The procedure for calculating and paying personal income tax by tax agents. IP as a tax agent
Tax agent for personal income tax - a person who is the source of income payment to the taxpayer (clause 1 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Tax agents for personal income tax are required to calculate and withhold tax from individuals - recipients of income (clause 1, article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Who is the agent, what duties he performs, the measures of his responsibility and the CCC for transferring personal income tax amounts - about this in our article.
Who is a tax agent for personal income tax?
The following persons are recognized as tax agents for personal income tax (clause 1 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Russian organizations;
- individual entrepreneurs;
- notaries and lawyers engaged in private practice or having law offices;
- separate divisions of foreign companies.
The tax base for personal income tax is recognized as payments to taxpayers at the expense of the tax agent (clause 9 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation of 06.02.2017 No. GD-4-8 / [email protected], Ministry of Finance of December 15, 2017 No. 03-04-06 / 84250).
If a company hires personnel under an employee provision agreement, then the functions of a tax agent for personal income tax remain with the executing organization, since it is it that makes direct payments to individuals under employment contracts (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06.11.2008 No. 03-03-06/8/618 ).
Individuals who are not registered as individual entrepreneurs and make payments in favor of individuals who are employees are not recognized as tax agents. In this case, the recipients of funds must independently calculate and pay personal income tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 13, 2010 No. 03-04-05 / 3-390).
The list of income subject to personal income tax is presented in Art. 208 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Duties of a tax agent - Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Tax legislation establishes what a personal income tax agent must do. Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation at number 230 contains a small but exhaustive list from which the duties of a tax agent for personal income tax are visible:
- calculate tax on payments to individuals;
- withhold tax;
- transfer tax amounts to the budget;
- report on the calculated, withheld and transferred to the budget income tax in accordance with the forms 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL within the prescribed period.
In order to fulfill its obligations, the withholding agent must be able to withhold tax. Payment of tax amounts should be made exclusively from payments to individuals. The tax agent is not entitled to pay taxes from his own funds. It is also forbidden to include clauses on the payment of tax amounts at the expense of a personal income tax agent in the terms of an employment or civil law contract (clause 9 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 11.07.2017 No. 03-04-06 / 43981, dated 30.08 .2012 No. 03-04-06/9-263). Also, it is impossible to shift the payment of personal income tax from the agent to the taxpayer himself.
Responsibility of a tax agent - penalties and a fine for non-payment
The obligations of a tax agent for personal income tax in relation to the transfer of tax amounts may not be fulfilled or partially fulfilled. Such situations often arise if the income is paid in kind or represents a material benefit received by an individual.
Read about the duties of a tax agent when paying income in kind to an employee in the material. “Individual received income in kind? Act as a tax agent .
Here it is necessary to carry out deductions from cash payments due to the person himself or to a third party on behalf of the recipient of income. The amount of the deduction corresponds to the amount of the payment arrears and the newly assessed tax, if any (paragraph 2, clause 4, article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If payments to the debtor for personal income tax are no longer made or the amount of payments is not enough to cover the debt, the tax agent for personal income tax is obliged to notify the tax authorities and the taxpayer about this. This should be done before March 1 after the end of the tax period (subclause 2, clause 3, article 24, clause 5, article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Sending a message relieves the agent of the obligation to withhold personal income tax from this person. The obligation to pay tax will arise from the taxpayer himself upon receipt of a tax notice from the IFTS.
It is also noted that if the tax agent did not report the impossibility of withholding personal income tax to either the tax service or the taxpayer or did not lose such an opportunity, then penalties may be charged on the amount of arrears to the tax agent for personal income tax based on the results of an on-site tax audit (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 22, 2013 No. BS-4-11/20951 and dated August 22, 2014 No. SA-4-7/16692). A notice of the impossibility of withholding tax must be sent even if the deadline for its submission is missed (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 16, 2012 No. ED-4-3 / [email protected]). To submit a message, the form 2-NDFL with a sign 2 is used.
For a life hack from the specialists of our site, see the article “[LIFE HACK] Checking whether it is necessary to submit 2-personal income tax with sign 2”.
Tax authorities, in addition to penalties, have the right to impose a fine for non-payment of personal income tax by a tax agent.
But the fine can be avoided if:
1. 6-NDFL submitted to the Federal Tax Service without delay;
2. The amount of personal income tax is correctly indicated in the form (without underestimation);
3. Tax and penalties are paid before the tax authorities find out about non-payment.
Such rules are effective from 01/28/2019 and apply to legal relations that arose before this date. We told the details.
CBC for transferring tax amounts
In 2019, the following KBK personal income tax are in force (order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/08/2018 No. 132n):
- 182 1 01 02010 01 1000 110 - code for transferring personal income tax from income paid by a tax agent to a taxpayer. The exception is income received in accordance with Art. 227, 227.1, 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 182 1 01 02020 01 1000 110 - code for the transfer of personal income tax received by an individual - an individual entrepreneur, a notary or a lawyer or a person engaged in other business activities under Art. 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 182 1 01 02030 01 1000 110 - transfer of tax on personal income received under Art. 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 182 1 01 02040 01 1000 110 - code for transferring tax on the income of foreign citizens carrying out activities in accordance with the patent. The personal income tax payment in this case is a fixed advance payment and is made on the basis of Art. 227.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The nuances when paying personal income tax can be found in the heading "Terms and procedure for paying personal income tax in 2018-2019".
How to make a refund of overpaid personal income tax by a tax agent?
If the tax agent overpaid personal income tax, then he, in fact, reduced the income of an individual by such an action. The affected employee has the right to apply to the employer with an application for a refund of the overpaid amount of tax. Tax legislation in paragraph 7 of Art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines that the statute of limitations for such cases is 3 years, during which it is possible to write an application.
After receiving a written request from an employee, the tax agent already writes an application to his IFTS and attaches documents that can confirm the fact of overpayment. The tax authorities will make a decision within 10 days and inform the employer about it. The tax agent is given the right to choose one of two ways to pay off the debt that has arisen:
- Set off the overpayment against future personal income tax payments.
- Transfer the identified amount of overpayment to the taxpayer's account.
If it is not possible to return the tax through the employer, the taxpayer has the right to apply for a tax refund directly to the Federal Tax Service. How to apply for a personal income tax refund in this case, see our article.
Results
An employer has obligations as a withholding agent in relation to income tax on payments to employees. The employer must timely calculate, withhold and transfer personal income tax to the budget, as well as report to the budget on income tax amounts. Failure by a tax agent to fulfill his duties is a reason for a fine by the regulatory authorities.
If income is taxed at a rate of 13 percent, calculate the tax base on an accrual basis monthly:
If the amount of tax deductions for a year is greater than the amount of income received during that period, the tax base is zero. Do not carry over the difference between income and tax deductions to the next year. An exception -deduction for the construction or purchase of housing .
This procedure for determining the tax base for personal income tax at a rate of 13 percent is provided for in paragraph 3 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Situation: is it possible to transfer to the next month the difference between the amount of tax deductions and the amount of income subject to personal income tax?
Yes, you can.
If the amount of tax deductions exceeds the amount of taxable income, the personal income tax base is considered equal to zero. The resulting difference cannot be carried over to the next tax period. This is stated in paragraph 3 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, this rule does not prohibit the transfer of the difference between the amount of deductions and the amount of income from one month to another within one tax period. The tax period for personal income tax is recognized as a year (Article 216 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain any restrictions on the application (transfer, summation) of tax deductions within one year.
If in certain months of the year the employee had no income at all, accumulate deductions in this tax period (sum up on a cumulative basis from the beginning of the year). In such a situation, the right to deduction can be exercised in the month when the employee has income. The condition for the transfer of the deduction is an employment or civil law contract concluded between the employee and the organization (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 7, 2011 No. 03-04-06 / 10-81 and dated August 19, 2008 No. 03-04-06- 01/254, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 11, 2005 No. 04-2-02/35).
Similar explanations are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 22, 2009 No. 03-04-06-01 / 269.
Monthly personal income tax withheld at a rate of 13 percent, calculate using the formula:
| Personal income tax withheld at a rate of 13% | = |
| The Federal Tax Service is developing a bill to change the. The text of the document has not yet been published. It will be possible to refund VAT in a shorter period of time. It's connected with reducing the time of desk audit from 3 months to 2.
Who is considered a tax agent?
One of the most confusing, at first glance, issues when deciding to open your own business is the payment of taxes. A businessman has questions what taxes are paid from what to do if he decides to hire employees. Here he should deal with such concepts as "taxpayer" and "". As an employer, he pays taxes on the income of his subordinates. Thus, he acts as tax agent. Its functions will include all and transfers of monetary amounts to the budget. And his in this case are the taxpayers.
Tax agent for VAT
One of the types of tax intermediary companies is a VAT tax agent. The abbreviation VAT stands for value added tax. According to, VAT tax agents will be considered merchants who purchase goods (it should be remembered that in this case, “goods” is a legal term that includes both works and services) from foreigners who are not tax registered in the Russian Federation. Here, the amount to be transferred to the budget is determined as the amount of profit from the sale of the above goods.
VAT agents are also those persons who lease property from the state or the municipality, as well as those who bought it. These are the two main activities in which value added tax (VAT) is paid.
Entrepreneurs and organizations that act as intermediaries in the sale of their services by foreign citizens on the territory of the Russian Federation also become VAT agents. Also those who sells confiscated property, bought up values, ownerless things.
Is an individual entrepreneur a tax agent for personal income tax?
Tax agent for personal income tax is a businessman who pays taxes on the income of his subordinates. At the same time, he maintains independently developed tax registers. Their form can be any, the main thing is that in the future it would be possible to issue a certificate to the employee in the form 2-NDFL and fill out the reporting form 6-NDFL (since 2016, it has been provided quarterly to the tax office).
Tax registers must contain information on the amount of profit, the date of payment to the employee, the codified type of payment, the status of the taxpayer, the date the tax amount was transferred to the budget, and the details of the relevant payment document. If the employee applied for a deduction, then the data on this deduction.
The monetary value of the tax is determined in accordance with. If taxes are paid at the standard thirteen percent, the calculation is made on an accrual basis from the beginning of the tax period every month. The merchant pays taxes only on the real income of his subordinates. Available tax rates are calculated separately for each amount of actual income. The total amount of taxes paid may not exceed 50% of the employee's cash incentives.
If the total tax less than 100 rubles, then it will have to be added to the tax for the next month and paid in the prescribed manner to the budget (no later than the last month of the current year). In addition, an individual entrepreneur in this case cannot pay taxes for an individual not from his income, but from other amounts. The merchant pays taxes only on the income that the employee receives from him. If a subordinate works somewhere else part-time, then another employer pays taxes for him.
For those who pay tax at the rate 13% , a tax deduction is provided.
For employees, several types of tax deductions are provided: standard, deduction for a child, for training, property. The list of persons eligible to receive the above benefit, among them:
- citizens affected by the Chernobyl accident,
- persons associated with participation in nuclear tests (underground),
- WWII participants,
- disabled since childhood of I and II groups.
Tax deductions are paid to a citizen after he applies in writing to the employer with an appropriate application, provides supporting documents for receiving the deduction due.
Tax deduction can be get it from the tax office, providing there a declaration in the form of 3-NDFL, a copy of the child's birth certificate. If the child is studying at a university full-time - a certificate from the university, institute and similar educational institution.
The merchant, who is an employer, submits reports to the tax office in due time for both for and for his own.
An example of tax deductions for employees
Situation: Single mother Alena N., working for IP Kasyanov I.K., with a salary 16 000 rubles submitted an application to receive a tax deduction, moreover, in the document she indicated that she wanted to receive a deduction for herself and for the undeclared father of the child. Provided an application, a copy of the birth certificate (with a completed column about the father). According to Art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation the woman is entitled to the standard child tax credit. But in this case, not twice. To obtain the desired deduction, either a statement of refusal of such payment by the second parent, or a death certificate in this case of the father, or a court order declaring the father missing is required.
A woman should pay attention to the fact that the amount not subject to tax in 2016 will be 1400 rubles, and the total annual income should not exceed 350 thousand. 1400 rubles is not the money that Alena N. will receive from the entrepreneur I.K. Kasyanov. The amount of the deduction due to her will be calculated by accountants in a certain form.
In order to receive a positive response to her request, she should address the issue of depriving her father of parental rights or recognizing him as missing.
Conclusion
- An individual entrepreneur as a tax payer will be tax agent for personal income tax or VAT.
- Individual entrepreneur as a tax agent for personal income tax pays and records taxes on the income of subordinates who are entitled to various kinds of deductions. They are provided at the request of employees.
- The right to a tax deduction can be used by participants in the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant and the liquidation of its consequences, as well as all those listed in Art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- The merchant must tax registers, where information about the tax history of each employee of the enterprise is entered.
The most popular questions and answers to them on the activities of a tax agent
Question: Hello. My name is Alexey, I am an individual entrepreneur. The other day I decided to conclude
The procedure for calculating personal income tax
The procedure for calculating personal income tax always raises a lot of questions, both for novice accountants and for experienced accountants. It is understandable, personal income tax paid on most of the income of individuals is far from such a "simple" tax as it seems at first glance.
We will talk about how personal income tax is calculated in this article.
The procedure for calculating personal income tax is regulated by Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), according to which individuals - residents and non-residents of the Russian Federation - are recognized as payers of personal income tax.
To determine the amount of his tax liability, the taxpayer must know the tax base and tax rate at which income is taxed.
According to the general rule established by paragraph 1 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax base of the taxpayer includes all taxable income received by him both in cash and in kind, or the right to dispose of which he has arisen, as well as income in the form of material benefit determined by in accordance with Article 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, the tax base is determined separately for each type of income, for which different tax rates are established. The tax base for income from equity participation is determined separately from other income, in respect of which the tax rate provided for by paragraph 1 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, that is, the rate of 13%, is applied, taking into account the specifics established by Article 275 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (paragraph 2 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
Note that today, depending on the status of an individual and the type of income he receives, the tax can be calculated at the following rates - 9%, 13%, 15%, 30% and 35%. Moreover, the rate of 13% is considered the general tax rate, all others are special.
In accordance with the provisions of Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, both taxpayers themselves and tax agents - persons from whom and as a result of relations with whom individuals receive income can calculate the tax base for personal income tax.
Note that only individual entrepreneurs and persons engaged in private practice (Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), as well as individuals upon receipt of income (Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) independently calculate and pay personal income tax:
- from the sale of property belonging to them by right of ownership and property rights, except for the cases provided for in paragraph 17.1 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when such income is not subject to taxation;
- from individuals and organizations that are not tax agents, on the basis of concluded employment contracts and civil law contracts, including when receiving income under employment contracts or lease agreements for any property;
- upon payment of which the tax agent did not withhold tax;
- in the form of remuneration paid to them as heirs (successors) of authors of works of science, literature, art, as well as inventions, utility models and industrial designs;
- in cash and in kind from individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs, by way of donation, except for the cases provided for in paragraph 18.1 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when such income is not subject to taxation;
– from winnings paid out by organizers of lotteries and organizers of gambling, with the exception of winnings paid out at a bookmaker’s office and sweepstakes;
- in the form of a cash equivalent of real estate and (or) securities transferred to replenish the target capital of non-profit organizations in the manner established by Federal Law No. 275-FZ of December 30, 2006 "On the procedure for the formation and use of the target capital of non-profit organizations", with the exception of cases provided for in paragraph 3 of clause 52 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- from sources outside the Russian Federation (this provision applies to individuals - tax residents of the Russian Federation, with the exception of Russian military personnel specified in paragraph 3 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, foreigners who are employed by individuals for personal, household and other similar needs not related to entrepreneurial activities, on the basis of a patent, independently calculate and pay personal income tax to the budget (clause 5 of article 227.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In all other cases, the calculation and payment of personal income tax is made by the source of income payment - the tax agent. Similar explanations on this matter are contained in numerous letters from regulatory authorities, for example, in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 2, 2015 No. 03-04-06 / 31829, the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 12, 2015 No. BS-3-11 / 14 and so on . Recall that, by virtue of Article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax agents are recognized as persons who, in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are responsible for calculating, withholding from the taxpayer and transferring taxes to the budget system of the Russian Federation.
According to paragraph 1 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Russian organizations, individual entrepreneurs, notaries engaged in private practice, lawyers who have established lawyer offices, as well as separate subdivisions of foreign organizations in the Russian Federation, from which or as a result of relations with which the taxpayer received income specified in paragraph 2 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are recognized as tax agents for personal income tax.
Moreover, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when paying most types of income to a taxpayer, the calculation and payment of tax to the budget is carried out by a tax agent in accordance with the rules of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, offsetting previously withheld tax amounts, and in the cases and in the manner provided for in Article 227.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, also taking into account the reduction by the amount of fixed advance payments paid by the taxpayer.
The only exception is income, in respect of which the calculation of amounts and payment of tax are made in accordance with Articles 214.3, 214.4, 214.5, 214.6, 226.1, 227 and 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
We remind you that in accordance with Article 209 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, resident taxpayers pay personal income tax both on income received by them from sources in the Russian Federation and abroad, and non-residents pay tax exclusively on the amount of income received by them from sources in the Russian Federation. An open list of both types of income is given in Article 208 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The general procedure for calculating personal income tax is established by Article 225 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
According to this article, the total amount of tax is calculated based on the results of the tax period in relation to all income of the taxpayer, the date of receipt of which relates to the corresponding tax period.
To determine the total amount of tax, the taxpayer needs to analyze the income received by him and determine the tax base. If there is a receipt of income taxed both at general and at special rates, then the tax bases are determined separately for each tax rate. If there is income from equity participation, then the tax base for this income is determined separately from other income, in respect of which the general rate is applied.
With regard to income taxable at the general tax rate, the tax base is determined as the monetary expression of such income subject to taxation, reduced by the amount of tax deductions provided for in Articles 218-221 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
With regard to income from equity participation in an organization, as well as in respect of income taxed at special rates, these deductions do not apply.
Then, for each tax base, the tax amount is calculated as the corresponding tax rate, a percentage of the corresponding tax base.
The total amount of tax is the amount received as a result of adding the amounts of personal income tax calculated from each tax base.
The same principle of tax calculation is duplicated in Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes the specifics of tax calculation by tax agents.
Consider the procedure for calculating personal income tax on a specific example.
Example
Since the beginning of 2015, an employee of the organization has been paid monthly wages in the amount of 25,000 rubles.
In January, the employee received a gift from the company worth 6,000 rubles.
According to the results of the 1st quarter in April 2015, the employee was paid dividends in the amount of 10,000 rubles.
The employee has a child aged 5 years.
Let's calculate the amount of personal income tax for April 2015.
In terms of income taxable at a rate of 13%, the following income is included in the tax base by a tax agent:
100,000 rubles - the employee's wages on an accrual basis for the period January - April.
2,000 rubles - the value of a gift exceeding 4,000 rubles (clause 28 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
On the basis of subparagraph 4 of paragraph 1 of article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the employee is entitled to a standard deduction for one child in the amount of 1,400 rubles. The specified deduction is valid until the month in which the taxpayer's income, calculated on an accrual basis from the beginning of the tax period by the tax agent providing this standard tax deduction, exceeded 280,000 rubles.
Therefore, for January - April 2015, the employee is provided with a standard deduction for a child in the amount of 5,600 rubles.
The tax base at a rate of 13% from January to April 2015 is 96,400 rubles (100,000 rubles + 2,000 rubles - 5,600 rubles).
The amount of tax at a rate of 13% is 12,532 rubles (96,400 rubles x 13%).
As follows from Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income received by an individual in the form of dividends from equity participation in the activities of organizations is taxed at a rate of 13%. The tax agent determines the tax base for the specified income separately from other income, in respect of which the rate of 13% is applied (paragraph 2 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This means that the tax base, in relation to the specified income, is 10,000 rubles.
The amount of personal income tax is 1,300 rubles (10,000 rubles x 13%).
The total tax amount will be 13,832 rubles (12,532 rubles + 1,300 rubles).
Since the amount of tax withheld from the employee's income in January-March amounted to 9,464 rubles ((75,000 rubles + 2,000 rubles - 4,200 rubles) x 13%).
Consequently, the amount of tax for April will be 4,368 rubles (13,832 rubles - 9,464 rubles).
Note, that Article 225 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation was supplemented from January 1, 2015 with a provision according to which a taxpayer carrying out a type of entrepreneurial activity in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation at the place of his registration, in respect of which a sales tax is established in accordance with Chapter 33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, has the right to reduce the amount of tax, calculated at the end of the tax period at the general rate, for the amount of the sales tax paid in this tax period. Note that this provision does not apply if the taxpayer fails to submit, in relation to the business object for which the sales tax has been paid, a notice of registration as a payer of the sales tax. This innovation was introduced by the Federal Law of November 29, 2014 No. 382-FZ "On Amendments to Parts One and Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation".
Consider what obligations a tax agent has for personal income tax when renting from an individual, as well as what tax to pay personal income tax for individuals. the person renting the premises.
Obligations of the tenant as a tax agent for personal income tax
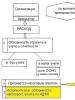
Using the leased property to conduct its activities, the tenant makes rental payments and incurs cash costs. Since as a result of the disposal of funds there is a decrease in the welfare of the tenant, he incurs rent costs. By virtue of the law, the organization has obligations to the state to record expenses in tax and accounting registers in accordance with the norms of tax and accounting legislation, respectively.
In addition, the tenant, when paying income in the form of rent to an individual who is not an entrepreneur, has obligations of a tax agent for personal income tax in relation to this individual - the lessor. That is, the tenant needs to calculate personal income tax on income in the form of rent, withhold tax when paying income to an individual and transfer it to the budget (clause 2, article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What does it mean? Tax obligations arise from an individual, but will the enterprise be responsible for paying the tax?
Get 267 1C video lessons for free:
The fact is that a feature of paying personal income tax is the payment of tax through intermediaries (tax agents) from most of their income. State certain provisions of Ch. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation instructs enterprises to calculate and transfer personal income tax to the budget for another taxpayer - an individual. In the terminology of tax legislation, this means that the company is recognized as a tax agent for personal income tax.
It is the organization recognized as an agent that will deal with all issues of tax calculation, withholding when paying income, and paying to the budget. It is impossible to shift the payment of personal income tax from income in the form of rent to an individual, even if this is specified in the lease agreement. For clarification, you can refer to the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 9, 2016 No. 03-04-05 / 12891.
The need to fulfill the duties of a tax agent for an organization arises due to the provisions of paragraphs 1 and 2 of Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as a result of payment to an individual who is not an individual entrepreneur of income in the form of rental payments under a lease agreement.
Since the Russian organization was the source of payment of income to an individual, it must act as a kind of intermediary between the taxpayer - the individual who received the income and the state represented by the tax authorities in order to ensure that personal income tax enters the budget in the correct amount and in the correct time from the paid income.
But the functions of a tax agent are not limited to this.
The entire list of obligations that the state imposes on a tax agent is contained in Art. 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Here are all the obligations of the tenant organization to the state when paying income in the form of rent:
Insurance premiums when renting from an individual
According to the lease agreement, the tenant bears the costs in the form of rent, and by virtue of Law No. 402-FZ and Ch. 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is obliged to the state to reflect the expense in the registers of accounting and tax accounting. Also, the tenant is recognized as a tax agent in relation to personal income tax and is called upon to fulfill the duties of a tax agent for personal income tax, listed in Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (see table above).
It should be said that the rent paid to an individual under a property lease agreement does not entail the obligation to pay insurance premiums to the PFR, FSS, FFOMS and FSS for injuries (clause 4, article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, article 5 of the Federal Law of July 24 .1998 No. 125-FZ). You can learn more about this from.
General conclusion. The accountant needs to understand the economic implications of the transaction in order to properly account for income, expenses, and obligations to the partner and the budget system. To do this, we offer a graphic illustration of what has been said: