Contribution to the health insurance fund. Medical insurance premiums. Loan interest insurance premiums
This article will discuss such a concept as "payments for insurance" for compulsory medical insurance and the stages of their payment, what changes have occurred this year.
A person is constantly faced with medical care, which takes him a lot of finances. The best option to compensate for the costs is to insure.
All individuals in Russia have the right to free healthcare. An insurance policy will help with this. How to apply for it, what is needed for this, whether it is necessary to pay contributions and what is their size - more on that later.
Basic Information
Faced with the concept of "insurance for medical care", many do not know what it is, why it is necessary to issue a policy. It is necessary to understand this term.
What it is
Insurance means the creation of a fund from which funds are allocated for medical treatment.
In this case, the insurer must pay contributions. Since the concept has a probabilistic nature, not everyone will need an insured event.
There is a possibility of redistribution of risks among the insured - a contribution can be made by one person (the insured), and another person (the insured) can use the funds.
There are also disadvantages of insurance:
The amount of the deposit depends on the profit of the insurer, and the guarantees for the provision of medical care are the same for everyone.
The MHI policy guarantees that a person in trouble will be able to use free medical care in any region of the Russian Federation.

The insured may have only one policy, which is in his hands. The insurance organization is obliged to familiarize the insured persons with the rules and obligations.
Who needs it
Medical insurance - protection of the individual and her health. Being in another country, treatment without a policy will be expensive, and they may even refuse medical care.
Depending on the age of the person, the type and complexity of the disease, the price of the policy will be different. CHI insurance policy is required for the following categories:
Whether a person works or not - insurance does not depend on this, this service is mandatory.
To obtain a policy, you must visit an organization that deals with insurance (CMO) and provide it with documents (persons under the age of 18 are not eligible, as they are considered incompetent).

For minors, insurance occurs in those HMOs in which parents are served or by law.
If the application is not provided by the person himself, but through a representative, then it is needed. Package of documents:

Legal regulation
The population of Russia has the right to the protection and protection of their health. This includes the provision of medical and social assistance, favorable working conditions, and health improvement.
Health care is carried out regardless of gender, race, nationality or language. Together with legal citizens of Russia, foreigners (who live on its territory) and refugees also have this right.
In case of illness, loss of legal capacity, a person is obliged to provide medical care of any type.
For example, preventive measures, diagnostic) and social measures, that is, care for the sick, payment of disability benefits.
Also, the population of the Russian Federation has the right to free medical care in health care systems - state type or municipal.
Compulsory medical insurance for the working population is an innovation. It guarantees equal rights for all segments of the population in the provision of medical care.
The basic program includes:
- help with acute chronic diseases;
- life-threatening situations;
- ambulatory treatment;
- home diagnostics;
- preventive measures: vaccinations, examinations;
- hospital treatment;
- dental assistance.
FAQ
People making contributions for the payment of compulsory insurance for medicine have a lot of questions. Let's consider the most frequent ones.
Exemption from payment
This benefit is used by organizations of the disabled ().
Also, no payment is charged to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (during the election campaign) for:
- funds of candidates for local authorities;
- income received from the election campaign by members of the commission.
Such a decision can only be made by the territorial CHI fund ().
To consider the issue, you need to provide an application for exemption from paying fees and photocopies of documents - a certificate of registration of the organization.

Nuances for IP
Self-employed individuals pay their own health insurance premiums. The calculation takes place at a standard rate, taking into account the minimum wage.
To calculate the contribution, it is necessary to multiply the minimum wage by the tariff and the number of months for which the contribution is paid as an individual entrepreneur. In 2019, the minimum wage is 5965 rubles, that is, the contribution is 3650.58 rubles.
Starting from this year, the amount is not rounded, but paid in kopecks. An individual entrepreneur has the right to make a contribution in installments or all at once for a year. There is no need to report to any organization for this.
An entrepreneur has a choice - in addition to the general taxation system, special ones can be used (subject to the conditions of this regime).
Choices:
A contribution of 1% (additional) is added to the budget of the FFOMS to the established amount if the entrepreneur's income is more than 300,000 rubles per year.
For example - the profit amounted to 400,000 rubles, which means that the DP is calculated as follows - (400,000 - 300,000) * 0.01. this amount should be paid for health insurance.
- Taxes may be less than the amount of the contribution that was paid for a certain period.
- The due date of the fee may reduce the amount of the fee. That is, if you pay immediately by quarters, you can count on a smaller amount.
- The additional contribution also affects the reduction in the amount of tax.
- If the simplified tax system and UTII are applied at the same time, there are no employees, then the tax is also reduced.
- If the amount of the premium for insurance is greater than the amount of tax, then the excess finances are not transferred to another period.
