What does primary documentation mean in accounting. What should an accountant always remember? Advance reports in "1C"
In the current practice, primary accounting documents are understood as papers reflecting the facts of economic life (transactions, movement of goods and materials, etc.). They are issued at the time of the transactions or after their completion, to confirm the facts that have happened. On their basis, the accountant makes entries in the accounting program of the enterprise, accepts amounts for tax accounting.
In what form is the "primary"
According to the explanations of the Ministry of Finance, the company has the right to independently determine which forms of "primary" to use. The decision made is fixed in the accounting policy of the organization. Practice shows that business entities use one of three options:
- Unified forms offered by the State Statistics Committee.
- Samples developed by the company independently and fixed by internal acts.
- Combined options: primary documents in a unified format, supplemented by certain fields.
The right of business entities to independently develop primary forms does not apply to the following types of documents:
- cash documents (in particular, consumables and receipts);
- strict reporting forms;
- shipping bills.
For them, the Ministry of Finance introduces unified forms to the rank of mandatory ones.
If the company that concluded the transaction did not determine the form of the “primary” in the contract, the counterparty has the right to issue documents based on its own samples. To avoid issues of regulatory structures, the company should state in its accounting policy that it accepts papers on forms developed by its suppliers and buyers.
Important! The presence of a “primary” mediating a particular operation is a mandatory requirement for its reflection in accounting and tax accounting.
Mandatory details of the "primary"
According to Art. 9 402-FZ, primary accounting documents must contain the following mandatory details:
- the name of the business paper, for example, "Act of Accepted Works";
- number according to the internal numbering rules of the compiling company;
- date of preparation of the document;
- the full name of the company issuing the "primary";
- the nature of the business transaction that took place (for example, the shipment of goods to the buyer, cash deposit at the cash desk, acceptance of work performed, etc.);
- measurement of the occurred economic fact in monetary or natural form;
- position and full name of the employee responsible for the execution or registration of the operation;
- handwritten signature of the authorized person.
The list of persons entitled to sign primary accounting documents is determined by the head of the organization. It is fixed by his order.
Some forms contain additional details in relation to the standard list. For example, the waybill must contain information about the car, its owner and driver.
Is it necessary to affix an imprint of the organization's seal on the "primary"? This is not a mandatory requisite, you can’t do without it only if its presence is provided for by the sample enshrined in the company’s accounting policy.
Varieties of primary documents
The current legislation does not establish a closed list of 2018 primary accounting documents. Their diversity is determined by the field of activity of the economic entity. For one firm, a consignment note is required, for another, an act of writing off literature from the library.
The most common types of documentation include:
- consignment note - mediates transactions for the acceptance and transfer of goods and materials;
- acceptance certificate - is issued in situations where one party accepts the results of work carried out by the second;
- payroll - compiled when paying staff salaries;
- OS-1 - reflects the receipt or loss of an object of fixed assets (except for real estate);
- INV-1 - consolidates the results of the inventory;
- advance report - confirms the expenses of an employee who arrived from a business trip;
- cash documents (checks, PKO, RKO, etc.);
- payment order;
- accounting statement, etc.
This list of primary accounting documents is not complete. Companies of different lines of activity use the necessary forms to reflect the ongoing transactions.
Depending on the method of implementation, the "primary" is paper and electronic. The second option is used in companies where electronic document management is configured. It helps to simplify and speed up the processing of business papers, to debug the interaction between counterparties.
According to the norms of the current legislation, all types of "primary" are stored in the company for five years. The countdown is from the end of the reporting year. For example, papers issued in 2018 must be kept until 2023 inclusive. Violation of this rule will lead to proceedings with the tax service, the imposition of penalties on the organization.
Primary accounting represents the initial stage of the systemic perception of the registration of individual operations that characterize the economic processes and phenomena occurring in the organization. Its objects are: the procurement, acquisition and expenditure of material resources, production costs, the movement of semi-finished products and the remains of work in progress, the volume of output, its shipment and sale, settlements with suppliers, buyers, customers, banks, financial authorities, founders, etc. .
Initial information about economic processes and phenomena is reflected in primary documents.
Primary accounting document- this is a written certificate of a business transaction that has legal force and does not require further explanation and detail.
The primary accounting document must have:
- name - the financial and economic content of the business transaction. A document that does not have a title, as well as a document with an unclear, poorly readable title, will not have legal force;
- the name, and in some cases addresses and bank accounts of the parties (legal entities and individuals) participating in this business transaction. The primary document, which does not contain the name and corresponding attributes of at least one of the parties to the business transaction, loses its targeting and cannot be executed;
- compilation date. In the absence or indistinct writing of the date, the document loses its targeting in time. In fact, such a document has no legal force;
- the content of the business transaction (documentation object) arising from the name of the document in which it is available in a general form;
- indicators of ongoing business transactions. The absence of meters in the document deprives it of an accounting and calculation base;
- signatures of responsible persons - the director of the organization and the chief accountant.
Documents are filled out by accounting staff clearly, legibly by hand writing in ink or ballpoint pen paste, on a typewriter or using computer technology.
As a rule, standard forms in the form of forms that are interdepartmental in nature are used for documents. This includes forms of orders, invoices, invoices, coupons, statements, etc. Primary documents should be drawn up at the time of the transaction, and if this is not possible for objective reasons, then immediately after it is completed.
If an error occurs in on-farm accounts, then you can apply the negative or reverse entry method. In this case, the erroneous entry is repeated in red ink or standard colors (blue, black) with its conclusion in a rectangular frame.
A red color or a rectangular frame will invalidate the erroneous entry, after which a correct entry is made. It is possible to correct errors in the accounts by crossing out and further correcting (an erroneous entry is crossed out with one line and a correct entry is made under it indicating the date of correction and the signature of the accountant, if necessary, a certificate is drawn up disclosing the need for correction and the cause of the error).
There should be no corrections, erasures, blots in cash and bank documents.
In working with any document, the accountant relies on certain principles and methodological foundations enshrined in official documents.
Based on primary documents, entries are made in accounting registers, cards, statements, journals, as well as on disks, floppy disks and other media.
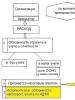
Accounting documents are external and internal
External Documents enter the organization from the outside - from government agencies, higher organizations, banks, tax inspectorates, from founders, suppliers, buyers, etc., they are compiled according to standard forms. Examples of such documents are, payment request-order, payment request, supplier invoice, etc.
Internal documents compiled directly in the organization.
There are the following types of internal documents:- administrative;
- acquittal (executive);
- combined;
- accounting arrangement.
managerial- these are documents that contain orders, instructions on the production, performance of certain business operations. These include orders of the head of the organization and persons authorized by him to carry out business operations.
Exculpatory(executive) documents certify the fact of business transactions. These include receipt orders, acts of acceptance of materials; acts of acceptance and disposal of fixed assets; documents on acceptance from workers of finished products, etc.
Combined documents are both administrative and executive. This includes receipt and expenditure cash orders, payroll statements for the issuance of wages to employees of the organization, advance reports of accountable persons, etc.
Accounting documents are compiled in the case when there are no standard documents for records of business transactions, as well as when summarizing and processing supporting and administrative documents. These are certificates, distribution sheets, etc.
Accounting documents are also divided into one-time and accumulative. One-time primary documents are used in the execution of each business transaction. Cumulative documents are drawn up during a certain period of gradual accumulation of homogeneous business transactions. At the end of the period, these documents calculate the totals for the relevant indicators. Examples of accumulative documents are two-week, monthly work orders, limit cards for the release of materials from the organization's warehouses, etc.
Accounting documents are divided into primary and summary
Source documents generated at the time of the business transaction. An example of such documents are waybills for the release of materials from the organization's warehouses to workshops.
Summary Documents compiled on the basis of primary documents, for example, payroll.
At the time of fixing the data in the primary documents, accounting information arises that is not automatically recorded. All its quantitative and qualitative characteristics are subjected to logical, arithmetic and legal control before the preparation of primary documents. Such control is carried out both by employees involved in maintaining primary accounting, and by employees of management services.
By signing receipts and debit cash orders, payroll statements, payment orders and claims, other banking documents, the head of the organization thoroughly analyzes each business transaction.
In the process of obtaining accounting information, the following stages are distinguished:- preliminary work before drawing up primary documents;
- preparation of primary documents;
- approval of primary documents;
- the work of the accounting department in the preparation and processing of primary documents.
The collection of accounting information involves the appropriate work of various services of the organization. This stage is characterized by the highest level of analyticity and efficiency of accounting.
The second stage of the accounting process is the processing of accounting information. It involves direct participation in the receipt of accounting information by employees of functional management services. So, when accounting for inventory items on the basis of primary documents, grouping and generalization of data in the inventory cards of materials is provided. On a monthly basis, data from cards and books is transferred to reports on the movement of material assets. Warehouse managers and heads of departments submit these reports to the accounting department of the organization on time.
Managers are also involved in data processing. So, with the help of employees of various management services, the culprits of shortages and losses are identified.
After checking the arithmetic calculations, the legality and expediency of the completed business transactions, accounting documents are registered, and then their data are economically grouped in the system of synthetic and analytical accounting accounts by recording in accounting registers.
Accounting registers are counting tables of a certain form, built in accordance with the economic grouping of data on property and the sources of its formation. They serve to reflect business transactions on.
Accounting registers, depending on the structure, are divided into chronological and systematic. In chronological registers, business transactions are reflected in the sequence in which they were performed. Systematic accounting registers serve to group business transactions according to established criteria.
Accounting registers are maintained in the form of accounting books, cards, statements, journals, as well as machine media.
Synthetic accounting is carried out in systematic registers, and analytical accounting - in analytical registers. Entries in registers are carried out both manually and using computer technology.
The totality and location of the details in the register determine its form, which depends on the characteristics of the objects taken into account, the purpose of the registers, and the methods of accounting registration. Accounting registration refers to the recording of business transactions in accounting registers.
In account books, all pages are numbered and bound. On the last page indicate the number and certify it with the signatures of authorized persons. In some books, for example, the cash book, the pages are not only numbered, but also laced with twine, sealed with a wax seal. Depending on the volume of accounts in the book, one or more pages are allocated for one or another account. Accounting books are used for synthetic and analytical accounting.
Cards are made of thick paper or loose cardboard, not fastened together. They are stored in special boxes - file cabinets. Cards are opened for a year and registered in a special register to ensure control over their safety.
Statements differ from cards in that they are made from less dense paper and have a larger format. They are stored in special folders called registrars. Sheets are opened, as a rule, for a month or a quarter.
Entries in accounting registers should be clear, concise, clear, legible. After registering a business transaction in the accounting register, an appropriate mark is made on the primary document to facilitate subsequent verification of the correct posting. At the end of the month, the results are summed up for each page of the accounting registers. The final records of systematic and analytical registers must be verified by compiling turnover sheets.
After the approval of the annual report, accounting registers are grouped, bound and deposited in the current archive of the organization.
Ways to correct erroneous entries in accounting registers
Exist three ways to correct erroneous entries in accounting registers: corrective, additional entry, reversal.
Corrective method can only be applied if errors were discovered before the balance sheet was drawn up, or if they took place in the accounting registers, without affecting the correspondence of the accounts. This method consists in striking out with a thin line the incorrect text, number, amount and inscription next to or above the correct text or amount with the appropriate reservation.
For example, if instead of 100 rubles. 200 rubles are reflected, then 200 rubles should be crossed out. and write "100 rubles" on top, and indicate on the side: "200 rubles crossed out and 100 rubles written on top, corrected to believe (date, signature)".
On monetary documents, no corrections and blots are allowed, even those specified, especially in numbers.
Additional entries are made in cases where the amount of a business transaction is erroneously underestimated. For example, the supplier transferred 150 rubles from the current account. This business transaction is reflected in the correct correspondence of accounts, but its amount is underestimated to 100 rubles. The following accounting entry was made: the debit of the account "Settlements with suppliers", the credit of the account "Settlement account" - 100 rubles.
But since the suppliers should transfer 150 rubles, then for the missing amount of 50 rubles. it is necessary to make an additional posting: debit of the account "Settlements with suppliers", credit of the account "Settlement account" - 50 rubles.
Additional postings are made in the current or next month. This error correction rule is applied in two cases: if the data of the primary document is not recorded in a separate line in the accounting register and when an erroneously underestimated amount of a business transaction is reflected in the accounting register.
Reversal method consists in the fact that the incorrect entry, mostly digital, is eliminated by a negative number, i.e., the incorrect correspondence and the amount are repeated in red ink. At the same time, a correct entry is made in ordinary ink. Reversals occur when invoices are incorrectly corresponded or when an exaggerated amount is recorded.
When summing the results of operations, entries made in red ink are subtracted.
Without a piece of paper, you are nobody! And with a piece of paper - a businessman conscientiously and professionally conducting his business. Or a competent accountant who helps him. Proper execution of documents in accounting is important both for the formation of accounting data and for determining the organization's tax liabilities. And if you want to secure the most precious thing - do not treat documents condescendingly, and carefully study what requirements they must meet. At least read this article to get started!
Specialists of accounting services, representatives of small businesses who keep records on their own, need to know the basic requirements for the procedure for creating, processing, moving and storing documents.
1. The concept of a document
2. Types of primary accounting documents
3. Forms of primary accounting documents
4. Approval of primary accounting documents
5. Mandatory details of accounting documents
6. Registration of documents in accounting
7. Power of attorney to sign primary documents
8. Schedule of workflow of accounting documents
9. Register of primary documents
10. Correction of accounting documents
11. Storage of accounting documents
12. Responsibility for the storage of primary documents
So let's go in order.
1. The concept of a document
The concept of "document" in the regulatory acts on accounting is not disclosed. Let's use the definition established by GOST R ISO 15489-1-2007:
Document: identifiable information recorded on a tangible medium created, received and stored by an organization or individual as evidence when confirming legal obligations or business activities (clause 3.3 of GOST).
What documents are primary? Primary documents are documents containing initial information about operations, processes. These are the documents on the basis of which accounting entries are made.
