PUBLIC SYSTEMS DVS. Why in engines need a supervision: their types and principle of operation The degree of supercharged in modern DVS
The task of increasing the power and torque of the engine was always relevant. The engine power is directly related to the working volume of cylinders and the amount of fuel-air mixture supplied in them. Those. The more fuel burns in the cylinders, the higher the power develops the power unit. However, the simplest solution is to increase the power of the engine by increasing its working volume leads to an increase in the dimensions and mass of the structure.
The number of the supplied working mixture can be raised due to an increase in the rotation of the crankshaft (in other words, to implement in the cylinders per unit of time a larger number of working cycles), but there will be serious problems associated with increasing inertia forces and a sharp increase in mechanical loads on the part of the power unit, What will lead to a decrease in the motor resource. The most effective way in this situation is precipitation.
Imagine engine inlet tact internal combustion: Motor at this time works as a pump, besides very ineffective - the air filter is on the way, the bends of intake canals, in gasoline engines - also the throttle valve. All this certainly reduces the filling of the cylinder. Well, what is required to increase it? Raise pressure in front of the intake valve - then the air in the cylinder "will fit" more. When preproofing, the filling of cylinders of fresh charge is improved, which allows you to burn more fuel in the cylinders and get a higher engine power at the expense of this.
In the engine, three types of boost are used:
- resonant-work used kinetic energy Air volume in intake manifolds (the supercharger in this case is not needed)
- mechanical - In this embodiment, the compressor is driven by a strap from the engine
- gas turbine (or turbocharging) - the turbine is driven by the stream of exhaust gases.
Each method has its advantages and disadvantages that determine the scope.
As already noted at the beginning of the article, for better filling of the cylinder, it should be lifted in front of the intake valve. Meanwhile, the increased pressure must not be constantly constantly - enough so that it rises at the time of closing the valve and "exhausted" the cylinder with an additional air portion. For short-term increase in pressure, the compression wave is quite suitable, "walking" through the inlet pipeline during the operation of the motor. It is enough just to calculate the length of the pipeline itself so that the wave, reflecting several times from its ends, came to the valve at the right moment.
The theory is simple, but the embodiment requires a lot of ingenuity: the valve with different crankshaft revisions are open different times, and therefore the inlet pipes of the variable length are required to use the effect of resonant pressure. With a short intake manifold, the motor works better at high speeds, with low revolutions, a long intake path is more efficient. Variables of the length of intake pipelines can be created in two ways: or by connecting the resonant chamber, or through switching to the desired inlet channel or its connection. The last option is called even dynamic superfluous. Both resonant and dynamic supervision can accelerate the flow of air intake post.
The effects of the superior, created by the oscillations of the head of the air flow, is in the range from 5 to 20 MG. For comparison: with a turbocharger or mechanical supervision, you can get values \u200b\u200bin the range between 750 and 1200 MG. For completeness of the picture, we note that there is still an inertial supervision, in which the main factor in creating an overpressure in front of the valve is a high-speed stream pressure in the inlet pipeline. It gives a minor increase in power at high (more than 140 km / h) speeds. Used mainly on motorcycles.
Mechanical superchargers (by English Supercharger) allow pretty simple way significantly raise the power of the motor.
Having a drive directly from the engine crankshaft, the compressor is able to download air into the cylinders with minimal revs without delay to increase the pressure of the boost strictly proportional to the motor turnover. But they have disadvantages. They reduce the efficiency of the DVS, since part of the power generated by the power unit is consumed on their drive. Mechanical supercharging systems occupy more space, require a special drive (toothed belt or gear drive) and enhance increased noise.
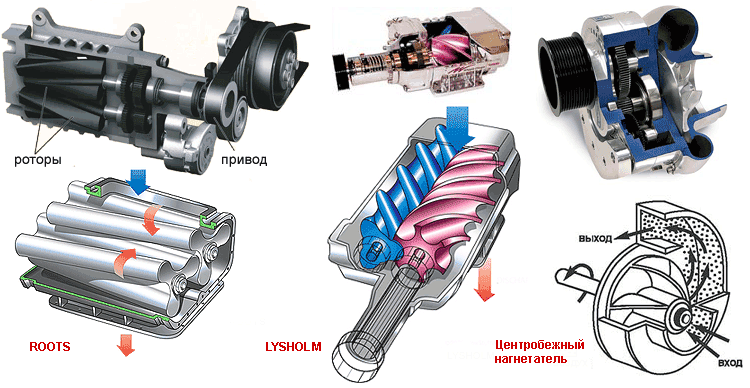
There are two types of mechanical superchargers: bulk and centrifugal.
Typical representative of volumetric blowers is the roots supercharger and the Lysholm compressor.
Roots design resembles an oil gear pump. Two rotors rotate in opposite sides inside the oval case. The axes of the rotors are interconnected by gears. The peculiarity of this design is that the air is not compressed in the supercharger, but outside the pipeline, falling into the space between the case and the rotors. The main disadvantage is in a limited pressure. No matter how impeccable details of the supercharger, the air begins to seep back, reducing the efficiency of the system. Fight methods are a bit: increase the rotation speed of the rotors or make the supercharger of two- and even three-step.
Thus, it is possible to increase the total values \u200b\u200bto an acceptable level, however, multistage structures are deprived of their main dignity - compactness. Another minus is uneven discharge at the exit, because the air is served by portions. In modern designs, three-dimensional spiral-shaped rotors are used, and intake and outlet windows have a triangular form. Due to these triggers, the bulk-type superchargers practically got rid of the pulsating effect. The low speed rotation speeds, and therefore, the durability of the structure with low noise led to the fact that they generously equip their products such love brands like Daimlerchrysler, Ford and General Motors.
Volumetric blowers raise power curves and torque without changing their forms. They are effective on small and medium turnover, and this is best affected by the dynamics of overclocking. The only problem is that such systems are very whimsical in manufacturing and installation, and therefore quite roads.
Another way to fill in the intake manifold air under excess pressure at one time suggested Lysholm engineer (Lysholm). His demanded of his brainchilder, or Double Screw (double screw). The design of Lockolma is reminded by a conventional meat grinder.
Inside the case there are two complementary screw pumps (auger). Rounding in different directions, they capture air portion, compress and drive it into cylinders. This system is characterized by internal compression and minimal losses, thanks to precisely verified gaps.
In addition, screw supervises are effective in almost the entire engine speed, silent, very compact, but extremely expensive due to complexity in the manufacture. However, they do not discern such famous tuning studies as AMG or Kleemann.
Centrifugal superchargers in design resemble turbocharging. Overpressure in the intake manifold also creates a compressor wheel (impeller). Its radial blades are captured and discarded the air into the circumferential tunnel with centrifugal force. Difference from turbocharging only in the drive. Centrifugal superchargers suffer similar, albeit less noticeable inertial defect, but there is another important feature. In fact, the magnitude of the pressure produced is proportional to the square of the speed of the compressor wheel.
Simply put, it should rotate very quickly to inflate the necessary air charge into the cylinders, sometimes tens times exceeding the engine speed. Centrifugal supercharger is effective in high speed. Mechanical "Centrifugals" are not so capricious in service and durable gas-dynamic fellow, since they work at less extreme temperatures. Unpretentious, and therefore, the cheapness of the design has gained them popularity in the field of amateur tuning.
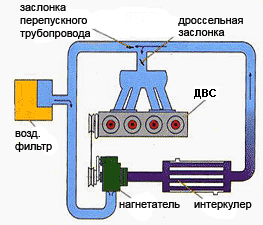
The mechanical supercharger control circuit is pretty simple. With full load, the valve of the bypass pipeline is closed, and the throttle is open - the entire air flow enters the engine. When working with partial load, the throttle is closed, and the pipeline valve opens - excess air returns to the input of the supercharger. The incoming charge air cooler (Intercooler) is an almost indispensable component of not only mechanical, but also gas turbine supervision systems.
When compressing in the compressor (or in the supercharger), the air heats up, as a result of which its density decreases. This leads to the fact that in the working volume of the cylinder of air, and, consequently, oxygen is placed in mass less than it could fit in the absence of heating. Therefore, the compressed air before serving it into the engine cylinders is pre-cooled in the intercooler. By its design, this is an ordinary radiator, which is cooled or a flux of incident air or coolant. A decrease in the temperature of the superior air of 10 degrees allows to increase its density by about 3%. This, in turn, allows you to increase the engine power about the same percentage.
Gas turbine supervision
Turbocompressors are more widely used on modern car engines. In fact, it is the same centrifugal compressor, but with another drive scheme. This is the most important, one can say, the fundamental difference between the mechanical blowers from "turbo". It is the actuation diagram to a large extent determines the characteristics and areas of application of certain structures. The turbocharger, the impeller impeller sits on a single shaft with a turbine impeller, which is built into the exhaust manifold of the engine and is driven by the exhaust gases. The speed of rotation may exceed 200.000 rpm. There is no direct connection with the engine crankshaft, and the air supply control is carried out due to the pressure of the exhaust gases.
The advantages of turbocharging include: increasing the efficiency and engine efficiency (mechanical drive takes power from the engine, the same uses the exhaust gas energy, therefore, the efficiency increases). The specific and general efficiency of the engine should not be confused. Naturally, for the engine operation, the capacity of which increased by the use of turbocharging, requires more fuel than for a similar non-infant motor of less power. After all, the filling of cylinders with air improves, as we remember, in order to burn a greater amount of fuel in them. But the mass fraction of fuel per unit of power per hour in the engine, equipped with TC, is always lower than that of a similar structure of the power unit devoid of superior.
Turbocaddv makes it possible to achieve the specified characteristics of the power unit with smaller dimensions and mass than in the case of an "atmospheric" engine. In addition, the turbo video motor is better ecological indicators. Advance of combustion chambers leads to a decrease in temperature and, consequently, a decrease in the formation of nitrogen oxides. In gasoline engines, a higher combustion of fuel is achieved, especially in transient modes of operation. In Diesels, the additional air supply allows you to move away the border of the appearance of the smoke, i.e. to fight emissions of soot particles.
Diesels are significantly better adapted to the superior, and to the turbocharger in particular. Unlike gasoline engines in which the pressure of the superior is limited by the risk of detonation, it is such a phenomenon. Diesel can be added up to reaching limit mechanical loads in its mechanisms. In addition, the absence of air injection in the inlet and the high degree of compression provide greater pressure of the exhaust gases and their smaller temperature in comparison with gasoline engines. In general, just what is needed to use the turbocharger. Turbocompressors are easier in the manufacture, which pays a number of flaws inherent in them.

With a low engine speed, the number of exhaust gases is small, respectively, the efficiency of the compressor is low. In addition, the turbocharged engine, as a rule, has so-called. "Turboyamu" (in English "Turbo-Lag") is a slow response to an increase in fuel supply. You need to sharply accelerate - press the gas pedal to the floor, and the engine "thinks" and only then picks up. The explanation is simple - it takes time, while the motor will rotate, the pressure of the exhaust gases will increase, the turbine will be promoted, the impeller impeller will be unloaded - and finally, "go" air. Get rid of these shortcomings, designers are trying in different ways. First of all, a decrease in the mass of rotating parts of the turbine and compressor. The rector of the modern turbocharger is so small that it easily fits on the palm.
Reducing the mass is achieved not only by the design of the rotor, but also by the choice of appropriate materials for it. The main complexity at the same time is the high temperature of the exhaust gases. Metal-ceramic turbine rotor is about 20% lighter made of heat-resistant alloys, and besides, it has a smaller moment of inertia. Until recently, the service life of the entire aggregation limited the durability of bearings. In fact, it was liners like crankshaft liners that were smeared with oil under pressure. The wear of such sliding bearings was, of course, great, but the balls could not withstand the huge frequency of rotation and high temperatures. The output was found when it was possible to develop bearings with ceramic balls. However, worthy of surprise is not the use of ceramics - bearings are filled with a constant reserve of plastic lubricant, that is, the channel from the standard oil system of the engine is no longer needed!
Get rid of the disadvantages of the turbocharger allows not only a decrease in the inertia of the rotor, but also the use of additional, sometimes quite complex compound pressure management schemes. The main tasks are to reduce the pressure at high engine revolutions and increase it at low. To fully solve all problems can be using a turbine with a variable geometry (Variable Nozzle Turbine), for example, with movable (swivel) blades whose parameters can be changed widely.
The principle of operation of the VNT turbocharger is to optimize the flow of exhaust gases sent to the turbine impeller. On low engine speeds and a small amount of exhaust gases VNT, the turbocharger guides the entire flow of exhaust gases on the turbine wheel, thereby increasing its power and pressure pressure. With high speed and high levels of the gas flow, the VNT turbocharger has mobile shovels in the open position, increasing the cross-sectional area and removing the part of the exhaust gases from the impeller, protecting itself from exceeding the revolutions and maintaining the pressure of the boost on the engine the required engine, excluding the overdue.
Combined systems
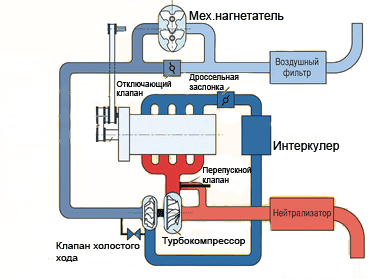
In addition to single boost systems, two-stage supervisions are often found now. The first step is a drive compressor - provides an effective supervision in small circulation of DVS, and the second - turbocharger - utilizes the energy of exhaust gases. After reaching a power unit sufficient for normal operation of the turbine of revolutions, the compressor turns off automatically, and when they are dropped, it comes into effect.
A number of manufacturers are installed on their engines at once two turbocharger. Such systems are called "Buturbo" or "Twinturbo". There is no fundamental difference in them, for only an exception. Buturbo implies the use of different diameter, and consequently, the performance, turbines. Moreover, the algorithm of their inclusion can be both parallel and consistent (sequential). On low revs, the turbocharging of a small diameter is quickly spinning, and the "Elder Brother" is connected to it.
Thus, the acceleration characteristic of the car is aligned. The system is expensive, so it can be found on prestigious cars, such as Maserati or Aston Martin. The main task of "Twinturbo" is not to smooth the "turboyama", but in achieving maximum performance. This uses two identical turbines. Mounted "Twin-" and "Buturbo" both on V-shaped blocks and in the row motors. Options for connecting turbines are also identical to the "Buturbo" system. What is the point? The fact is that the performance of the turbine directly depends on its two parameters: diameter and speed of rotation. Both indicators are very capricious. An increase in diameter leads to an increase in inertia and, as a result, to the notorious "turboyama". The speed of the turbine is limited by permissible loads on materials. Therefore, two modest and less inertial turbines can be more efficient than one large.
First, change the oil in time and the oil filter. Secondly, use only oil intended for engines equipped with turbocharging, which is originally designed for more high temperaturesthan usual. But on the road, everyone can happen, and if you had to pour an unknown oil, then do not drive, move slowly. Engine This oil will survive, but the turbocharger is not necessarily. Arriving home, immediately change the oil and oil filter.
And finally, the third, the most important condition for the normal operation of turbocharging. In the life of the turbine there are two most responsible points: the start of the engine and its stop. When you start a cold engine, the oil in it has a high viscosity, it hardly pumps on the gaps; Thermal clearances have not yet been established; Heating of different parts of the compressor, and therefore the thermal expansion, go at different speeds. Therefore, do not rush, let the engine warm up.
If you need to stop, never shuffle the engine immediately. Depending on the ride mode, let him work at idle 2-5 minutes (in winter it is longer). During this time, the turbine shaft will reduce turnover to the minimum, and the parts directly contact with the exhaust gases are smoothly cooled. In this situation, the turbo timer will significantly facilitate life. He will make sure that the drilled car engine worked for several minutes at idle, the overseas elements of the turbocharger, even if the owner already left and closed his car. However, many security alarms have such a function.
Purpose of the supervision of DVS is to increase the mass filling of the engine cylinders with fresh charge. This is usually achieved using special devices or boost units. Engines with such systems are called combined. The supervision systems are very diverse on the principle of operation and, accordingly, according to the signs of classification.
In the combined engine, air or combustible mixture is compressed in compressors in the cylinders. Advance is considered low, if in the compressor to< 1.9. Низкий наддув позволяет повысить мощность двигателей на 20-25%. При среднем наддуве ( к = 1.9-2.5) удается повысить ее на 25-50%. Высокий наддув ( к > 2.5) Even more increases power, but its use is often not justified due to a significant increase in the mechanical, thermal tension of parts and nodes.
Superior engine cylinders can be either dynamic or carried out using a special supercharger (compressor). In modern MFCs for boosting, both bulk (rotary gear, screw, piston) and bladeed centrifugal compressors are used. Gas turbines are most often radially axial, less often - axial.
There are three superchard systems with superchargers: with a drive compressor, with a turbocharger and combined (Fig. 11.1).
Fig.11.1. Circuit Systems Plug DVS
In the first diagram, the drive compressor through an increaseing gear is connected to the engine crankshaft. To drive the turbocharger (scheme 2) use the energy of exhaust gases entering the gas turbine . The compressor is installed on the same shaft with a gas turbine. . In the case of a combined system (circuit 3) of the first step is a drive compressor, and the second is a turbocharger. Two-stage reducing can be carried out by two successively by turbochargers or drive compressors.
On the tractor and car diesels most often used gas turbine supervision.
At the same time there are two main energy use options:
1. The energy consumed by the compressor is equal to the energy produced by the gas turbine. In this case, the turbocharger has only a gas connection with the engine (Fig.12.1.2). Such a scheme provides high economic indicators with maximum design simplification and is therefore most common. In such engines, the energy of exhaust gases is utilized, which allows in some cases to even increase the efficiency of the engine.
2. The energy generated by the gas turbine is not equal to the energy consumed by the compressor. The energy difference is transmitted from the engine to the turbocharger by applying the mechanical communication of the turbocharger rotor with the engine crankshaft, which complicates the design of the latter. Sometimes in these cases, instead of mechanical communication of the rotor turbocharger with a crankshaft, a combined boost system is used.
Mechanical communication is used in cases where it is necessary to transmit excess energy from the gas turbine to the engine at high pressures and gase temperatures before the turbine.
Possible two options Gas supply to gas turbine:
1) from the total exhaust pipeline;
2) separately from each cylinder or from a group of cylinders, in which, in accordance with the procedure for their operation, the time between two consecutive pressure pulses formed during the release of gases from cylinders is quite large (pulsed prediment).
In the first case, especially in engines, with a large number of cylinders and high speed, the pressure of gases in the exhaust pipeline is aligned, the amplitude of pressure fluctuations before the turbine is small and the process of supplying gases to the turbine can be considered as occurring at constant pressure. In the second case, the spent gases come to a gas turbine with variable pressure, which allows under certain conditions to increase the performance of superior.
The supply of gases to the turbine at constant pressure creates elevated resistance in the outlet of the engine compared with the release into the atmosphere. This worsens the cleaning of cylinders and reduces the filling of them with a fresh charge.
With a pulsed superpower after a period of release of gases from one cylinder to the beginning of the valve overlap, the pressure in the graduation path decreases sharply. As a result, the pressure drop between intake and graduation paths increases and clean the combustion chambers becomes more efficient. The work expended on the pushing out of gases is reduced. As the pressure of the superior and the increase in the average gas pressure in the graduation path, the positive effect on the use of pulsed superior is reduced, since pressure pulses are smoothed. The maximum effect in the pulse system is reached at p to < 0.15 MPa, with P to< 0.4 МПа применение импульсного наддува уже не дает эффекта. Для достижения наибольшего эффекта при импульсном наддуве выпускные трубопроводы делают по возможности короткими и меньшего объема. В импульсных системах используется кинетическая энергия отработавших газов, однако, ухудшается очистка цилиндров двигателя от отработавших газов, что является общим недостатком всех систем газотурбинного наддува.
In the autotractor diesel engines, with the number of cylinders 8 and more advantageously use systems with constant pressure in front of the turbine. The efficiency of such turbines is higher than impulse, and the release system is simpler.
It should also be noted smaller (compared to engineless engines), the adaptability and worst starter properties of the engines with superimposed.
Air coolers
When pressed, the air temperature behind the compressor increases, therefore, with an average and high superior, an intermediate air cooling between the compressor and the engine inlet pipe is carried out. This helps to improve the massive filling of cylinders, increasing the power and fuel engineering engine, to reduce the thermal tension of its parts, reduce the temperature of the gases before the turbine.
Air can be cooled with special coolers or by evaporative cooling - injecting easily evaporating substances (alcohol, ammonia, water, etc.). Apply two types of coolers: air-air and water-air. Apply both tubular and lamellar coolers.
Air-air cooler is installed in front of the oil and water radiators. Separation of atmospheric air through the cooler is carried out by the engine cooling system fan. The cooled air moves inside the brass cooler core tubes, similar to that used usually in the cooling system radiators.
With water-air cooling, water with a pump (special or existing in the engine cooling system) circulates through a cooler and radiator.
Although the heat exchange between the cooled air and the coolant, with other things being equal, occurs more intensively than between the cooled and coolant, overall air coolers are more efficient than the water-air, due to the larger temperature difference between the air and the cooling agent.
Always walked. There are many ways to increase it. You can increase the size of the cylinders, their number and engine speed. All these methods lead to an increase in the size and mass of the engine, an increase in the loads on its part.
There is more effective method Increase engine power. The idea is simple: the greater the oxygen molecules will be able to shook into the engine cylinder, the more fuel can be burned there and therefore getting more power without increasing the size and weight of the engine. This method is called.
In the usual engine, the combustible mixture is fed to the cylinders at a pressure of a smaller atmospheric. The presence of interference on the stream path (air filter, throttle, turns and roughness of the walls of intake channels) is affected. When pressed, the pressure at the entrance to the cylinder (in front of the intake valve) is significantly increased.
What types of boosts are applied on cars
On vehicles use two boosters: mechanical supervision and turbocharging.
Mechanical supervision Applied on cars from the thirties of the twentieth century. It is a compressor (volumetric or centrifugal) with a drive through the gears from the engine crankshaft. Well serves air, starting with minimal engine speed. But the engine power is used to operate the compressor, reducing its total efficiency.
Volume compressor According to the principle of action, it looks like an oil pump with outdoor gear gears: two three-time rotors are rotated in the housing, interconnected.
Mechanical supervision - compressor
Centrifugal supercharger - This is a wheel with blades located inside the case. The air comes through the axes of the wheel, the blades are discarded to the walls of the body and through the hole in it is fed to the engine cylinders. It works well on high revs, therefore, the drive is through the gearbox.

Centrifugal supercharger
Turbochards can often be found on modern cars. To increase the pressure on the engine inlet, the residual energy of exhaust gases is used. The unit called the turbocharger is a turbine and a compressor planted on one axis.

Turbocaddv - the principle of work
Exhaust gases are served on the turbine blades and spin it. Consequently, the compressor wheel begins to rotate, feeding the air into the engine cylinders. The efficiency of the engine is growing - the energy obtained in combustion of fuel is fully used. The use of turbocharging allows you to raise the engine power by 40 - 60%.
About minuses of the use of turbocharger
The speed of rotation of the turbocharger shaft reaches 200,000 rpm, which increases its sensitivity to the quality of lubricating oil.
In addition, the turbochargers are inherent in the phenomenon called "Turbians". The engine with delay responds to pressing the accelerator pedal. The reason is that the turbocharger is due to its inertia, it is necessary to increase the revolutions and increase air supply.
To combat this disadvantage, two turbo compressors are installed in parallel, large and small.

Double-stage turbocharging scheme:
1 is an adequer air cooler; 2 - bypass valve (bypass); 3 - high pressure turbocharger; 4 - Low Pressure Turbocharger; 5 - Exhaust valve of exhaust gases (Wastegate).
Little is unwinding faster and air supplied to them is enough before entering the work of a large turbine. A more effective way is to establish a guide apparatus on the turbine, whose blades, turning, change the angle of flow of exhaust gases, thereby regulate the speed of rotation of the turbine.
The task of increasing the power characteristics of the power unit was always relevant. There are quite a lot of methods for improving the power of the motor power, for example, it is possible to increase the overall sizes of cylinders, the number and number of motor revolutions. However, all the above methods lead to a significant increase in the overall dimensions and weight of the power unit, as well as an increase in the load on its structural elements.

There is much effective method Improve the power characteristics of the motor. The idea itself is pretty simple: the more air will be able to "shook" the air into the cylinder of the power unit, the more it is possible to burn fuel and as a result, to increase the power of the motor. This method is called - reducing the engine. Its main advantage is the fact that the overall dimensions and weight of the motor remains the same, but its power characteristics will be higher.
In the usual power unit, the combustible mixture is fed to the cylinders at a pressure that is significantly less atmospheric. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the presence of "obstacles" to pass the combustible mixture in the form of throttle, air filtering element, turns and rough surface of the channel walls. Performing a supervision of the engine under which fuel is fed significantly increases, which allows you to get high motor power.
Application of a mechanical scheme
Mechanical air blowers in order to increase the power of the power unit were used on vehicles in the 1930s. Then such devices were called compressors. Currently, they are mainly called turbocompressors, which, actually it will be discussed further. It is worth noting that the mechanical structures of such a plan are quite a lot, but despite this, the development of new modifications is relevant and now.

The above figure shows the air suppliers with the standard design of the mechanical type. Such turbochargers are distinguished by a simple design scheme and are not complicated.
However, there are not quite ordinary air blowers developed by various companies. One of them is a "comprex" wave air blower developed by ASEA-Brown-Boweri. The rotor of this turbocharger has axially placed cells. With rotational motions of the rotor, air falls into the chamber, after that it comes to the hole in the housing and through it the hot exhaust gases from the power unit fall into the cell. Interacting with cold air is formed by a pressure wave, which moves at high speed, due to which the air is supplanted into the hole of the exhaust pipeline to which the camera has time to come up for this period. Since the rotor all the time spinning the exhaust gases in this hole does not fall, but go through the rotor movement to the next. Such superchargers were used by many manufacturers of automotive vehicles, for example, Mazda applies them on some models of cars since 1987.

Another interesting development is a spiral supercharger - G40. For the first time it was used by the German Volkswagen car manufacturer in 1985.
In 1988, a new modification of the G-60 spiral supercharger was appeared, which possessed a higher power and was used on Corrado and Passat cars.

Structurally, such superchargers consist of two spirals, the first of which is stationary and acts as part of the case. The second spiral plays the role of the displacer and placed between two turns of the first. This helix is \u200b\u200battached to the shaft. The shaft is given due to the belt transmission of the power unit with the attitude of one to two.
The principle of operation of such a design is quite simple and is as follows: During the rotation of the shaft, the spiral located inside the hull carries out the vibrational movements and the sickle cavities are formed between them, moving towards the center and thereby move air from the periphery into the motor under low pressure. In this case, the amount of compressed air supplied directly depends on the rotational speed of the motor shaft.
Such a supercharger scheme has two important advantages: sufficiently high efficiency and wear resistance (due to the absence of rubbing structural elements).

Application of turbocompressors
Currently, non-mechanical air blowers, but turbochargers, are used to improve the power characteristics of the power unit. Such devices are much easier in production, which pays for a number of flaws that they are inherent.
Modern turbochargers from the above schemes are primarily different in their structural features and the principle of operation of the drive. In this case, a rotor with blades is applied, that is, a turbine, rotating due to the effects of the stream of exhaust gas of the power unit. The turbine rotates the compressor mounted on the same shaft, presented in the form of a wheel equipped with blades.
This principle of the actuator, determines the main disadvantages of the gas compressor. It should be noted that in this case the rotational speed of the motor is rather low, which means that the number of exhaust gases is also small, which negatively affects the performance of the turbocharger operation.

In addition to the engine with the installed turbocharger, it most often has the so-called, that is, the slow motion response to an increase in the amount of hot hot. At the same time, the driver should be dramatically pressing the gas pedal until it stops, and the power unit reacts only after a certain time. An explanation for such a phenomenon is quite simple - a certain amount of time on the promotion of the turbine is required, which is responsible for rotating the compressor.
Maximum leveled above the induced disadvantages of turbocharger developers tried to various methods. And first of all, the mass of structural rotating elements of the compressor and the turbine was reduced. The compressor rotor applied currently has become so small-sized, which is fitted on the palm. In addition, the rotor is lightweight significantly increases the efficiency of the compressor, even with low revolutions of the power unit.
However, a decrease in the size of structural parts, not the only method of improving the efficiency of the gas compressor. Today, new materials are applied for their manufacture, which help reduce the mass of the elements of the rotor, which makes it possible to improve its work. For example, quite often for these purposes, matching silicon carbide is used, which is resistant to high temperatures and is lightweight.
That is, with confidence it can be said that modern turbochargers are deprived of many shortcomings of previous models of such devices. Due to which such installations are successfully used on automotive vehicles from different manufacturers. The choice of turbo air blowers should be carried out on the basis of the original power of the machine, as well as the financial capabilities of the car owner. The installation of such aggregates should strictly be carried out on a hundred or auto repair shop.

What is better to choose a mechanical air blower or turbocharger
The increase in the speed indicators of its car is a very topical question for many vehicle owners. Today, this task can be solved in many ways, but the installation of a mechanical supercharger of air or a turbo compressor is in the greatest demand. So which of these two options is the best? We will try to answer this question in this article.
For this purpose, it is initially necessary to deal with the principle of operation of a mechanical and gas compressor.
Principle and features of the work of the mechanical scheme

There are several types of such devices:
- Volumetric air blowers. Such installations are fed into the power unit with the same portions regardless of independence from the speed mode, which is an advantage when driving on low motor turnover;
- Mechanical schemes of external compression air. Such compressors are perfectly suitable where there is a need for a large number of air supplied at low motor revolutions. The disadvantage of this approach is the ability to create an inverse air outflow, since the compressor itself does not provide the desired pressure. In addition, such installations have low efficiency;
- Installation of internal compression. Their use is relevant at high speed of the power unit, besides, the effect of reverse airflow is much smaller. The disadvantages of such schemes are: a sufficiently high cost (due to high demands on the material of execution) and the possibility of jamming, especially in the case of overheating;
- Dynamic air blowers. Such installations operate only to achieve a certain number of revolutions, but their efficiency is much higher in comparison with the above-tailed installations.
Since the mechanical air blowers function at the expense of the crankshaft of the motor by means of an additional drive, the compressor turns directly depend on the revolutions of the power unit.
Features of the work of the turbocharger
Such air blowers are functioning due to the energy obtained from exhaust emissions. In essence, the turbocharger is a combination of a centrifugal compressor and the turbine itself (wheels equipped with blades).
The principle of its action is as follows: the spent gases at high speed rotate the turbine, which is mounted on the shaft. At the other end of the shaft mounted centrifugal pump, the main task of which is the injection of a large amount of air to the cylinders.
In modern compressors in order to cool the air, which is served in the turbine, an intercooler is used.
Disadvantages and advantages of a mechanical and gas compressor

The turbocharger is perfect for use in order to enrich fuel oxygen. However, such schemes possess their shortcomings:
- the turbine is presented as a stationary device and, accordingly, there is a need to reference to the power unit of the vehicle;
- on low motor turnover, such a compressor is not able to provide a greater speed, but only on high its work is effective;
- when moving from low on high revs, the so-called "turboyama" is often formed, with the higher the power of the turbocharger, the more significant the effect will be.
It is worth noting that at present you can buy a turbocharger, which will be perfectly cope with its main task both on low and high speed of the power unit. However, their price is high enough, both on the equipment itself and on service. But despite this, many owners prefer the turbocompressors.
Mechanical air blowers in turn are easier to install and maintain. There are such devices both on low and high speed. In addition, they require too large temporary and financial costs when restoring and repaired. This is explained by the fact that, unlike the turbocharger, the mechanical supercharger is an independent device.
The turbine besides its high cost and complexity in the installation, is also quite demanding for quality and technical characteristics used fuel mixture.
Mechanical air blowers have a significant problem - a fairly large fuel consumption, with a relatively low efficiency. But at the same time they are easier in the structural plan and in service.
At the same time, the choice of one or another installation depends only on the driver and its wishes, as well as the original characteristics of the machine.
Video
Superior allows you to increase the power of the engine due to an increase in air density at the inlet to the cylinders, which makes it possible to effectively burn more fuel. In automotive engineering engines, gas turbine supervision systems are used using turbocompressors (TCR) or mechanical supervision using drive superchargers (PN). In TKR, the air is compressed by the compressor caused by the turbine, and the turbine is rotated by the exhaust gas stream (see Fig. 7.22). Mon, squeezing air, is driven from the crankshaft of the engine.
The turbocharger of the motor vehicle engine (Fig. 7.26) is an aggregate consisting of a housing and a rotor (turbine and compressor, combined in the sliding bearings). TKR may contain elements of controlling its work. Typically, the outer diameter of the wheels of centrifugal compressors and radial-axial TCR turbines 35 ... 90 mm, which provides enough high efficiency. The wheels of compressors are made of aluminum alloy, and the wheels of turbines are from high-alloyed cast iron, as they must withstand high temperatures. Ogs enroll in the spiral turbine case 6. It contains one or two sighting guide channels, which increase the speed of og. Then they are fed to the blades of the turbine wheel 7, causing its rotation. She is through the shaft 11 leads to rotation of the compressor wheel 2. Air through the intake nozzle of the compressor 1 Enters the entrance to the compressor wheel 2 where, under the action of centrifugal forces, its speed increases dramatically, and comes out of the wheel into the diffuser, where its speed is reduced, and the density is growing. Then air 4 Enters the spiral collection of the compressor body, from where it goes to the engine.
Fig. 7.26.
1 - compressor housing; 2 - the wheel of the compressor; 3 - air inlet; 4 - air yield compressed in the compressor; 5 - oil supply; 6 - turbine case; 7- turbine wheel; 8- OG after turbine; 9- Bearing housing; 10- EGR output from the engine; 11 - Rotor shaft; 12 - Oil relief
The drive supercharger type "root" in the form of two-linked rotors in the form of eights rotating in different directions is shown in Fig. 7.27. Rotors alternately approach the top edges of the case and capture the volume of air V, having atmospheric pressure p 0. This amount of air, practically no changing pressure, is pushed out in the output chamber of PN, where high pressure charge is r to. When reporting volume V. With the output chamber, the charge comes into it under pressure r to. The seal between the rotors, as well as the rotors and walls of the housing is achieved by creating a minimum gap. At high pressures at high frequencies, leakage are becoming significant, which reduces the degree of increase in pressure and the PDD of the supercharger. Therefore, the maximum degree of increase in pressure in such a pressure does not exceed 1.6 ... 1.7.
Comparison of the turbocharger and drive supercharger. TKR is significantly wider used to superhaood autotractor equipment than PN, as it provides more high pressure Superior and better economy, less noise, smaller mass and dimensions.

Fig. 7.27.
The worst economy of Mon Unlike TCR, which caused the energy of exhaust gases is due to the fact that the PN operates from the crankshaft. Being harshly connected with the crankshaft, the PN provides a higher pioneering pressure on small rotational frequencies and, unlike TCR, it does not have a delay of the rotor's promotion with a sharp increase in engine load ("turboyama"). It provides the best dynamics of cars with Mon, especially in the initial section of overclocking. At low loads, the power to the PN drive does not decrease, which makes the use of PN especially unfavorable. PN, disconnected on low loads and high rotational frequencies, is usually used on gasoline engines of passenger cars, for which the dynamics of acceleration is important, and the deterioration of efficiency does not matter much.
Advance air coolers (ONV). For automotive equipment engines, when compressing air in the compressor, the temperature increase is usually 40 ... 180 ° C. In case of intermediate cooling of air in ONV, the massive filling of cylinders is increased by increasing the density of air, which ensures the increase in power and improving engine efficiency. The use of ONV also reduces the temperature of the engine parts and the temperature of the gas in front of the turbine.
Air-air and liquid-air ONVs are used on motor engineering engineering equipment. In the first case, the influxing air is cooled due to blowing the ONV stream of oncoming air when the car and the flow of the fan is driving, and in the second - the liquid from the engine cooling system is mainly used.
Liquid-air ONV more compact than air-air. This is due to the fact that heat exchange from hot air to the coolant occurs intensively than to the cooling air. This heat exchanger provides a stable influx air temperature regardless of temperature. ambient. It is mainly established on high passability cars, tractors and special cars (career dump trucks, aerodrome technique, etc.).
Air-air It provides deeper cooling due to the fact that the temperature of the atmospheric air is below the cooling fluid temperature. Therefore, it is used in low powertrains by rendux and in the presence of an oncoming air flow, which refers to engines of passenger cars and main trucks.
Advance control system. With increasing engine speed increasing the pressure of the TCR increases in 1.3 ... 1.5 times. This is due to the difference hydraulic characteristics Piston (engine) and shovel (TCR) machines. Ideally, you can only configure TCR only on one mode of engine operation (usually the point of the external speed characteristic, located between the maximum torque and rated power modes), in which it will provide a predetermined pressure and have the highest efficiency. Then, with a reduction in the speed of rotation, the pressure will fall in relation to the optimal, and with increasing speed increase - increase. To solve these problems on engines, various ways of supercharged are applied.
Crossing out Bypassing the turbine, is the easiest way to match the operation of the engine and TCR (Fig. 7.28). TCR is configured to ensure high pushing pressure on the small and average frequencies of the diesel engine, and at a high speed of rotation, the further growth of pressure is limited by opening the bypass valve 5. It is installed at the entrance to the turbine 8. When opening it, part of the gas is sent, bypassing the turbine, to the graduation system. The engine control system adjusts the valve opening value, providing the required pressure pressure on each operation mode. However, when open byproof valve The engine efficiency is reduced, as part of the energy spent on the compression of air in the TCR compressor is lost.
Changing the flowring section by turning blades at the input of the OG in the turbine wheel. At low speed rotary blades 3 At the entrance to the turbine 1 at low speed (Fig. 7.29, but) Rotated to the maximum angle, providing minimal passage in the input of the OG in the turbine wheel 1. Then the gas speed at the entrance to the wheel will increase, which increases the frequency of rotation of the TCR rotor

Fig. 7.28.
- 1 - electromagnetic valve; 2 - Vacuum pump; 3 - vacuum chamber; 4 - TKR; 5 - the reversal valve from; 6 - entrance from the engine;
- 7 - the yield of compressed air; 8 - turbine; 9 - Compressor
and, accordingly, pressure pressure. With high engine speed (Fig. 7.29, b) shoulder blades 3 Rotated to a minimum angle, providing the maximum passage section at the input of the OG in the turbine wheel 1. Then the gas speed at the entrance to the turbine wheel decreases, which prevents improving pressure. At the same time, the backpressure on the release of cylinders is reduced, which leads to a decrease in the poverty operation and, as a result, to increase the power and efficiency of the diesel engine. In this case, the method of regulation on a small-sized TCR is significantly reduced by the efficiency of the turbine due to an increase in the resistance created by the blades on the movement of the gas flow, and the losses associated with leaks through the gaps between the blades and the walls of the turbine housing. There are also difficulties in ensuring the efficiency of rotary blades in the conditions of soot deposition. Therefore, TCR with this method of regulation is applied on passenger car engines with a working volume of more than two liters.
Changing the passage section for the supply of the GC wheel of the turbine with a sliding sleeve in the nozzle guide of the turbine. In TKR (Fig. 7.30), a moving horizontally sliding sleeve can close one of two channels located in the turbine housing and apply from to its wheel. This changes the passage and, accordingly, the speed of gas entry on the turbine blades. If open

Fig. 7.29. Regulation of TCR turbine by turning the blades: but - closed position of the blades, the minimum flow cross section and the maximum gas entry rate on the turbine wheel; b. - open position of the blades, the maximum passage section and the minimum gas entry rate on the turbine wheel; 1 - the turbine wheel;
2 - Rotary ring; 3 - swivel blade; 4 - drive lever; 5 - pneumatic regulator; 6 - the flow of exhaust gases is only one channel 2 (Fig. 7.30, but), The cross section on the movement of the gas flow is minimal, the gas velocity is maximum, the pressure pressure is rising. If both channels are open 2 and 3 (Fig. 7.30, b) then the passage section is the maximum, and the gas speed is minimal. At the same time, the pressure of the superior is reduced, and the backpressure on the release from cylinders is reduced. This method of regulation allows the use of TCR with small diameters of wheels, which can be used on small working volume engines.

Fig. 7.30. Regulation of the TCR turbine sliding sleeve: but - only one channel is open, leaving gases, in the turbine housing; b. - both channels, supplying gases, in the turbine housing are open; 1 - the turbine wheel; 2 - Channel in the turbine case; 3 - second channel in the turbine housing; 4 - sliding sleeve; 5 - bypass channel; 6 - drive sliding sleeve