- The right to tax reduction disappears when the entrepreneur recruits employees and pays them wages. If the individual entrepreneur stops paying employees, then the tax can only be reduced from the next period.
Reflection by postings
Medical insurance must be accompanied by postings:

Summing up, we can say that the purpose of health insurance is to guarantee that citizens receive first aid in the event of a problem situation.
Citizens of the Russian Federation have equal rights and opportunities. You can contact the insurance organization yourself or through an intermediary (in this case, you will need a power of attorney).
Every resident of the Russian Federation must have an insurance policy, regardless of citizenship.It is issued free of charge; to obtain it, you need a document that certifies the person.
Each time you seek medical care, the policy must be presented.The insured may be an organization, an individual entrepreneur.
However, they must be licensed. For the working population, these are organizations, enterprises, and individual entrepreneurs. For the unemployed - Councils of Ministers, district and regional districts.
Social insurance is an obligatory element of activity at numerous enterprises. The likelihood of accidents at work and outside it requires a guarantee that, in the event of disability, the worker will receive a payment on which he can live. Every year this legislation is re-evaluated and revised, but the essence remains the same. Consider the changes that have occurred with insurance payments this year, and what to expect in the next period.
In 2017, there will be several significant changes in terms of insurance premiums, the main thing is the transfer of the rights of non-budgetary funds to the tax authorities. It is no secret that the rates for contributions to the FFOMS act as second payments after taxes within the degree of importance, therefore, they are a value that is required to be paid. Amendments have already been made to the regulatory framework of the legislation, therefore, from 01.01.17, Federal Law No. 212 will enter into legal force.
Parameters that will remain the same
- Reporting periodic intervals and calculation time;
- persons obliged to make payment (individual entrepreneurs, notary and lawyer pros, other specialists in private practice);
- objects of payments and dimensional indicators of payment within the framework of reduced tariffs;
- basis for the calculation of contributions.
Contributions to the FFOMS in 2017 involve several changes in the framework of the submission of reports and payments.
- Reporting documentation, since it will be sent to the address of tax-type authorities;
- the timing of the reporting payments;
- eligibility criteria for the list of requirements and the use of reduced rates.
In general, there will be practically no changes in the organizational plan, however, there will be changes in terms of rates.
Indicators of rates for insurance payments 2017: table
Below are insurance premiums in 2017 (sacks): table.
From the given data, one can make sure that there are no changes in the framework of making payments by persons next year, and a new setting of limit values will be required to calculate the deductions for the OPS. If they are reached, there will be rate changes.
Rates 2017 within the reduced tariffs: table
Compared to the 2016 period, there have also been no changes, but the conditions that apply to the payer have changed, under which he will receive the right to use reduced tariffs.
| Policyholder | Interest rate indicator | ||
| FIU | FSS | Contributions to the MHIF | |
| Companies and individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system with an income of at least 70% of the total revenue of the simplified | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Sole Proprietors and Companies Licensed to Do Pharmaceutical Work | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Firms and entrepreneurs operating under the patent system | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Non-commercial organizations engaged in scientific research, charitable foundations | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Companies and individual entrepreneurs engaged in the field of information technology development | 8 | 2 | 4 |
| Business companies engaged in the development of utility models on the simplified tax system | 8 | 2 | 4 |
| Organizations operating within the framework of contractual relations with free economic zones | 8 | 2 | 4 |
| Organizations that pay dues to members of the courts and other meritorious persons | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Payers who have earned the status of a resident for advanced economic development | 6 | 1,5 | 0,1 |
Thus, the FFOMS, how many percent of 2017, depends on the type of activity of an individual entrepreneur or an entire organization, as well as on how actively it takes part in state and charitable financing. Also, based on the given tabular data, one can easily determine who does not pay contributions to the FFOMS.
Dimensional indicators of insurance premiums for IP 2017
The order in which the calculations of "entrepreneurial" payments are carried out has remained virtually at the same level. Contributions to the PFR and FFOMS are actually determined by the minimum wage rate, which is set at the initial stage of the year. If the annual revenue exceeds 300,000 rubles, in addition to fixed income, the entrepreneur will need to pay an additional amount of 1% to the Pension Fund.
In the first case, when the payment is 4,590 rubles, contributions to compulsory medical insurance are calculated as follows: the value of 7,500 rubles (minimum wage) is taken, multiplied by the number of months. in the reporting period (12) and at the % rate - 5.1%. Similarly, the calculation algorithm goes through for other cases.
Consideration of premium rates for accident insurance
An important role is also played by the FFOMS rate 2017 for social needs for injuries and other accidents. There is a certain table indicating that for entrepreneurs and organizations, occupational injury rates will remain unchanged. According to the law, there is an obligation for commercial units to annually prove the correctness of the rate, the documentation package must be submitted to the FSS before April 15. In 2017, this day is Saturday, but the current date rescheduling rule will simplify the procedure, so you should try to confirm the “injury cost” before the 17th. Contributions for compulsory health insurance in the FFOMS are determined by law and are based on the class of occupational risk.
From January 1 this year, government adjustments will come into force, on the basis of which objects are assigned to one category or another. There are 32 classes, on the highest of them the tariff is 8.5 units, and for the first class this value is only 0.2 units. In general, the higher the class score, the higher the rate for injury contributions. If the company has not confirmed the type and type of its activity, then the supervisory authority automatically assigns the highest risk class at the time of entry into the register of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs.
All the changes have contributed to the consolidation of the already established practice, the only difference is that now many actions are taking place in an official manner. Contributions to the compulsory health insurance fund are accrued according to the general scheme, although many conflict situations arose on this issue earlier, and the case could go to trial. Basically, it was the maintenance of the activities of companies, since there is no need to initially put firms in such a rigid framework.
Thus, the well-being of the company and employees depends on how competently and correctly the contributions are calculated and paid. Compliance with the norms of legislation and accounting for tables guarantees competent calculations and the absence of problems with debts and fines.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
But at the same time, you should be guided by the law in order to avoid mistakes and fulfill your obligations on time. What is the procedure for making payments?
General information
How does such an institution as the FSS function, what is it and what regulations are the main ones for payers of insurance premiums? Let's analyze the current legal framework.
Definitions
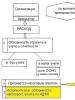
One of the main non-budgetary funds is the FSS (Social Insurance Fund). His work has two directions. This:
The amounts that are directed to compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability can be formed at the expense of:
- amounts of contributions that are mandatory paid by the insured;
- fines and penalties that may be charged to the payer in case of violation of the law.
Funds for the implementation of compulsory social insurance in case of disability of a temporary nature and in connection with motherhood are formed from:
- mandatory contributions to the insurance payment of persons;
- fines and penalties that will be levied in case of violations.
Those amounts that are transferred for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases are formed at the expense of:
- funds that are compulsorily transferred by policyholders (insurance premiums);
- fines and penalties for such payments;
- funds that come from insurers during the liquidation of the enterprise;
- other amounts that do not contradict the normative documentation of the Russian Federation.
The main objective of the Fund is to ensure the protection of employees of companies, not the case when they cannot fulfill their labor obligations for a certain period.
We list the functions of the FSS:
- provision of insurance coverage in the event of an accident at work or an occupational disease.
- insurance coverage in case of maternity (pregnancy and childbirth), which includes:
- Payment.
- Pregnancy benefits.
- A one-time allowance when registration with a specialist in the early stages of pregnancy is carried out.
- Newborn care allowance.
- providing sponsorship .
- providing financial assistance in the event of a preventive measure aimed at reducing the risk of injury at work and reducing the risk of occupational disease.
- provision of vouchers to sanatoriums for rest and treatment of preferential categories of citizens.
- providing disabled people with prostheses and technical equipment during the rehabilitation process.
Representatives will refuse to pay sick leave:
- Upon the onset of temporary disability due to injuries or illnesses that were not received at work.
- When caring for sick children or other family members.
- When caring for a minor child or a minor child with a disability, if their parent/guardian is sick himself.
- During quarantine, treatment in a sanatorium.
- When transferring insured persons temporarily for medical reasons to lighter work, payment for which is also made in a smaller amount.
That is, the FSS does not compensate for damage that is caused not at the workplace, but in everyday life.
Who are the payers?
Current regulatory framework
Payers of insurance premiums to the Social Insurance Fund should rely on such regulatory documents, which contain the rules for calculating and paying amounts:
- Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ.
The deadline for submitting reports and paying amounts to the budget may vary. The influencing factor is the category of the contributor. Calculations are submitted by.
The payer must pay insurance premiums at the end of each reporting period. Allowed:
Contributions for injury insurance are transferred every month within the time limits set for receiving salaries for the previous month at a banking institution.
The insured pays the sums insured in accordance with the terms established by the insurers (law No. 125-FZ, article 22).
When transferring, one should not make mistakes in the BCC, the name of the company or banking institution, otherwise the obligation to pay insurance premiums will not be considered fulfilled (Article 18 of Document No. 212-FZ).
If the last day on which the payment can still be made falls on a weekend, then it is transferred to the next business day. But this does not apply to all contributions.
For example, when paying contributions for injuries, you should rely on the rules of Law No. 125-FZ, which says that you need to pay on the working day that precedes the last one if it is a day off.
Payers are still obliged to ensure that records of accruals and contributions are kept. Accounting is carried out in relation to each person individually.
The amount of insurance premiums in the FSS
Payers are divided into 4 groups in accordance with general and reduced tariffs:
| Condition | Explanation |
| Persons who do not have to pay insurance premiums to the FSS | This applies to participants in the Skolkovo project, as well as if the individual entrepreneur |
| Persons who transfer 1.9% | These are the firms that work for the ESHN, they are agricultural producers. The rule also applies to a public organization of citizens with disabilities. |
| Persons who pay 2% | This applies to IT companies, residents of the technical innovative special economic zone, companies that were created after 13.08.09 by a budgetary institution |
| Persons who pay 2.9% | These are organizations on OSNO, USN, UTII |
Base for accrual
The basis for calculating the amounts of contributions is transfers that are made to individuals. In 2015, the limit was set at 670 thousand rubles ().
That is, insurance premiums will be paid to structures until the amount of payments to the employee does not exceed the standard. The regulation of the amounts is carried out by paragraph 4 of Art. 8 of Law No. 212-FZ.
How to make a calculation?
Accruals should not exceed the base limit. Calculations of the amount of base insurance premiums are carried out on an accrual basis from the beginning of the billing period.
When paying insurance amounts, the following points should be taken into account:
- Payments are determined according to the amount of payments that were accrued to the employee from the beginning of the year until the month when the calculations are made.
- When calculating, it is worth considering tariffs. From the accrued amounts, it is worth subtracting payments that are made every month, for the period from the beginning of the year to the current month.
- Insurance premiums may be reduced by the calculations made for the transfer of benefits for this type of insurance. Funds must be paid to specific accounts in the federal budget of the FSS.
Formula used:
Can overpayments be refunded?
Sometimes there is dissatisfaction among people on this occasion: the regional branch of the Fund carries out excessive collection of insurance premiums from enterprises.
The reason may be, for example, a failure in the programs. At the same time, the company does not always receive a request for the transfer of arrears. How to be in such situations? Is it possible to reimburse insurance premiums?
Payers have the right to return the amounts that are excessively collected, and with interest calculated according to the following formula: 
It will not be possible to collect additional amounts from the authorized body for the use of other people's funds, since it is not used in the field of social insurance.
To receive the amount due back, it is worth submitting (). You have 1 month to do this from the moment you found out about the debited amount in excess.
Usually, payers find out about this when they receive it on settlement accounts. If such deadlines are missed, then the issue will have to be resolved in court.
The application period is 3 years. When drawing up an application, keep in mind that you need to reflect not only the amount of the overpayment, but also the interest that the FSS must return.
The regional representative office will return the amount of interest specified in the application. But since you do not know exactly when the return will occur at the time of the appeal, the amount may differ from that reflected in the document.
The rest of the interest is calculated by the representatives of the Fund within 3 days from the date of receipt of the notice by the payer. The terms for the return of excessively transferred amounts may be delayed, since the authorities may reconcile all calculations.
The amount of interest in tax accounting does not need to be reflected. In accounting, you should use the following postings:
One direct wiring can also be used: Dt 51 Kt 91-1.
Emerging nuances
Even if you fulfill your obligations in full, you cannot foresee all the situations that may arise in the course of your activities.
So, in addition to the basics of paying funds to the fund, you should also understand the nuances: possible fines, arrears, etc.
What is the penalty for non-payment of contributions?
In case of late submission of payrolls to the social insurance fund, the payer will have to pay a fine of 5% of the amount payable in each month.
The minimum amount is 100 rubles, the maximum is 30%. If a person is late with payment by more than 180 days, then the penalties will be as follows:
| 30% | Fine |
| 10% | For each month when funds are not deposited |
The minimum amount is 1000 rubles. In addition, the leadership of the organization will also be responsible. The fine of the head is 300 - 500 rubles.
If reports on calculated insurance payments are not submitted on time, the payer will also be fined. Sanctions are mentioned in Art. 46 of Law No. 212-FZ and Art. 19 of Law No. 125-FZ.
When the calculation of insurance premiums is provided in violation of the law regarding the electronic submission format, the amount of the fine is 200 rubles.
If the amount is not fully paid due to incorrect calculations, then a fine is provided, the amount of which will be 20%.
In case of intentional non-payment, the person will pay 40%. If the document is not provided - 200 rubles for one certificate.
Reflection of posting arrears
Accruals for the mandatory type of insurance affect the size of the income tax base. They should be included in other costs and reduce taxable income in the period when the funds were accrued or paid to the FSS.
Refinements can be of three types:
How can I check the deductions?