Primary accounting documents- these are documents that draw up the facts of economic life (clause 1 of article 9 of law No. 402-FZ of December 6, 2011 "On accounting").
The main requirement for their preparation is that primary documents must be drawn up when the facts of economic life are committed, or immediately after their completion (if possible).
Examples of primary documents:
- incoming and outgoing cash orders,
- consignment note (according to the form TORG-12),
- advance report,
- accounting information.
2. Types of primary accounting documents
There is no harmonious classification, grouping of accounting documents in any normative act.
The following types of primary accounting documents can be distinguished depending on:
- place of compilation:
- internal,
- external,
- used forms of documents:
- unified (created according to the forms contained in the albums of unified forms),
- non-unified (created according to forms developed by the organization independently),
- type of information carrier:
- paper,
- electronic,
- amount of information:
- primary,
- consolidated,
- type of assets and liabilities, areas of accounting:
- accounting for fixed assets
- according to the accounting of MPZ,
- payroll accounting and payroll,
- accounting for cash transactions,
- others are similar.
3. Forms of primary accounting documents
Registration of documents in accounting involves the use of both independently developed and unified forms. Since 2013, the use of most unified forms is not mandatory.
All forms of primary documents are approved by the head of the organization. Currently the following types of unified forms are mandatory for use:
- on accounting for cash transactions (Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of August 18, 1998 No. 88, Instruction of the Bank of Russia of March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U),
- on accounting for labor and its payment (Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of 05.01.2004 No. 1),
- on the accounting of services for the transportation of goods (Government Decree No. 272 of April 15, 2011, Charters of various modes of transport).
Also, a payment order has a standard form, all its fields are we.
When drawing up unified forms, all provided lines (columns) are filled in. In the absence of any indicators, a dash is put in them.
Example 1
The supplier supplied the materials, provided TORG-12 and an invoice, the last lines of which were filled in as “delivery services”, there are no other documents.
Possible consequences - non-acceptance of VAT deductions and income tax expenses, recognition of the transaction as fictitious (imaginary), since the reality of the transaction (the fact of delivery of materials, and possibly the purchase of materials itself) has not been confirmed. A bill of lading is required.
Unified forms that are not mandatory for use are still used in organizations. Based on the internal needs of the company, such forms can be finalized, made more convenient, suitable for reflecting specific economic facts.
For example, you can remove the attribute "place of printing", refuse to use the mark "front / back side".
4. Approval of primary accounting documents
The organization is obliged to approve the forms of primary accounting documents used in its accounting policy (paragraph 4 of PBU 1/2008 "Accounting policy of the organization"). At the same time, it must be remembered that just a link to one of the albums of unified forms of documents is not enough.
The accounting policy (attached to the accounting policy) should list specific documents from the albums of unified forms that the company will use, as well as a list of persons entitled to sign primary documents (information of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. PZ-10/2012).
An example of registration of an application to an accounting policy can be found in our article "". Samples of independently developed forms are attached to the accounting policy with explanations for filling them out.
Forms can also be approved by other local regulations. For example, the Order on the approval of primary documents. A reference to such an order should be contained in the accounting policy.
5. Mandatory details of accounting documents
Requirements to mandatory details of primary accounting documents established by the Federal Law "On Accounting". There are only 7 such details:
- Title of the document,
- the date of the document,
- the name of the economic entity that prepared the document,
- the content of the fact of economic life,
- the value of natural and (or) monetary measurement, indicating the units of measurement,
- the names of the positions of persons responsible for the transaction,
- signatures of responsible persons with signature decoding.
Some documents that are not primary accounting documents may be used as such.
When reflected in the expenses of the rent, such documents are contracts and acts on the lease. In accordance with Articles 611 and 622 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in this case, it is mandatory to draw up bilateral acts of acceptance and transfer of accounting objects.
Example 4
The company rents office space. The documents on the basis of which the monthly rent will be calculated are the lease agreement and the act of acceptance and transfer of the leased property.
In accordance with Article 753 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, unilateral acts may be used as primary documents.
6. Registration of documents in accounting
Consider special cases that are often encountered in the preparation of documents.
Rejection of seals
The purpose of the seal is to certify the signature of the responsible person.
From 04/07/2015, organizations are not required to have a seal. Information about the seal must be specified in the company's Charter (Federal Law No. 82-FZ of 04/06/2015).
A seal is required only in cases established by federal law.
- Power of attorney to represent the interests of a legal entity in court (Article 53 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, Article 61 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation),
- documents submitted to the customs authorities (311-FZ of November 27, 2010),
- an act on an accident at work (Article 230 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation),
- double warehouse certificate (Article 913 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The seal is not a mandatory requisite, but its presence may be provided for in the form of the primary document approved by the head of the organization (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 08/06/2015 No. 03-01-10 / 45390).
Documents in foreign languages
Only documents in Russian are accepted for accounting (clause 9 of the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 34n).
There should be a translation into Russian, and the translation is line by line. It is not required to certify the translation (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 20, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/202). Cases where a notarized translation is required are stipulated by the 1961 Hague Convention.
Non-ruble meters in primary documents
Cost data in accounting documents may be reflected in rubles, currency, conventional units.
For comparison, in tax accounting, the requirement to fill out invoices for settlements in rubles only in rubles is established by Government Decree No. 1137 of December 26, 2011 (clause 1 of the Procedure for filling out invoices).
Electronic primary documents
The Federal Law "On Accounting" allows you to draw up primary documents both in paper and in electronic form.
An electronic document must contain all the required details of accounting documents and an electronic signature (ES).
There are three types of electronic signature - simple, enhanced unqualified, enhanced qualified. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation considers it possible to use any electronic signature (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of September 12, 2016 No. 03-03-06/2/53176).
7. Power of attorney to sign primary documents
An employee of the organization has the right to sign when one of the documents is executed:
- signing order,
- power of attorney to sign primary documents (articles 185 - 189 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Unlike an order on the right to sign, a power of attorney to sign primary documents can also be issued to a citizen who is not an employee of the organization.
By agreement of the parties, a facsimile can be used for signature (Article 160 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation of December 17, 2009 No. VAS-16259/09).
8. Schedule of workflow of accounting documents
A workflow schedule is a description in the form of a diagram or table of the procedure for creating, moving, processing and storing documents. The schedule can be approved as an appendix to the accounting policy, and in the form of a local regulatory act. In the latter case, the accounting policy should contain a reference to such an act.
The following must be indicated in the workflow schedule:
- terms of registration, transfer, processing and storage of documents,
- positions of persons who are responsible for the operations indicated in the workflow schedule (paragraphs 5.4, 5.6 of the Order of the Ministry of Finance of July 29, 1983 No. 105).
9. Register of primary documents
Keeping a journal of accounting for primary documents is more of a rule of rational workflow, rather than accounting.
To register incoming / outgoing documents, such a register of primary documents is necessary. We advise you to keep such a journal even in the case when accounting is carried out without using an accounting program.
When using, for example, the 1C program, a document accounting journal can be generated and printed at any time. So the register of documents of suppliers will be formed as "Register of documents" Receipt (act, invoice)", the journal of accounting of cash documents as "Register of cash documents".
In accounting, unlike tax accounting, it is possible reflection of the fact of economic life in the absence of primary documents, provided they arrive later.
In this case, the fact of economic life is reflected in the accounting in estimated value. Upon receipt of the document, the previously made posting is not reversed, but only adjusted on the date of receipt of the document.
This approach is confirmed in the following documents:
- PBU 21/2008
- Order of the Ministry of Finance dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n “Guidelines for accounting for inventories” (subsection 5 of section 1)
- Decision of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated 08.07.2016 No. AKPI16-443.
An exception to this order is documents on intermediary transactions. The intermediary must hand over all documents related to the transaction. If the report on the transaction is drawn up with errors or inaccuracies, the principal may raise an objection only within 30 days from the date of receipt of the report (Articles 999, 1008 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
10. Correction of accounting documents
Registration of documents in accounting is sometimes accompanied by errors and inaccuracies. In this case, corrections are required.
Corrections are prohibited only in cash and bank documents (for example, paper payment orders). All other documents can be modified.
Correction of accounting documents is carried out as follows:
- the incorrect entry is crossed out with one line so that the crossed out can be read,
- next to the correct value,
- the entry "Corrected" is affixed,
- the date of correction and the signature of the person who compiled the document with the decoding of his signature are put.
Such rules are established by the Federal Law "On Accounting" No. 402-FZ (clause 7 of Article 9) and Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1983 No. 105.
You don't need to print. An exception is corrections on a disability certificate, which are certified by a seal.
The person who created the document must make the correction. If this is not possible, for example, the person quit, then the correction is made by the newly hired employee, or his immediate supervisor.
11. How to store and destroy accounting documents
The procedure for storing a document is determined by Order of the Ministry of Culture dated August 25, 2010 No. 558. The total period for storing documents in accordance with Article 29 of the Federal Law "On Accounting" is 5 years. The manager is responsible for organizing the storage of documents.
Many documents have extended retention periods:
Accounting documents can be destroyed if their storage period has expired (clauses 2.3, 4.11 of the Order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia dated March 31, 2015 No. 526). The decision on destruction is made by an expert commission, which may be created annually, or may operate on an ongoing basis.
Based on the examination of documents, first, proposals are drawn up for the allocation for destruction of documents that are not subject to storage, and then directly an act on the allocation for destruction of documents that are not subject to storage. The act includes documents whose storage period has expired by January 1 of the year in which the act is drawn up.
The act must be approved by the head.
You can destroy documents:
- on one's own. In this case, it is necessary to draw up an act on the destruction of documents. Such an act must indicate exactly which documents, in what quantity and in what way were destroyed,
- P by transfer for destruction to a specialized organization. At the same time, an invoice is drawn up, which indicates the number of transferred documents and their weight (clause 2.4.7 of the Rules of the Rosarchive, approved by the decision of the Collegium of the Rosarchive of 02/06/2002). In this case, the act of destruction of documents is drawn up by a specialized organization.
12. Responsibility for the storage of primary documents
Penalties for working with primary documents are established by Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Sanctions are provided for gross violation of accounting requirements, including accounting (financial) reporting.
One of gross violations of accounting is an:
“the economic entity does not have primary accounting documents, and (or) accounting registers, and (or) accounting (financial) statements, and (or) an audit opinion on accounting (financial) statements (if the audit of accounting (financial) reporting is mandatory) within the established periods of storage of such documents.
Amounts of fines:
- on officials in the amount of five thousand to ten thousand rubles,
- for repeated commission - on officials in the amount of ten thousand to twenty thousand rubles or disqualification for a period of one to two years.
At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the fact that when checking, the absence of primary documents will also be understood as the case when there are documents, there are a sufficient number of them, but they are drawn up in forms that are not approved.
Tax Liability for not ensuring the safety of primary documents, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is also established (Article 120):
- During one reporting period - up to 10 thousand rubles,
- For more than one tax period - up to 30 thousand rubles,
- When the tax base is underestimated - 200% of the amount of unpaid tax (contribution), but not less than 40 thousand rubles.
If you still have questions about the preparation of primary documents in accounting, ask them in the comments below.
Documentation in accounting: the most important
Documents are the starting point of accounting.
Accounting documentation is part of the organization's management documentation system in accordance with the All-Russian Classifier of Management Documentation (OKUD), approved by the Decree of the State Standard of Russia dated December 30, 1993 No. 299.
Accounting documents can be divided into three levels: primary accounting documentation, accounting registers and reporting accounting documentation.
Let us dwell on the primary accounting documentation. These are documents that record the facts of a business transaction. The primary accounting document must be drawn up at the time of the transaction, and if this is not possible, immediately after its completion.
Sample forms of documents are approved by government agencies. Such forms of documents are called standard or unified.
Accounting documents are classified according to several criteria:
By appointment:
Administrative. For example: Orders on accounting policies, on granting vacations, on conducting an inventory, etc.
Exculpatory (executive). For example: incoming and outgoing cash orders, commodity-transport, invoices, waybills, acts, waybills, etc. Invoices are attachments to bills of lading. Compiled in the interests of the tax inspectorate
Accounting documents. For example: payroll, calculation of vacation pay, calculation of temporary disability benefits, calculation of depreciation and others.
Combined documents - contain those and other elements. For example, expenditure cash orders.
Place of compilation:
internal. For example: invoice for internal movement, PKO, RKO, acts.
external. For example: TTN, invoice
By the degree of generalization of business operations;
primary. For example: PKO, RKO, TTN, acts, invoices.
consolidated. For example: Cash report, commodity report, advance report, material report.
By order of use;
one-time. For example: PKO, RKO, acts.
cumulative. For example: daily intake sheet, limit intake card.
2.2. Details of accounting documents
Documents consist of separate indicators, which are called details (from the Latin word "required, necessary").
The set of details of the document determine its form.
In order for a document to meet its purpose, it must be drawn up in accordance with the form adopted for this category of documents.
But in any case, the document must contain the following mandatory details:
Name of the document (form)
Form Code
Date of preparation
Name of the organization that compiled the document
Business transaction meters
Surnames and positions of responsible persons, their personal signatures.
If the document is an external document, then in addition to personal signatures, the organization's round seal must be affixed to the document.
An electronic document contains the same information as a paper document The content of an electronic document can be viewed on a computer screen. An electronic document can be printed in paper form. An electronic document can be reproduced in a huge number of completely identical copies, it can be instantly sent to another computer in another part of the globe using e-mail.
But an electronic document is easier to fake than a paper one, unless, of course, special security measures are taken.
The problem of protection against forgery of electronic documents is solvable. In Russia, as in many other countries of the world, the Law on Electronic Signature has been adopted, aimed at solving this problem.
Electronic documents are already widely used in communication between enterprises and banks and tax authorities.
All documents in the accounting department are carefully checked from three sides: legal, in terms of execution, and arithmetic.
Verified documents are recorded in the document registration log.
Corrections to cash and bank documents are not allowed. Corrections can be made to other primary accounting documents only upon agreement with the participants in business transactions, which must be confirmed by the signatures of the same persons who signed the documents, indicating the date of the corrections.
Currently, special attention is paid to the unification and standardization of documents. Unification of documents is the development of a single form of documents in Russia for processing homogeneous business transactions in various organizations. In Russia, the forms of cash documents, bank documents, etc. have been unified.
They are mandatory for all areas of activity. Along with unification, the standardization of documents is important. Standardization is the establishment of the same standard sizes of standard document forms. When conducting accounting, it is important to establish a rational workflow, i.e. an optimal system for the formation of accounting documents, their acceptance for accounting, movement around the enterprise, their current storage and transfer to the archive. This provides a high degree of accounting reliability with minimal time and cost.
This material will give you an idea about:
users of accounting information;
functions of the enterprise for the organization of accounting;
primary accounting documents, their types and mandatory details;
document flow;
accounting registers and their types;
accounting accounts and their structure;
a simplified working chart of accounts for a small business;
various forms of accounting organization.
1. Documents in accounting
In accordance with Article 9 of the Law "On Accounting", all business transactions carried out by the organization must be documented by supporting documents. These documents serve as primary accounting documents on the basis of which accounting is maintained.
Primary accounting documents are accepted for accounting if they are drawn up in the form contained in the albums of unified forms of primary accounting documentation, and documents, the form of which is not provided for in these albums, must contain the following mandatory details:
- Title of the document;
- date of preparation of the document;
- the name of the organization on behalf of which the document is drawn up;
- the content of the business transaction;
- business transaction meters in physical and monetary terms;
- the names of the positions of the persons responsible for the performance of the business transaction and the correctness of its registration;
- personal signatures of the said persons.
The primary document is a written evidence of a business transaction (payment for goods, issuance of cash against a report, etc.).
The enterprise in the process of activity can use independently developed forms of primary documents, taking into account the established requirements for primary documents. The forms of such documents are approved by the order on the accounting policy of the enterprise.
All primary documents can be divided into the following groups:
- organizational and administrative;
- acquittal;
- accounting documents.
Organizational and administrative documents- these are orders, instructions, instructions, powers of attorney, etc. These documents permit the conduct of certain business operations.
supporting documents- this includes invoices, requirements, receipt orders, acceptance certificates, etc. These documents reflect the fact of conducting a business transaction and the information contained in them is entered into accounting registers.
Some documents are both permissive and justifying. These include, for example, an expense cash warrant, payroll, etc.
Accounting documents completed by an accountant. Among them are various reports, certificates. The information contained in them is also entered into accounting registers.
Accounting registers are specially adapted sheets for registering and grouping credentials. In appearance, accounting registers are:
- books (cash, main);
- cards (accounting for fixed assets, accounting for materials);
- magazines (free or graphed sheets).
According to the types of records produced, registers are divided into:
- chronological (logbook);
- systematic (general ledger of accounts);
- combined (magazine orders).
According to the degree of detail of the information contained in the accounting registers, they are:
- synthetic (general ledger of accounts);
- analytical (cards);
- combined (journals-orders).
Primary documents received by the accounting department (accountant) must be checked:
- in form (completeness and correctness of the document, filling in the details);
- arithmetically (calculation of sums);
- by content (connection of individual indicators, absence of internal contradictions).
For the correct conduct of primary accounting, it is developed and approved workflow schedule, which determines the procedure and terms for the movement of primary documents within the enterprise, their receipt by the accounting department. The schedule for the movement of primary accounting documents may take the following form:
Entries in primary documents must be made by means that ensure the safety of these records for the time specified for their storage in the archive.
After acceptance, information from the primary document is transferred to accounting registers, and a mark is made on the document itself to exclude the possibility of its double use (for example, the date of entry in the accounting register is put down).
Primary and summary accounting documents can be drawn up on paper and computer media. In the latter case, the organization is obliged to produce at its own expense copies of such documents on paper for other participants in business transactions, as well as at the request of the bodies exercising control in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, the court and the prosecutor's office.
Organizations are obliged to store primary accounting documents, accounting registers and financial statements for the periods established in accordance with the rules for organizing state archives, but not less than five years.
For archiving, documents are selected in chronological order, completed, bound and filed into folders. The submission of documents to the archive is accompanied by a certificate.
An account is a way of grouping and reflecting changes in funds (property), their sources and obligations of an enterprise.
Operations on the accounts are reflected in the monetary meter, that is, all property, its sources and obligations (debts) of the enterprise are evaluated, and its value is recorded on the accounts.
The funds of the enterprise can either increase or decrease. For separate accounting of increase and decrease in funds, the account is divided into two parts. The left side of the account is called debit, and the right side of the count is called credit.
Graphically, an account is usually presented in the form of a table consisting of two columns:
Depending on what is reflected in the accounts, they can be:
- active;
- passive;
- active-passive.
On the active accounts the accounting of the enterprise's funds and their movement is reflected (for example, fixed assets, inventories, finished products, cash, settlements, etc.).
An active account increases in debit, that is, transactions that increase it are reflected on the left side (debit) of the account.
The active account balance - the balance at the end and at the beginning of the period - is also written to the debit.
Active account structure:
On the passive accounts the sources of funds of the enterprise (for example, the authorized capital or authorized capital, profit) and the obligations of the enterprise (for example, a bank loan, unpaid wages, etc.) are reflected.
The passive account increases with the credit, that is, the operations that increase it are reflected in the right side (credit) of the account.
The balance of the passive account - the balance at the end and at the beginning of the period - is also recorded on credit.
Passive account structure:
On the active-passive accounts The balance can be either credit or debit.
The chart of accounts is approved by the Ministry of Finance.

3. Forms of accounting
Accounting forms differ in the number of registers used, their purpose, appearance and content.
There are three main forms of accounting:
- memorial order;
- journal-order.
The simplest form is “”, since any operation on the primary document (or a group of homogeneous operations) is recorded in the book “Main Journal”, which combines the business transaction log (chronological entry) and synthetic accounts (systematic entry). The book "Magazine-main" looks like this:

First, the account balances at the beginning of the reporting period are recorded in this book, then all transactions on documents, after which the turnover for the reporting period is determined (in this case, the correctness of the entry is checked: the amount of turnover for the reporting period must be equal to the sum of the debit turnovers of all accounts and the sum of turnovers on the credit of all accounts) and account balances at the end of the reporting period are revealed. According to the balances on the accounts, the final balance sheet is drawn up.
This form is used in enterprises with a small number of employees and with a small number of operations. The book can be kept by one accountant.
The accounting scheme "magazine-main" looks like this:


Memorial-order form of accounting based on the separate maintenance of chronological and systematic records. Registration of accounting entries is carried out by special documents - memorial warrants, which are compiled on the basis of primary documents. Memorial orders are registered in a special journal (chronological record) and based on them are made ledger account entries(systematic record).
The general ledger account form is built with a breakdown of debits and credits for each offsetting account and looks like this:

The general ledger in this form is also called the checklist.
Only the current turnover for the reporting period is taken into account on the ledger accounts. Therefore, according to the ledger accounts, a turnover sheet is compiled for synthetic accounting accounts (at the same time, the completeness and correctness of the recording of business transactions is checked; the total of the debit and credit turnovers of the accounts is compared with the total for the registration journal). It also determines the balances of accounts at the end of the reporting period, for which a new balance sheet is drawn up.
Compared to the main journal, the memorial-order form does not limit the number of transactions recorded, specifies changes in the funds in the accounts, expands the possibilities for the division of labor between accounting workers and automation of accounting.
The scheme of this accounting form is as follows:

However, in this form of accounting, the same entries are repeated many times in various accounting registers, which increases the amount of work. There is a simplified version of this form for small businesses - using accounting records: fixed assets, accrued depreciation (wear and tear); inventories and finished products; production costs; cash and funds; settlements and other operations; settlements with suppliers; wages.
The statement is an accounting account, which reflects the initial balance, debit and credit turnover for the reporting period based on documents broken down by offsetting accounts, the balance at the end of the reporting period. For example, the cash register form looks like this:
The data of the statements are summarized in a chess sheet, on the basis of which a turnover sheet is compiled. According to the balance sheet, a balance sheet is drawn up.
The scheme of the simplified form of accounting is as follows:

At journal-order form of accounting on the basis of primary documents, accumulative statements and development tables are compiled. At the same time, homogeneous transactions related to a specific account are recorded in the journals in chronological order according to the corresponding accounts. At the end of the month, each journal calculates the total turnover on the corresponding accounts. These totals are accounting entries (memorial orders) for entry in the general ledger accounts.
Cumulative journals are called order journals. Order journals are built on a credit basis, i.e. transactions are recorded on the credit of a particular account in correspondence with the debit of different accounts.
The order journal looks like this:
The monthly turnover totals from the order journals are transferred to the general ledger accounts, which have the following form:
The credit turnover is transferred to the general ledger account in one total amount per month, since it is contained in an expanded form in the warrant journal. The debit turnover in the general ledger account is posted in correspondence with other accounts. In the general ledger account, the debit turnover is collected as data is posted from different order journals. Upon completion of the posting of turnovers from the order journals to the ledger accounts, the totals for the debit of each account are calculated, the balance at the end of the month is determined and the balance sheet is drawn up.
The journal-order form of accounting can be presented in the following form: