousand rubles * income tax rate of 20%)
–
deferred tax liability 40 thousand rubles.
=
120 thousand rubles
Current income tax (declaration) =
Tax base 600 thousand rubles.
*
Income tax rate 20%
=
120 thousand rubles
Still have questions about accounting and taxes? Ask them on the accounting forum.
Deferred tax liability: details for an accountant
- Temporary tax differences: causes and features of accounting
18/02. Deferred Tax Assets (Deferred Tax Liabilities) In this article, we will continue... ;BP), which gives rise to a deferred tax liability (DLT). Taxable temporary differences increase ... correspondence with the credit of account 77 "Deferred tax liabilities". Deferred tax assets (DTA) are accounted for... . Examples of temporary tax differences arising Deferred tax liability (TLD) Taxable temporary differences are formed ...
- Changes to PBU 18/02: permanent and temporary differences and assets will be accounted for in a new way
PNA); deferred tax assets (ITA); deferred tax liability (IT). It was decided that the abbreviations "PNO ...
- The procedure for filling out the balance sheet in a general form. Example
12 months) loans and credits. Deferred tax liabilities. Line 1420 is filled in by tax payers ... with a breakdown). Line 1420 "Deferred tax liabilities" = Kt 77. Line 1430 ...
- How to evaluate a business by order of the owner on your own in two hours
Between deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities. Enter this value in the cell... balance of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities. The model considers the adjustment of the final cost ...
- Deferred tax asset from the loss of a consolidated group of taxpayers
Taxpayers." KONA is not credited against the deferred tax liabilities of the responsible member of the CTG and is presented ... and may be credited against its deferred tax liabilities. Likewise, changes in attributable to...
- Advance income tax payments. Examples
- Accounting policy of LLC in "1C: Accounting 8", ed. 3.0
The emergence of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities. The composition of the forms of financial statements In ...
- Tachograph. Accounting and taxation
Her deferred tax liability (IT), which is reflected in the credit of account 77 "Deferred tax liabilities" ... IT (1000 X 20%) 77 "Deferred tax liability" 68 / Income tax 200 ...
- Let's talk about tariff regulation
A tariff difference (by analogy with a deferred tax liability), which indicates a possible decrease ...
- About Calculating Equity for Controlled Debt
07.2010 N 66n, deferred tax liabilities are reflected. According to paragraph 15 of the Regulations on ... .11.2002 N 114n, the deferred tax liability is understood to mean that part of the deferred tax ... in subsequent reporting periods. So deferred tax liabilities are not tax payable...for the respective reporting period? Are deferred tax liabilities included in liabilities? 2. In...
- On the timing of the start of application by some NFIs of the industry accounting standard for IT and IT
... "Industry Accounting Standard for Deferred Tax Liabilities and Deferred Tax Assets Non-Credit ... NFO Industry Standard for Accounting for Deferred Tax Liabilities and Deferred Tax Assets. According to ...
... "Industry Accounting Standard for Deferred Tax Liabilities and Deferred Tax Assets Noncredit ... Less Expenses" applies the GAAP for deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets. Bank... "Industry Standard for Accounting for Deferred Tax Liabilities and Deferred Tax Assets by Noncredit...
Information on whether a legal entity has deferred tax liabilities is collected on account 77. This measure affects only entities that need to calculate income tax. The article analyzes account 77 “Deferred tax liabilities”, discusses the basics of accounting, typical postings, offsetting accounts, and presents a training video.
Discrepancies in profit calculation
For tax and accounting purposes. accounting, the moment of making a profit does not always coincide. A peculiar procedure for accounting for accounting profits often differs from the data for the year of tax returns.
Such examples are possible, for example, with a different method of calculating depreciation. Accelerated depreciation in tax accounting is unacceptable for accounting. The expenses incurred in determining the taxable base will exceed the expenses in the accounting records.
Sample depreciation in different accounts, leading to the formation of IT
| Initial data | Reflection in accounting | Reflection in tax accounting |
| Acquisition of OS, initial cost | 960 000 rubles | 960 000 rubles |
| Depreciation method | Linear | non-linear |
| Depreciation group | 3 | 3 |
| Depreciation accrued | 20,000 rubles (960,000/4 years/12 months) | 53 760 (960 000*5,6/100) |
Subject to the above conditions, the taxable temporary difference is RUB 53,760 - RUB 20,000 = RUB 33,760.
What is a deferred tax liability
If expenses in accounting appear later and in a larger amount than in tax accounting, at the same time, incomes are determined by earlier dates, then conditions arise for the emergence of IT in the organization.
Factors affecting the discrepancy between the calculation of income and expenses in tax and accounting:
- use of legal by a person of the cash method when accruing in tax accounting, that is, receiving revenue from the shipment of goods before receipt of real payment;
- differences in depreciation of property.
The resulting taxable temporary differences lead to an increase in tax in the future.
For the deferred tax liability, the formula is: taxable temporary difference*current income tax rate.
Video lesson “Accounting for deferred tax liabilities on account 77: postings, examples”
Video lesson on accounting for account 77 “Deferred tax liabilities”. Typical postings, complex cases and examples are considered. Conducted by Gandeva N.V. chief accountant, teacher of the site “Accounting and tax accounting for dummies”. Click on the video below to watch ⇓
Deferred tax liability in accounting
The reflection of the differences that arise when determining profit is fixed in RAS 18/02, which determines the costs of profit, in particular:
- Divides the resulting differences into permanent and temporary. Constants include factors in the occurrence of income or expenses in one or another accounting, and are not reflected in the opposite. There are permanent tax liabilities. Temporary differences arise due to different terms and methods of determining income and expenses in accounting, leading to the formation of deferred tax liabilities.
- Reflects income tax in subsequent periods. The resulting conditional income or expense in accounting is adjusted by the amount of deferred liabilities and multiplied by the tax rate. The amount received is reflected in the tax return.
Enterprises that are entitled to apply simplified accounting statements may not use the provisions of PBU 18/02. These include small organizations, non-profit institutions, participants in the Skolkovo project. The decision made must be fixed in the accounting policy.
Those entities whose evaluation criteria classify the organization as a medium-sized business are required to use account 77 in accounting.
The procedure for determining the current income tax is supposed to be prescribed in the accounting policy. Enterprises are given the opportunity to choose one of 2 ways:
- taking into account IT based on current accounting data;
- focusing only on the amount of tax received, neglecting the accounting information.
However, in any case, the amount of the current tax should duplicate the information from the declaration for the relevant period. If the second method of determination is chosen, organizations must also keep records of the resulting obligations.
Account 77: his correspondence
IT, formed on account 77, corresponds with two accounting accounts - 68 and 99. The resulting entries reflect the following results:
Dt 68 - Kt 77 - deferred tax, which reduces the amount of income or expense.
Dt 77 - Kt 68 - repayment of deferred tax, is formed when income tax is charged at the end of the reporting period.
Dt 77 - Kt 99 - IT is canceled subject to the disposal of the asset or the circumstances that formed it earlier.
Accounting for account 77 itself should be kept separately for each type of assets or liabilities that affect the appearance of deferred tax.
Calculation of deferred tax liability and reflection in accounting
Organizations reflect received IT in accounting, depending on the circumstances.
Example. The Polyus institution sold goods for Vesna LLC in the amount of 170,000 rubles (excluding VAT). Payment from the buyer was received only in the amount of 100,000 rubles. Polyus LLC applies the cash method in determining tax. The rest of the debt was paid off the following year. Based on the results of the reporting period, the following entries appear in Polyus LLC:
Dt 62 - Kt 90 - 170,000 rubles - revenue in accounting for shipped goods;
Dt 51 - Kt 62 - 100,000 rubles - payment from Vesna LLC;
Dt 68 - Kt 77 - 14,000 rubles (debt 70,000 * tax rate 20%) - IT is reflected.
When compiling a book. reporting the amount of 14,000 rubles will be reflected in the balance sheet as a deferred income tax liability.
In the subsequent period, after the closing of the receivables of Vesna LLC, the following entries will appear:
Dt 51 - Kt 62 - 70,000 rubles - the final payment was received from the buyer;
Dt 77 - Kt 68 - 14,000 rubles - repayment of IT.
Accounting is a complex system in which everything is interconnected, some calculations follow from others, and the whole process is strictly regulated at the state level. There are a lot of terms and concepts in it that are not always clear to people without specialized education, but it is necessary to understand them in certain situations. This article discusses such a phenomenon as the reflection of deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet, what kind of phenomenon it is, which requires other nuances of the issue.
Balance sheet
The concept of the balance sheet is necessary in order to proceed to the main issue of the article - deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet. This is one of the main elements of financial statements containing information about the property and funds of the organization, as well as its obligations to other counterparties and institutions.
Balance sheet, also known as the first form of accounting. reporting, presented in the form of a table, which reflects the property and debts of the organization. Each individual element is reflected in its own cell with an assigned code. The assignment of codes is carried out through a special document called the Chart of Accounts. It is officially approved by the Ministry of Finance and is used by all organizations operating in the territory of the Russian Federation. The users of the information contained in Form No. 1 are both the organization itself and third-party interested parties, including the tax service, counterparties, banking structures and others.
Assets and liabilities
The balance sheet is divided into two columns: asset and liability. Each contains lines with a certain property or its source of formation. How do you know if deferred tax liabilities on the balance sheet are an asset or a liability?
There are two groups in the asset balance: current and non-current assets, that is, which are used in production for less than one year and more, respectively. All this - buildings, equipment, intangible assets, materials, long-term and short-term
The liability also reflects the sources of formation of funds listed in the asset: capital, reserves, accounts payable.
Deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet - what is it?
In accounting, there are two concepts that are similar in name, and therefore can be misleading to an uninformed person. The first is a deferred tax asset (abbreviated as IT), the second is a deferred tax liability (abbreviated as IT). At the same time, the goals and the result of applying these accounting phenomena are opposite. The first phenomenon reduces the amount of taxes that the organization must pay in the following reporting periods. At the same time, the amount of the final profit in the reporting period will be reduced, since the tax payment will be higher.
Deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet is a phenomenon that causes an increase in net income in a given reporting period. This happens due to the fact that in the following periods the amount of taxes paid will be greater than in the current one. From this, the conclusion is that deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet are a liability, since the company uses these funds at a given point in time as profit, undertaking to pay them in the reporting periods that follow this one.

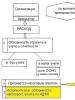
How phenomena such as IT and SHE are formed
The organization simultaneously maintains several types of accounting, namely accounting, tax and management. The emergence of deferred tax assets and liabilities is due to temporary differences in the maintenance of these accounting areas. That is, if in the accounting type of accounting, expenses are recognized later than in tax accounting, and income is recognized earlier, temporary differences in the calculations appear. It turns out that a deferred tax asset is the result of the difference between the amount of tax paid at the moment and calculated with a positive result. The obligation, accordingly, is the difference with a negative result. That is, the company must pay taxes.

Reasons for the temporary difference in settlements
There are several situations in which there is a time gap in the calculations of accounting and tax accounting. You can list them as follows:
- Obtaining by the organization the opportunity to defer the payment of taxes or installment payments.
- The company from work accrued penalties to the counterparty, but the money was not received on time. The same option is possible with the proceeds from the sale.
- In the financial statements, a smaller amount of expenses is indicated than in the tax.
- In boo. accounting and tax use different methods of depreciation, as a result of which there was a difference in the calculations.
Reflection in Form No. 1
Since liabilities relate to the sources of formation of funds and property of the organization, they relate to the liability of the balance sheet. In the balance sheet, deferred tax liabilities are current assets. Accordingly, in the table they are reflected in the right column. This indicator refers to the fourth section - "Long-term liabilities". This section contains several amounts related to different sources. Each of them is assigned its own individual code, which is also called the line number. Deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet are line 515.

Calculus and adjustments
ITs are taken into account strictly in the period in which they were identified. In order to calculate the amount of liabilities, it is necessary to multiply the tax rate by the temporary taxable difference.
It is gradually repaid with decreasing temporary differences. Information on the amount of the obligation is adjusted on the analytical accounts of the relevant item. If the object on which the obligation arose is withdrawn from circulation, in the future these amounts will not affect income tax. Then they need to be written off. Deferred tax liabilities in the balance sheet are account 77. That is, the entry for which liabilities for retired taxable objects are written off will look like this: DT 99 CT 77. Liabilities are written off to the profit and loss account.

Calculation of net income and current tax
Current income tax - the amount of the actual payment made to the state budget. The amount of tax is determined based on the difference between income and expenses, adjustments to this amount, deferred liabilities and assets, as well as permanent tax liabilities (TLT) and assets (TLT). All these components add up to the following calculation formula:
TN \u003d UD (UR) + PNO - PNA + SHE - IT, where:
- TN - current income tax.
- UD (UR) - specific income (specific consumption).
This formula uses not only deferred but also permanent tax assets and liabilities. The difference between them is that in the case of constants there are no temporary differences. These amounts are always present in accounting throughout the entire process of the organization's business activities.
Calculation of net profit is made according to the formula:
PE \u003d BP + SHE - IT - TN, where:
- BP - profit recorded in accounting.

Stages of calculation and reflection in accounting
To reflect all the above phenomena and procedures in accounting, certain postings are used based on the approved accounting chart of accounts. At the first stage of generating postings and making calculations, it is necessary to reflect the following operations:
- DT 99.02.3 KT 68.04.2 - the transaction reflects the product of the debit turnover of the account by the tax rate - these are permanent tax liabilities.
- DT 68.04.2 KT 99.02.3 - the product of the loan turnover and the tax rate is reflected - these are permanent tax assets.
Permanent tax assets are formed in the balance sheet if the profit according to accounting data is higher than according to tax data. And accordingly, on the contrary, if the profit is less, tax liabilities are formed.
At the second stage of calculations losses of the current period are reflected. It is calculated by the difference between the product of the final debit balance by the tax rate in tax accounting and the final debit balance of account 09 of accounting. Based on the above, we form the postings:
- DT 68.04.2 KT 09 - if the amount is negative.
- DT 09 KT 68.04.2 - if the amount is positive.
At the third stage of calculations, the amounts of deferred tax liabilities and assets are derived, taking into account temporary differences. To do this, it is necessary to determine the balance of taxable differences in general, calculate the balance at the end of the month, which should be reflected in accounts 09 and 77, determine the total amounts for the accounts, and then adjust them according to the calculations.
We talked about temporary differences in accounting and tax accounting in ours and noted that such differences are deductible (VVR) and taxable (NVR). VVR lead to the formation of a deferred tax asset (ITA), and NVR - to the formation of a deferred tax liability (IT) (clauses 11, 12 PBU 18/02). To summarize information on the presence and movement of IT, the Chart of Accounts and the Instructions for its use are account 77 “Deferred tax liabilities” ().
Accounting on account 77
77 accounting account is a passive synthetic account. The credit of account 77 reflects deferred tax, which reduces the amount of contingent expense (income) of the reporting period (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
Debit account 68 "Calculations on taxes and fees" - Credit account 77
The value of IT, reflected in this posting, is determined by the formula:
IT \u003d HBP * C,where C is the income tax rate in force in the reporting period.
In the general case, the IT is 20% of the NVR (clause 2, article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the occurrence of IT is reflected in the credit of account 77, then the debit of this account takes into account the reduction or full repayment of IT on account of accruals of income tax for the reporting period:
Debit account 77 - Credit account 68
If the object for which IT was accrued retires, the deferred tax liability is written off (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
Debit account 77 - Credit account 99 "Profit and loss"
Analytical accounting on account 77 is carried out by types of assets or liabilities, in the assessment of which an NVR arose.
In the balance sheet, the balance of IT is reflected in liabilities as part of long-term liabilities in line 1420 “Deferred tax liabilities” (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 02.07.2010 No. 66n).
Account 77 "Deferred tax liabilities": an example
Taxable temporary differences that lead to the formation of an IT, in particular, may arise as a result (clause 12 of PBU 18/02):
- the use of different methods of depreciation for the purposes of accounting and tax accounting;
- recognition of proceeds from the sale of products (goods, works, services) in the form of income from ordinary activities of the reporting period, as well as recognition of interest income for accounting purposes at the time of accrual, and for taxation purposes - on a cash basis;
- application of various rules for the reflection of interest paid by the organization on loans and borrowings for accounting and taxation purposes;
- other similar differences.
The simplest case of the occurrence of IT is the difference in the methods of calculating depreciation, as a result of which the amounts of depreciation expenses in accounting and tax accounting do not match.
For example, for the first year of depreciation of an item of fixed assets, depreciation amounted to:
- in accounting - 250,000 rubles;
- in tax accounting - 320,000 rubles.
Ceteris paribus, this difference leads to the fact that the accounting profit for this year will be more than the tax profit by 70,000 rubles (320,000 rubles - 250,000 rubles). Therefore, IT arises: Debit account 68 - Credit account 77 in the amount of 14,000 (70,000 x 20%).
As the accounting depreciation begins to exceed the tax depreciation, IT will be repaid: Account 77 debit - Account 68 credit.
If income is recognized in accounting earlier than it is determined in tax accounting, and income, accordingly, arises and is recorded later, a temporary (deductible) difference arises. IRR is the receipts or costs that are recorded in the course of compiling financial profit in the current period. The temporary (deductible) difference is the amount by which taxable income is greater than accounting income. In subsequent periods, this amount will disappear.
Prerequisites for the emergence
Temporary (deductible) differences arise when:
- The amount of accrued income (for example, depreciation of fixed assets) in accounting is greater than in tax accounting.
- An entity using the cash basis accrued expenses but did not actually pay them.
- The loss for the previous year was not used in the current one and was carried over to the next one.
- In this period, income tax was overpaid and it should be included in the account of future deductions.
The temporary difference gives rise to deferred tax. It, in turn, leads to a decrease in profit deductions in the coming periods.
NVR
Temporary taxable differences appear if expenses in accounting are recognized later than in tax accounting, and income, respectively, earlier. This causes the fact that in the current period the profit subject to taxation is less than the accounting one. However, this will change in the coming reporting cycles. In the following periods, the amount of financial profit will be less than that of the tax.
Causes of NVR
A temporary taxable difference may arise if:
- The company applying the cash method, penalties, sales proceeds were accrued, but the money was not received.
- The amount of accrued expenses in the financial statements is less than in the tax.
- The company received an installment plan or deferral of income tax deductions.
NVR may also arise due to the use of different depreciation methods for tax and accounting, when the accrued amount in the latter is less than in the former.

Deferred tax assets and liabilities
If the temporary (deductible) difference is multiplied by the mandatory contribution rate to the budget, then the amount of profit deductions that has already been paid, but will be credited in the future, will be obtained. This value is called a deferred tax asset (ITA).
SHE represents the positive difference between the actual, current contribution to profit and the conditional expense of the payment calculated from profit. Deferred assets can be written off from the account. 09/00 in subsequent periods. If depreciation is provided for in the upcoming cycle, then in the financial statements it is not charged on the fixed asset, but in the tax one it is charged. The temporary taxable difference is determined in the same way as the deductible difference, but it has the opposite sign. This value leads to an increase in profit deductions in the coming periods. The amounts to be paid in addition are IT (deferred tax liabilities).
IT calculus
Deferred tax liabilities are recognized in the cycle in which the related temporary differences arise. The calculation is carried out according to the formula:
IT = Rate of payment on profit x NVR.
To better understand the essence, you can take VAT on revenue when establishing the moment when the obligation to pay to the budget appears. This VAT is fixed on the account. 76 as an upcoming payment. Accounting for deferred tax liabilities on deductions to profit will also be carried out (account 77).

Adjustments
As NVR is reduced or completely eliminated, deferred tax liabilities will be gradually paid off. In the analytics of the corresponding article, the information will be adjusted. If there is a disposal of an object of liability or an asset on which accruals were made, these amounts will not affect the amount of income tax in future periods. In this case, IT is written off.
Records deferred tax liabilities in the profit and loss account. They are reflected in the debit account. 99, credit sc. 77. In the reporting period, when determining the indicator on line 2420 "Change in deferred tax liabilities", the amount of newly appeared IT and the repaid amount shall be entered. In the process of filling in lines 2430 and 2450, the principle of "debit minus credit" must be applied. From the income turnover according to 77 and 09, the expense is subtracted and the sign of the result is determined. In the report, a negative (in brackets) or a positive value is indicated for the corresponding lines. If the change in deferred tax liabilities is in the direction of increase, then this will lead to a decrease in profit deductions, and if in the direction of decrease, then, on the contrary, to an increase.

Current income tax
It is the amount of the actual payment for the reporting period to the budget. This value is determined in accordance with the size of the contingent expense/income and its adjustments for amounts that form permanent deductions, deferred tax assets and liabilities. Thus, the formula is used:
TN \u003d UD (UR) + PNO - PNA + SHE - IT.
The scheme for calculating TN is provided for in PBU 18/02 (clause 21). To check the correctness of the calculation, you should use an alternative method:
ТН = taxable profit in the reporting period x income tax rate.
If the company does not make permanent contributions to the budget, then the absolute difference between the contingent payment accrued from financial profit and the current one will be equal to the deferred tax asset minus deferred tax liabilities. This value will affect the amount of current payments on profit.

Deferred tax liability: transactions
According to the structure of the income statement, the following formula is used to determine net profit:
PE \u003d BP + SHE - IT - consumer goods,
where BP is the value of accounting profit; TNP - current tax.
This formula shows deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities reflected in the balance sheet at:
- deb. sch. 09, credit. sch. 68.
- deb. sch. 68, credit. sch. 09.
- deb. sch. 68, credit. sch. 77.
- deb. sch. 77, credit. sch. 68.
They adjust the amount of income tax. However, these items are not included in net income. In order to reflect the way the current contribution to income is calculated and at the same time give information on net income for distribution, two items can be shown: deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities that affected the account. 68 and 99. In this case, the latter can be entered in an explanatory note or on a free line.

Practical use
How to show deferred tax liabilities? Let's take the following example.
The company purchased a computer program. Its cost is 8 thousand rubles. The developers have limited the period of its use. In this regard, the manager ordered that the costs of the program be written off over a period of two years. In the financial statements, the purchase amount is included in the costs of future periods. The cost of the program in tax accounting is allowed to be written off as expenses at a time. As a result, the NVR was formed. The contingent deduction for profit will be greater than the current one by the amount of the deferred liability:
IT \u003d UNP - TNP \u003d 8000 * Sn \u003d 1600 rubles.
In the financial statements, this is reflected in:
- Dt 99/00 Kt 68/09 - UNP.
- Dt 68/09 Ct 77/00 - IT.

In this case, 77/00 acts as a passive balance item, which accumulates tax amounts subject to additional payment in the coming reporting periods. IT is written off from the account. 77/00 in upcoming cycles. In this case, the computer program has already been written off for tax accounting and does not affect expenses in any way, and in accounting, the write-off concerns the part of the program that falls on the current financial cycle:
- Dt. 20/00 Kt 97/00 - part of the cost of the program (excluding VAT).
- Dt 19/04 Ct 97/00 - VAT amount.
In this case, the current income tax will be higher than the conditional one, part of it should be paid in addition, and for posting the account. 77/00 you get a debit turnover:
- Dt 99/00 Kt 68/09 - UPN.
- Dt 77/00 Kt 68/09 - write-off of IT.