A person may not be aware of the resulting insurance premium arrears. In some cases, the main reason is the missed deadlines for payment, in others - the incorrect calculation of payments.
In order not to be held liable for violations, it is worth monitoring deductions to extra-budgetary structures, and requesting a report on the use of insurance premiums to the FSS.
To verify the information, you should contact the regional branch of the FSS with a written request drawn up in any form. You will need to take a document with you that will confirm your identity.
You can also wait for a written notification-receipt for payment of insurance premiums from the authorized body, although it does not reach the addressee in all cases.
An employee can also control whether the employer pays for him in the Social Insurance Fund or not by asking him to present, which reflects the real income of an individual.
Is an employee subject to medical treatment?
For example, the employer expressed a desire to cover the costs of the operation for the employee of the company. Is this amount taxable? For the amount of compensation for treatment costs, the administration must charge insurance premiums to the FSS.
But if the amount of financial assistance did not exceed the limit of 4 thousand rubles, then the accruals can not be made. The basis for this is paragraph 11 of Part 1 of Art. 9 of document No. 212-FZ.
Prospects for CB Administration
Let's figure out what problems are relevant and how they are solved.
World experience shows that the most reliable is the method of three-channel financing, in which:
Public funds are directed towards the implementation of universal payments and to provide minimum insurance benefits if the above amounts are not enough. Thus, 3 entities are responsible for the risks.
The insurance and savings principles give the concept that there can be no gratuitous social assistance, that it is necessary to invest sums in the development of companies. The FSS receives certain percentages, which are set by government agencies.
To ensure the coordination of the work of the entire social insurance system, as well as to carry out republican events, to implement programs, a certain part of the funds received is also directed to the federal level fund.
The amounts of insurance premiums that are legally alienated are the property of the insured person and cannot be withdrawn.
They are not used outside the insurance system, are not taxable other payments and do not need to be deducted from them. Funds can be managed by such an entity - a fund or an insurance fund, which finances all activities.
In order for the system of market relations to be more stable, the fund and the cash desk have commercial rights to manage the amounts of social insurance, if most of it is directed to the social insurance system. The question of how the state budget funds are involved in such a system is relevant.
If state financing of part of the costs in the field of social security is refused, the share of the insured's contributions may increase, or it may be impossible to reimburse the insured person for 100% of the transferred salary.
But the fact that state budget funds are involved creates precedents for government intervention in the financial activities of the social insurance system.
Financing is carried out in funds on residual principles, and the existing budget deficits cannot meet the needs of all citizens.
Therefore, the creators of the social insurance financing model offer 2 options that are alternative:
| Compensate for lost wages in the amount of 80% of the average profit of insured persons | Of these, 73% - from the profit of the organization, 7% - from the amounts that have been accumulated. The rest (20%) can be reimbursed with the participation of the state budget or social insurance structures, which are accumulated through the commercial type of management. In case of a shortage of funds in the first stages, the established minimum will be reimbursed |
| The amount of insurance indemnities will be 75% - this is the minimum | Including from the organization's money, 55% of the specified amount is paid and 25% - at the expense of the state budget. The balance can be distributed between the firm (75 percent) and the insured person (25 percent). The minimum compensation for lost wages is taken as a certain average amount from previously paid compensations, when the amount depended on the length of service of the employee |
Those funds that were not spent in the current budget period may be at the disposal of the insured, who send money to meet the needs of the insured person.
Video: FSS, an example of filling out the calculation of 4-FSS and NS without sick leave and maternity
This can ensure the principle of repayment of amounts that are not spent. The Fund will profit from commercial and auditing management, as well as from fines, penalties and other regressive measures.
The modern insurance system is improved in comparison with the previous one. But there are still many problems in the way that government bodies have to solve.
Having understood the peculiarities of paying insurance premiums to the FSS, you will be able to transfer them on time in accordance with the established tariffs and terms.
What is a 4-FSS report, what does the form look like in 2019, and what are the rules for filling out the document in the current year? This will help to understand the instructions for the formation of the form. Every year, entrepreneurs and accountants are faced with the need to submit reports to the structures of the Social Insurance Fund in the form ...
Recent legislative reforms have made it possible to send reports and other types of documents to the Social Insurance Fund using a special telecommunications channel - through the gateway. Files must be encrypted in a special way, as required by law. This process...
Relatively recently, a reform of the current legislation regarding the payment of compensation for sick leave was carried out. This led to the need to form a special structure - the Social Insurance Fund. The consequence of this is additional reporting, strictly mandatory for payers ...
Correspondence of the area of the enterprise with the proposed range of products.- Study of the premises of the enterprise for ventilation, pollution, lighting and some other indicators.- Study of production equipment, technology for the preparation, storage and sale of food products. Documentation for the current and general disinfection of the premises and equipment. - Clear price tags on goods indicating the exact price, production time and shelf life of the goods, signatures of responsible persons with the date. - Measurement of illumination, air temperature, humidity in the premises. - Study of storage periods and sale of goods. - Providing the consumer with complete and adequate information about the drug by putting it on the price tag.
Difference foms and fss
Examples of such bodies: 6. The Federal Antimonopoly Service (FAS) is an executive authority that almost any business may encounter in the course of its activities. The powers of this service are quite wide: - control and supervision of compliance with legislation in the field of competition in commodity markets; - protection of competition in the financial services market; - control of food prices; - control of fuel prices; - control over the placement of orders during open auctions in electronic form; - control over compliance with the legislation on advertising; - control over the implementation of foreign investments.
7.
Federal Customs Service (FTS). Communication with this service you can not avoid in the implementation of foreign economic activity. 8. The Federal Migration Service (FMS) will be of interest to you, and you to her, if you have foreigners among employees.
9.
Insurance contributions to the PFR, FSS and FOM
For non-working citizens, the state acts as an insurer under compulsory health insurance, thanks to which a range of medical services is available to them in the same volume as for working ones. In 2011, Federal Law No. 326 “On Compulsory Medical Insurance in the Russian Federation” was adopted, which classified persons of foreign citizens with temporary registration or residence permits, stateless persons and refugees as insured under compulsory medical insurance.
Attention
Thanks to the law, it is now possible to choose the most suitable medical institution and doctor. The right to demand compensation for moral, material or physical damage caused to you by medical or insurance organizations is also legalized.
Insurance contributions to the FMS are the responsibility of any organization
STS applying benefits for calculating contributions 20 0 0 20 — IT organizations 8 4 2 14 — Residents of a technology-innovative or tourist-recreational special economic zone 8 4 2 14 — Business companies established by budgetary scientific institutions 8 4 2 14 — Project participants Skolkovo 14 0 0 14 - Payers to ship crew members in respect of payments to ship crew members 0 0 0 0 - Pharmacies on UTII in relation to employees engaged in pharmaceutical activities 20 0 0 20 - Non-profit organizations on the simplified tax system 20 0 0 20 - Charitable organizations on STS 20 0 0 20 — Individual entrepreneurs applying the patent taxation system 20 0 0 20 — Participants of the FEZ Crimea and Sevastopol 6 0.1 1.5 7.6 — Residents of the territory of advanced social and economic development 6 0.1 1.5 7.6 — Terms of payment of insurance premiums in 2018 Insurance premiums to the funds are transferred every month until the 15th day of the next month.
The Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation
Addition 2016: If a special assessment of working conditions was not carried out, then the following rates apply:
- 9% - in relation to employees specified in subparagraph 1, paragraph 1, article 27 of Law No. 173-FZ;
- 6% - in relation to employees, the list of which is given in subparagraphs 2-18 of paragraph 1 of article 27 of the same law.
If a special assessment was carried out, then the rate depends on the established class of working conditions. For harmful and dangerous class rates are set from 2 to 8%.
Reporting on insurance premiums The following reports must be submitted to the FIU:
- RSV-1.
Download a sample of filling RSV-1 in 2016. These reports are submitted quarterly by the 15th day of the second month following the reporting period.
Thus, reports are submitted until May 15 for the 1st quarter, until August 15 for the half year, until November 15 for 9 months and until February 15 for the year. You can read how the RSV-1 submission deadlines have changed since 2015 here.
Insurance contributions to PFR, FFOMS and FSS in 2017
Info
Taxes from our income are distributed among three money-boxes - the so-called off-budget funds: to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation (PFR), the Social Insurance Fund (FSS) and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (FOMS). What all these organizations have in common is that they, being components of the country's financial system, have a strict focus on the use of funds and are spent for those purposes that are not included in the state budget.
The funds of these funds are formed mainly from the mandatory contributions of individuals and legal entities:
- the pension fund takes 22% of the employee's taxable income;
- social insurance fund - 2.9%;
- health insurance fund - 5.1% of the insurance tariff.
These contributions come in the form of mandatory monthly payments. Let us dwell in more detail on deductions to the health insurance fund.
Insurance premiums in 2018
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs doing business in the territory of the Russian Federation are required to charge insurance premiums. From 2017, the Federal Tax Service (Chapter 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) will become the administrator of the contributions.
You will need to report and pay insurance premiums to the account of the tax office.
- Contributions for mandatory pension insurance are 22%.
- Compulsory health insurance contributions.
Employers pay medical contributions at the rate of 5.1% of the taxable payments transferred to the employee for the reporting period.
- Contributions for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with motherhood.
Contributions paid to this fund amount to 2.9% of taxable payments (through these contributions, the FSS pays sick leave benefits, maternity and other benefits).
On the activities of the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (FFOMS)
In the budget expenditures of the FSS, the main share falls on the payment of benefits for temporary disability, pregnancy and childbirth, at the birth of a child, for caring for a child until he reaches the age of one and a half years, for burial. In 2000, the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 entered into force No. 125-FZ “On Compulsory Social Insurance against Industrial Accidents and Occupational Diseases” (as amended on July 17, 1999). Insurance tariffs for compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases are set for groups of sectors (sub-sectors) of the economy in accordance with occupational risk classes. Insurance payments are made in connection with the death of the insured and to pay for the additional expenses of the insured for his medical, social and professional rehabilitation.
In this case, it is possible to slightly postpone the payment of wages and the transfer of insurance premiums to the funds, but the reporting must still be provided, however, zero. Calculation of the amount of contributions Contributions to the MHIF are payments in the amount of 5.1% of the amount of wages and bonuses paid to each employee.
This amount is paid from the settlement account of the organization, reducing its income. However, at the same time, income tax, tax on the simplified tax system or tax on UTII can be reduced by the amount of insurance premiums, but not more than 50%.
The amounts of contributions are paid every month on the day of the issuance of salaries to employees according to a certain CSC to the budget. Contributions to the MHIF are a guarantee to each employee that in case of illness, he will definitely receive temporary disability benefits. The first three days of illness are paid for by the employer, and the next period - at the expense of the budget.
Difference foms and fss
As soon as the salary calculated from the beginning of the year on an accrual basis reaches this limit, only the 10% rate will be applied for all categories of citizens. In 2013, the marginal base for calculating insurance premiums was 568,000 rubles. In 2014 - 624,000 rubles. In 2016 - 800,000 rubles. Thus, in 2014, a rate of 22% applies to wages within the marginal base, and a rate of 10% applies to wages above this base.
All these 10% will be the insurance part of the pension. Supplement 2016: Pension contributions are made at a rate of 22%, this rate is applicable until the total salary of an employee reaches the mark of 800,000 rubles from the beginning of the year, contributions to the Pension Fund are deducted from income above this amount at a rate of 10%. In addition to the basic rates, there are also additional rates in the Pension Fund, which apply only to certain categories of workers.
All subjects of economic activity, except for taxes, are obliged to pay contributions to the FSS(Social Insurance Fund), a pension fund (hereinafter referred to as the PFR) and for compulsory health insurance (hereinafter referred to as FFOMS) for themselves and for employees, if any. Today we will talk about tariffs for 2018 and find out if there are any changes in the new reporting period.
Individual entrepreneurs pay insurance fees, consisting of two parts:
- In 2018 fixed contributions to the PFR amount to 26,545 rubles, and in the MHIF - 5,840 rubles.
- Additional contributions to the FIU and FFOMS are accrued if the entrepreneur's annual income exceeds 300 thousand rubles and, as in the past year, is 1% of the amount of annual income reduced by the limit.
For example, if the income for the year was 500 thousand rubles, then the additional fee \u003d (500,000 - 300,000) / 100, that is, another 2 thousand rubles will need to be added to the fixed amount.
When calculating the additional part of the fee, all individual entrepreneur incomes are taken into account, regardless of the applicable taxation regime.
The total amount of contributions to the pension fund and health insurance cannot exceed 212,360 rubles.
Funds can be transferred from a current account, payment card or in cash. Payment is accepted both at bank branches and through online services.
When compiling a payment order, it is necessary to correctly indicate the budget classification code (hereinafter BCC):
- 182 102 021 400 611 101 60 - fixed and additional fees to the PFR;
- 182 102 021 030 810 131 60 - contributions to the MHIF.
If the codes are entered incorrectly, the money will be credited to the light of other payments, this will lead to arrears in fees and penalties. Codes are entered in the appropriate field, if there is no such column - in the "Recipient" field.
Contributions to the PFR and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund for employees
 If an individual entrepreneur acts as an employer, he is required to pay insurance premiums for employees. Insurance premiums do not have a fixed part and are calculated according to general tariffs, based on salaries, bonuses, vacation pay and other monetary compensations:
If an individual entrepreneur acts as an employer, he is required to pay insurance premiums for employees. Insurance premiums do not have a fixed part and are calculated according to general tariffs, based on salaries, bonuses, vacation pay and other monetary compensations:
- contributions to the FIU for individual entrepreneurs for employees make up 22% of the total amount of funds paid out per month;
- 5.1% is deducted to the Medical Insurance Fund;
- for social insurance 2.9%, as well as contributions for injuries from 0.2 to 8.5% (the coefficient depends on the main type of activity).
Injury fees are transferred to the FSS department in which the individual entrepreneur is registered as an employer, while indicating BCC - 393 102 020 500 710 001 60. All other payments are sent to the tax account to which the entrepreneur belongs, indicating the following codes:
- pension insurance - 182 102 020 100 610 101 60;
- social insurance in case of disability associated with childbirth and - 182 102 020 900 710 101 60;
- medical insurance - 182 102 021 010 810 131 60.
Carefully calculate the amounts due to the funds in order to avoid penalties. If it turns out that you mistakenly reduced the amount of the contribution, you will have to pay a fine of 20% of the underpaid amount. And if it turns out that the understatement was done intentionally, then 40%.
Do individual entrepreneurs pay contributions to the FSS?
 According to the Tax Code, an individual entrepreneur pays social insurance contributions:
According to the Tax Code, an individual entrepreneur pays social insurance contributions:
- If he acts as an employer and labor activity is carried out on the basis of. In this case, the businessman pays fees for all employees and submits reports in the 4-FSS form, in accordance with the general rules.
- An individual entrepreneur may not pay contributions for himself, but in this case you should not rely on disability benefits or in connection with childbirth and maternity.
- If desired, social contributions are also paid when using hired personnel on the basis of a civil law agreement.
Fee payment features
There are a number of situations when individual entrepreneurs pay contributions in an amount less than that established by law, or are completely exempt from payments:
- When registering as an individual entrepreneur not at the beginning of the reporting period (for example, in March or August), then the amount of the fixed part of the fee will be less. It is calculated from the number of calendar days from the date of registration to December 31.
- Entrepreneurs have the right not to pay fees to the FSS for themselves if they are temporarily unable to work or are on maternity leave.
- From payments to the pension fund and medical insurance are exempted business entities located:
- in military service by conscription;
- on maternity leave to care for a child under 1.5 years old, a child with a disability or a person over 80 years old;
- in a remote area, in connection with the performance of military service by one of the spouses;
- abroad, in connection with the performance of diplomatic duties of one of the spouses.
To be exempted from paying fees for one of these circumstances, it is necessary to submit applications with supporting documents to the regional offices of the relevant funds.
Social insurance contributions for employees are not charged if the employee's annual income exceeds 755,000 rubles. But if the income exceeds 876,000 rubles, then 10% of the excess amount will need to be transferred to the pension fund. For example, the income amounted to 1 million rubles, then the fee \u003d (1,000,000 - 876,000) x10% \u003d 12,400 rubles.
Deadline for payment of contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the Social Insurance Fund
 Deadline for payment of contributions to the FSS, PFR and MHIF are established by law, as well as for tax payments. The rules and dates for the payment of fees are regulated by Article 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Deadline for payment of contributions to the FSS, PFR and MHIF are established by law, as well as for tax payments. The rules and dates for the payment of fees are regulated by Article 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The fixed part of the contributions must be transferred before December 31 of the current reporting year, the additional part is paid no later than July 01, 2019. We recommend paying the fixed part of the tax on a quarterly basis, before the date of tax transfer. This will allow you to use and legally reduce the amount of tax.
Fees to the FSS for employees and themselves are payable no later than the 15th day of the month following the reporting month.
Attention! Failure to comply with the terms of payment of insurance fees in accordance with Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation threatens not only with a fine, but also with tax, administrative and even criminal liability.
Who can apply for the reduced rate
 There are several conditions that need to be met in order to use the reduced rate IP to pay fees:
There are several conditions that need to be met in order to use the reduced rate IP to pay fees:
- annual income should not exceed 79 million rubles;
- to carry out the type of activity specified in the list given in paragraph 1 of paragraphs. 5 st. 427 NK;
- the share of profit from this type of activity should be 70% or more of the total income.
Under such conditions, the entrepreneur has the right to use such coefficients: 20% should be deducted to the pension fund, deductions are made to the FSS only for injuries, and no fees are paid to the health insurance fund at all.
Conclusion
On January 1, 2018, Federal Law No. 335-FZ of November 27, 2017 came into force, which brought changes to the system for paying insurance premiums. The amount of fixed fees for individual entrepreneurs has become lower and now does not depend on the minimum wage.
The maximum amount of contributions to pension insurance from an amount exceeding the income of 300 thousand rubles, on the contrary, increased.
Some changes have been made to the list of activities that allow the application of reduced tariffs and the deadline for payment of additional contributions has been postponed. Everything else remains the same.
Remember that fixed contributions must be paid even with a zero declaration, otherwise the tax office has the right to impose a fine and.