How to remove spasticity after a stroke. What is spasticity and how to deal with muscle spasticity. Seizures after a stroke: treatment
It was extremely difficult to relieve spasticity after a stroke. The point is in the emerging contradiction. We stubbornly restored strength and endurance. They did this with the help of special exercises with a high load and a bunch of repetitions.
For the treatment of spasticity, this is a hindrance and harm. When removing spasticity, you need a relaxing massage and light movements in exercises. In order to continue recovery from a stroke, it is necessary to conduct mutually exclusive activities. But we came up with a simple solution. Make two groups of classes.
First: to restore strength and endurance. The second to treat spasticity, restore balance and coordination. The decision turned out to be very correct. True, we didn't get it right away and for some time did exercises to relieve spasticity along with exercises for strength and endurance. In time, they noticed that spasticity increases from active exercises.
What is spasticity
Spasticity manifests itself in stiffness. Impossible to make fast or abrupt movement. Constantly tense muscles block freedom. Feeling like you are a very rusted Terminator))).
Stress leads to early fatigue.
Stroke recovery can actually be blocked by spasticity. It is difficult to recover skills when the limbs seem to be tied with elastic bands and are always in a tense, unnatural position. To relieve spasticity after a stroke, we use elementary exercises. The main thing is to do them easily, without stress.
Muscle spasticity is an involuntary contraction of muscles, cramps or spasms due to impaired conduction of nerve impulses after trauma to the spinal cord and brain.
Most often, this condition manifests itself at night, but it can also significantly complicate life during the day.
The mechanism of formation of spasticity
The main reason for the formation of seizures, experts call the imbalance of the inhibitory effect of the motor elements of the cerebral cortex on the cells in the structure of the spinal cord.
The natural result is the disinhibition of the tonic reflex - muscle spasticity is formed in the injured limbs of a person.
In a normal state, a person does not have to think about the sequence of phenomena produced in the muscles: which of them first need to be reduced, then relaxed - our brain has brought such an activity to automatism.
After a stroke or injury, the death of cellular elements that are responsible for special inhibitory impulses in the motor neurons of the brain and spinal cord occurs. Reflex arc: limb - spinal cord - the brain ceases to be a single system - coordination is impaired.
Spasms do not form immediately - for weeks, and even months. Leads to significant secondary changes in muscles and joints - enhances the negative effect of paresis on the motor system.
The severity of limb spasticity
The first signs of the onset of muscle spasticity formation are observed in the first day after injury, and subsequently tend to increase.
The degree of severity can change under the unfavorable influence of negative factors, for example:
- when the emotional mood changes - the person has a tendency to depressive states;
- when weather conditions change - fluctuations in temperature or illumination parameters;
- in case of excessive physical overload caused by the early physical activity of the victim, contrary to the recommendations of the doctor.
With an increase in the intensity of the load on the muscle fibers in the limbs, their motor activity becomes difficult, symptoms of pain in them are observed, of varying severity.
According to the severity of spasticity, the following forms are distinguished:
Spasticity of the legs in a mild form is manifested by rapid fatigue of the muscles of the legs, a feeling of “muscle clogging” from physical activity, while walking becomes easier on the heel, then it becomes difficult to pull the toes towards you and straighten it at the knee.
In a severe form of spasm: one or two legs are fixed in bent at the knee or hip joints, and the foot is turned inward or outward. When walking without special shoes or, deformities or contractures may occur. 
Manifestation of hand spasticity in a mild form: difficulty in extension
fingers and straightening of the arm in the elbow joint, a sign of a severe form is bent at the elbow and shoulder joints, while the hand is clenched into a fist.
If spasticity is present for a long time without treatment, contracture develops, that is, the joint is not fixed in a physiological state for the body.
In the future, the spasm will only have a negative effect on the conduct of recovery measures. In addition to limbs, it will worsen recovery in the spine: increased muscle tone causes pain in the back - symptoms of vertebral sciatica.
Experts note: than before adequate treatment with modern drugs was started, and also, the less the severity of spasticity, the better the prognosis of rehabilitation measures will be.
Even if the symptoms are significantly pronounced, and the treatment of seizures for certain reasons began at a later time interval - a decrease in spasticity significantly improves general well-being.
How to treat spasticity using different methods
The most important requirement for treatment is that it is as painless as possible, since the pain is exacerbated by spasticity.
An important point is the control over the activity of the pelvic organs - the prevention of inflammatory manifestations in them, as well as timely measures to prevent the occurrence of contractures, etc.
 A complex of modern treatment for getting rid of spasticity:
A complex of modern treatment for getting rid of spasticity:
- drug tactics (midocalm, baclofen);
- methods;
- orthotics;
- surgical correction.
The complex of treatment is selected only individually, in direct proportion to the localization of the focus and the severity of the spasticity. It is necessary to take into account the technical capabilities of the medical institution.
Spasticity after a stroke or brain injury necessarily requires medication. Treatment should be carried out in stages - with a gradual increase in the therapeutic dose of medications, possibly by replacing the drug.
 Today, two subgroups are in demand:
Today, two subgroups are in demand:
- Drugs with a central mechanism of action on a negative focus - inhibition of the reflex.
- Peripheral drugs - significantly reduce the stretching reflex at the level of the spinal cord elements: muscle relaxants.
As with other subgroups of even the most modern drugs, the above ones have their own contraindications, so only a highly qualified neurologist should deal with their appointment.
Orthotics and plaster
Treatment of spasticity by prolonged laying of human limbs, in such a position when the muscles are optimally stretched, and tonic reflex activity is reduced, is called orthotics by specialists. It helps to reduce hypertonicity in the extremities - pathological symptoms can be reduced many times over.
In case of severe spasticity, it is even recommended to apply a special plaster splint or splint to prevent the development of contracture. It is the splint that fixes the limb in the most acceptable position - in which the muscle fibers are located in a stretched position.
Orthotics treatment is carried out from one to two hours, in direct proportion to the person's sensations - when the pain sensations increase, the procedure is completed.
Physiotherapy for muscle stiffness
- local use of cold - helps to reduce excessive reflexes and maximize the range of motion, improve muscle activity;
- local use of heat - excellently contributes to a temporary decrease in tone. carried out using ozokerite or paraffin applications, the course is at least twenty procedures;
- nerve endings - an excellent technique that allows you to achieve the maximum response in the affected areas, the duration of the treatment course is prescribed by a specialist.
Exercise therapy development
 Treatment with exercises aimed at optimal relaxation of the fibers in the muscles is a long-proven, well-proven rehabilitation method for treating spasticity.
Treatment with exercises aimed at optimal relaxation of the fibers in the muscles is a long-proven, well-proven rehabilitation method for treating spasticity.
Dosed therapeutic stretching allows you to lower their tone for a couple of hours, maximize the range of motion in the affected limbs.
A kinesiotherapist knows that a decrease in tone will be observed only for a certain time and therefore it must be effectively used for other complex exercises that were difficult due to spasticity.
Surgical intervention is determined by a specialist according to strictly individual indications, when conservative methods have already exhausted themselves, and there is no pronounced positive dynamics.
Removing spasticity is an important task. It greatly interferes with everyday life, takes away strength and hinders movement. This makes it difficult to recover lost skills and stamina. To fully carry out recovery from a stroke, it is imperative to cure spasticity. We are doing this in parallel with other tasks.
With an integrated approach and the beginning of therapeutic measures at the earliest possible stage, drug treatment - the normalization of muscle tone contributes to the maximum acceleration of the patient's recovery.
In the treatment, methods such as myostimulation, botox, of course, therapeutic exercises, medications (mydocalm, baclofen) and sparing surgery have shown themselves well.
What is, the causes of spasticity, prevention and treatment updated: November 21, 2017 by the author: author
According to WHO statistics, today strokes take the 3rd place (after the pathology of the heart and blood vessels and oncological diseases) among the causes of death (among the adult population of the planet).
Patients who have had a stroke have a high likelihood of long-term disability, and during the first year there is a high risk of recurrence of cerebral circulatory disorders (more than 8% of cases).
Acute cerebrovascular diseases with foci in the brain and spinal cord are often accompanied by the development of neurological and mental defects: paresis, paralysis, impaired coordination and the occurrence of convulsive seizures.
Most often, seizures occur in patients with a stroke in the frontal lobe of the brain and with subarachnoid hemorrhagic strokes (accumulation of blood in the cavity between the soft and arachnoid membranes of the brain).
A seizure may develop:
- during acute circulatory disorders in the brain, while convulsions are one of the symptoms of a stroke;
- during an exacerbation of the disease (a few months after the stroke).
The appearance of repeated convulsions after a stroke does not mean incorrect treatment - it may be a symptom of a repeated stroke, indicate a large area of necrosis with the involvement of motor zone neurons in the process, or the formation of a cyst necrosis zone (fluid-filled cavity) in place that irritates the motor zone of the brain .
Frequent, prolonged or poorly controlled seizures in the acute period of the disease indicate a high risk of death and are considered a sign of significant primary damage to brain tissue or progression of the pathology, especially in hemorrhagic strokes.
Epileptic seizures in a patient after a stroke are considered:
- as the probability of developing a second stroke;
- the presence of cysts or other neoplasms formed in the area of necrosis;
- the occurrence of infectious-inflammatory or neurodegenerative processes in patients after a stroke.
In any case, if seizures occur, a complete examination of the patient in a hospital setting and determination of the cause of seizures is necessary.
Table of contents [Show]
Causes of seizures after a stroke
The main cause of seizures after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke is the death of brain neurons. In the acute period of the disease and the formation of a necrosis zone, the body tries to limit it, restore normal blood circulation in the tissues and keep the maximum possible number of neurons and their connections with other nerve cells capable of functioning, so the body is looking for the possibility of redistributing the functions of dead neurons between other brain cells. As a result of these self-protection mechanisms, a cavity filled with liquid is formed at the site of the necrosis focus. In most cases, this formation does not interfere with a person, but in some cases, periodic irritation of neurons occurs, which manifests itself in the form of local convulsions or generalized epileptic seizures.
The main cause of seizures after a stroke, experts consider the location of necrosis foci and the formation of post-stroke foci in the form of cysts, adhesions or other pathological formations in the lobe of the brain responsible for movement (re-irritation of motor neurons in the seizure area).
Predisposing factors for seizures after a stroke are:
- nervous strain and stress;
- physical or psycho-emotional fatigue;
- adverse reactions after taking certain medications and others.
Signs of seizures after a stroke
Seizures are paroxysmal involuntary contraction of a muscle or group of muscles, their twitching, lasting from a few seconds to several tens of minutes.
Convulsions after a stroke most often take the form of short-term attacks of muscle contraction throughout the body (generalized convulsions), or their local occurrence - cramps in the legs, arms, neck muscles, face. After the cessation of a generalized convulsive seizure, quite often there is a blackout or sleep due to the shock state of the brain.
The clinical picture of convulsions after a stroke is different: from mild neurological tremor, single contractions of certain muscle groups (tics) to severe clonic-tonic generalized convulsive seizures.
Most often, convulsions in patients after strokes are manifested:
- in the form of clonic contractions of the muscles of the face or short-term tonic convulsions of certain muscles of the face and neck (“mask-like face”, tilting or turning the head to one side, distortion of the face on one side);
- tonic prolonged contractions of the muscles of the limbs in the form of a sharp numbness and / or complete loss of motor control (syndrome of "wooden leg or arm" or legs and arms on one side of the body);
- generalized epileptic seizures in the form of various episodes of convulsions - tonic or clonic convulsions or their combination - clonic-tonic seizure.
Leg cramps after stroke
In the legs after a stroke, the following are most often observed:
- local convulsive contraction of the muscular apparatus of the foot or calf muscles or short-term but painful tonic cramps in the calf muscles and / or toes or foot (crampia).
- pronounced and sufficiently long tonic leg cramps in the form of numbness or persistent movement disorders (“wooden leg”)
These pathological signs are always associated with a serious lesion of the brain or its motor centers of the cerebral cortex.
It is important to know that seizures almost always occur on the side opposite to the lesion in the brain.
Seizures after a stroke: treatment
If any symptoms of convulsive readiness appear in patients after a stroke, an EEG of the brain, CT or MRI (if necessary) should be performed to determine the source of irritation. To eliminate convulsive readiness, a course of anticonvulsants (finlepsin or carbamazepine) is prescribed.
Traditional medicine offers several methods of treatment:
- the use of alcohol infusion of linden (flowers) - 1 teaspoon before meals;
- collection of herbs including spring adonis, thyme and goose cinquefoil or decoctions of these herbs separately;
- garlic, chopped and infused with unrefined vegetable oil - 1 teaspoon orally 3 times a day.
It is important to remember that when using any non-traditional methods of treatment, you cannot stop the course of anticonvulsants on your own.
Emergency care for seizures after a stroke
If convulsions occur, the patient should not be left alone: during this period, the patient may at any time need an ambulance:
1) you need to calm the patient, open the windows to provide oxygen access to the brain cells, remove tight clothing;
2) in the event of seizures:
- place a pillow or soft cushion under the patient's head;
- to prevent biting of the tongue between the teeth, it is necessary to carefully insert a dense tissue;
- if the patient ate something before, remove food debris or dentures from the oral cavity;
- remove objects that the patient can hit his head on;
- when hoarse breathing occurs, turn the patient on his side and make sure that there are no objects restricting breathing (belt, tie),
- in case of pain in the muscles - rub the limb, neck, face or warm up the spasmodic muscles by mixing olive oil with mustard (1: 1) and apply the slurry to the site of the cramp;
- you can give the patient aspirin to improve blood circulation in the vessels.
Be sure to call a doctor or an ambulance team, even with a quick relief of a convulsive attack.
Similar articles:
seizure
Convulsive state
Hormetonia
Heart spasm
Cramp in the water
A stroke is an extremely severe lesion of the brain, which entails the appearance of focal or general cerebral neurological symptoms. Quite often, convulsions can occur during a stroke, significantly worsening the patient's condition. But in some cases, they can occur after a certain period after stroke (from one week to several months), when there is confidence that the threat to the patient's life has passed and a recovery period has begun. Why convulsions appear after an exacerbation can only be determined during diagnostic measures.
The occurrence of an epileptic seizure can be expected with the localization of the focus of stroke in the frontal lobe of the brain, mainly with subarachnoid hemorrhage.
What are the causes of post-stroke seizures?
Seizures after a stroke develop, both with ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. The reasons for such consequences are the death of structural and functional units of the nervous tissue of the brain. Due to circulatory disorders, necrotic foci appear in one of the departments, during this period the protective properties of the body are triggered, preventing the subsequent progression of pathological processes and aimed at restoring normal blood circulation.
A necrotic area of the brain after a stroke leads to irritation of neurons, which subsequently cause convulsions.
These protective processes in the body lead to the formation of fluid-filled cavities in necrotic areas. This condition does not bring pain and discomfort, but provokes irritation of neurons, resulting in seizures.
There are other reasons too:
- a cyst in the frontal lobe of the brain: an attack is a harbinger of a recurrent stroke;
- infectious processes: infection can occur during surgery or in the postoperative period, resulting in a convulsive state;
- other reasons: stressful and depressive situations, physical overwork, the use of medications.
Seizures after a stroke are an extremely dangerous condition that can be a harbinger of the recurrence of a stroke or cerebral infarction.
Clinical picture
Depending on the cause, the severity of symptoms differs in each patient: in some patients, this is a slight tremor of the upper and lower extremities, in others, severe epileptic seizures.
Timely recognition of signs of the onset of a convulsive state can save a person's life. Symptomatic complex:
- a person stops responding to people around him, does not answer questions;
- dizziness may occur;
- some patients fall into convulsive syncope;
- there is tension in the muscles of the upper and lower extremities;
- then the increased muscle tone turns into convulsive twitches;
- with severe convulsions throughout the body, a person bites his tongue;
- spontaneous urination is possible.
As a rule, an epileptic seizure lasts no more than a few minutes. After which the patient loses consciousness, this state is similar to a long sleep.

Types of seizures
An attack after stroke develops according to one of the types:
- clonic: cramps appear in the legs and arms, in one of the halves of the body, or involve a certain muscle group; a convulsive attack is replaced by short periods of relaxation;
- tonic: intense muscle tension, characterized by a long duration; leg cramps are more common, but spasms in muscles in other parts of the body may also occur.
First aid for convulsions after a stroke
In a convulsive state in a patient who has had a stroke, it is necessary:
- call an ambulance;
- if a person has fainting with convulsions, it is necessary to provide him with a supine position;
- provide fresh air access to the room, if possible, free the patient from tight clothing;
- the head should be in an elevated position, while it is necessary to make sure that there are no sharp and heavy objects that the patient may be injured in case of loss of consciousness with convulsions;
- check for the presence of food residues, saliva or vomit in the oral cavity, and then remove them; in the presence of removable dentures, they are removed;
- if the attack is accompanied by breathing with wheezing, it is necessary to turn the patient on his side and control the respiratory function;
- in convulsions with prolonged seizures, it is necessary to keep the person at all times to prevent injury;
- if the condition is accompanied by severe muscle spasms, while maintaining consciousness, you can rub the muscles or apply a compress of mustard and olive oil.
The main treatment is prescribed only by a neuropathologist after establishing the causes.
Seizure treatment regimen
To eliminate the underlying cause, diagnostic measures are carried out, consisting of CT, MRI, examination of cerebral vessels, general blood and urine tests. After receiving the results, the doctor prescribes the most effective treatment, individually in each case. In true epilepsy, therapy consists of a more extensive set of medications.
The main drug in the treatment of seizures is Finlepsin (Carbamazepine).
Also, the following drug treatment is used to eliminate seizures:
- antithrombotic drugs: for cramps in the legs and arms, drugs are used that reduce blood clotting, which improves blood flow through the vessels, one of the easiest drugs is aspirin;
- drugs to improve blood circulation and oxygen saturation of the affected areas of the brain;
- neurometabolic stimulants (nootropics) - improve brain activity.
Treatment is carried out according to the scheme prescribed by the doctor, in each case the dosage and duration of administration are different. It is possible to foresee an attack and determine the effectiveness of the therapy using an encephalogram.
The main drug in the treatment of seizures is Finlepsin.
As a rule, a few days after taking the medicine, leg and arm cramps disappear, and the sensitivity in the muscles returns. Also, fainting and dizziness disappear, clarity of mind returns.
With adequate and timely treatment, the chances of getting rid of seizures and preventing the development of a second stroke increase.
What complications can occur with seizures after a stroke?
A convulsive state is an extremely dangerous consequence of a stroke, and without therapy it can lead to serious complications. Deterioration of the condition is possible with convulsions with loss of consciousness in the period of stroke.
With a convulsive state, the following consequences occur:
- re-development of a stroke - poses a threat to the patient's life;
- coma - there are convulsions after a stroke provoke a long or short-term loss of consciousness; with more intense and pronounced attacks, a person may fall into a coma;
- disability - persistent convulsions that are difficult to treat indicate serious disorders in the brain, which leads to disability without the possibility of recovery;
- death of the patient - if convulsions occur frequently, and therapy does not give positive results, one can assume the presence of internal bleeding, which is not amenable to therapy and, as a result, death occurs.
To eliminate the symptoms of this condition and prevent possible serious complications that threaten life, it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner. Only emergency medical workers can stop an attack, so you should not make a decision on taking any medications on your own.
Leg cramps: causes, treatment, symptoms.
To know how to deal with something, we must always know the reasons for its occurrence. Is no exception and the occurrence leg cramps causes which we will consider in this article. And also we will give some of the best and most relevant tips for the treatment of folk remedies and traditional medicine. As for cramps in the legs, all kinds of external and internal stimuli can serve as their causes, and their essence can be extremely different. In cases of the occurrence of these conditions, not only in the legs, but also in other parts of the body, the causes must be looked at in each case individually.
At its core, these are involuntary and independent of the patient's contractions, the so-called striated muscles, which are also commonly called skeletal. Such states, as many people know, have the nature of attacks, which at any time can differ greatly from each other. Namely, they can be episodic or regular.
Seizures can also be clonic (short-term muscle contractions, as well as their relaxation) and tonic (here we are talking about a duration of up to three or even more minutes). It is also customary to distinguish the following types of seizures, namely, when almost all the muscles of the body contract, they are generalized, when only some muscle group contracts, they are localized.
Tonic leg cramps have their own causes, first of all, a violation of the human blood composition, both biochemical and electrolyte. This happens when the body loses a large amount of salts, when the concentration of directly calcium, magnesium or potassium decreases. It may also be due to an insufficient amount of vitamin D in the body. Other causes of leg cramps include sunstroke or heat stroke, and as a result, an increased temperature of the human body. These conditions are often manifested in those people who simply overstrained their muscles (after prolonged or sharp physical exertion or exercise, as well as convulsions of musicians or typists in those parts of the body that are most involved in their work).
It is worth noting such causes of seizures, not only, by the way, of the legs, as the occurrence of a kind of focus of irritation in the motor part of the brain. As a rule, this is noticed when a person begins to have a stroke, or during the rehabilitation period after it. Also here you can add infectious infections of the nervous system.
We list some more reasons: alcohol intoxication, lack of sugar in the blood, or vice versa, an overdose of hypoglycemic substances in people who have diabetes, innervation of the spine in patients with osteochondrosis. It is worth noting that convulsions are not uncommon in absolutely healthy people. And in these cases they can be explained by the reaction of the body to some very strong stimuli.
Everyone will probably be interested in what to do if you suddenly have a cramp, what are the initial and necessary measures that you can immediately take. Firstly, you need to stand on the cold floor and try to walk around or just walk a little, secondly, rub these muscles carefully and with strong energetic movements of the hands, thirdly, lie down and stretch your leg so that the toe can be possible at the same time pull the other way around, fourthly, you need to take a couple of teaspoons of mustard, one teaspoon of olive oil. Lubricate all this gruel exactly the place that is located above the muscles that are spasmodic. It is also best to take some kind of painkiller, aspirin, for example, because in addition to the analgesic effect, it will improve blood microcirculation in the vessels. Keep in mind that you need to take it in cases where you have no contraindications to this, namely the risk of bleeding.
Now, speaking about leg cramps and the causes of their occurrence, let's go directly to medicinal plants and folk recipes.
1. You can use a plant such as spring adonis. Take a couple of teaspoons of pre-chopped herbs for one glass of boiling water. You need to use such a remedy: for adults - a tablespoon three times a day; children - 2 years of age - 5 - 6 drops, up to 6 years - 15 drops, 12 years - 2 teaspoons 5 times throughout the day.
2. 2 teaspoons of birch buds must be taken in a glass of boiling water and brew this infusion as regular tea. Just drink it in three doses.
3. You can just eat cloves. but not more than 620 mg with added sugar.
4. If convulsions have overcome your legs or arms, then you can wipe the corresponding places with mustard oil.
5. You can also use ordinary poppy petals to fight convulsions, which we grind into a very fine powder and prepare a decoction in milk and honey. They can also be infused with vodka.
6. With a variety of convulsions, a decoction of goose cinquefoil can be extremely useful. But it should be borne in mind that it is used in most cases as a special prophylactic, since its effect is long.
7. It will also be very useful to consume 2 teaspoons of ordinary honey during meals, and this course has a strictly limited scope in its duration, namely, this must be done for 7 days.
8. Mix 4 parts of olive oil with one part of wormwood seeds, previously crushed in a mortar. Then we put the whole thing to infuse for 8 hours. After that, put a couple of drops on sugar and consume.
9. If you want to use wormwood to fight leg cramps and their causes, then you will need to take 30 grams of lobes of this medicinal plant per half liter of beer, you can also use vodka. Boil it all for a short time - about 5 minutes and use 3 times a day, one tablespoon.
10. We take 4 tablespoons of dried flowers of ordinary pharmaceutical chamomile and simply pour them with a glass of boiling water, and boil the whole thing after that for 10 minutes and filter. Such a remedy is always used after eating a third of a glass 3 times.
11. There are also such folk remedies that are not associated with any specific recipes and medicinal herbs at all, for example, it helps many with a cramp to take a stick of simple sealing wax in their hand, in which muscles spasm. Moreover, it can help other people very well if you take a piece of iron in the same hand, but it should not be steel or cast iron. Just a prick with a pin can also immediately stop a leg cramp and the cause of it.
12. There is also a specialized folk recipe for the treatment of leg cramps with salt, because often the reasons for this are salt deficiency. In half a glass of water, simply dissolve half a teaspoon of salt and drink it all.
But in conclusion, I would like to note that you can easily fight against leg cramps and motivating causes with folk methods, but it would be best if you do not neglect a preliminary consultation with your doctor!
Cramps in the legs. Causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
The site provides background information. Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious physician.
convulsions are a state of continuous contraction of a muscle that is not amenable to voluntary relaxation. This condition causes a strong painful reaction, because at the time of convulsions, the muscle experiences an acute lack of oxygen and nutrients. In addition, in a short period of time, it releases a large amount of waste products that irritate the nerve endings, causing pain.
According to statistics, seizures happen at least once in a person's life. They become the cause of excitement with frequent repetition. In some cases, seizures are a symptom of a disease such as epilepsy. In other cases, seizures develop in healthy, at first glance, people.
Most often, seizures are recorded in people engaged in the following activities:
- athletes;
- loaders;
- public transport inspectors;
- traders in the markets;
- employees of water companies;
- swimmers;
- surgeons.
Interesting Facts
- Leg cramps are a signal that there is a certain pathology in the body that caused their appearance.
- Cold environments increase the likelihood of seizures.
- Smokers are 5 times more likely to have seizures than non-smokers.
- Proper first aid for leg cramps prevents their recurrence in 95% of cases.
How do muscles work?
Knowledge of the structure and mechanism of muscle contraction is necessary for an accurate understanding of the causes of leg cramps. Without this information, the ways in which numerous factors influence the occurrence of seizures cannot be fully disclosed and explained.
Muscle structure
From the point of view of human physiology, the mechanism of muscle fiber contraction is a long-studied phenomenon. Since the purpose of this article is to highlight the issue of leg cramps, it would be reasonable to pay special attention to the work of only striated (skeletal) muscles, without affecting the principles of smooth functioning.
Skeletal muscle consists of thousands of fibers, and each individual fiber, in turn, contains many myofibrils. A myofibril in a simple light microscope is a strip in which tens and hundreds of nuclei of muscle cells (myocytes) lined up in a row are visible.
Each myocyte has a special contractile apparatus along the periphery, oriented strictly parallel to the cell axis. The contractile apparatus is a collection of special contractile structures called myofilaments. These structures can only be detected using electron microscopy. The main morphofunctional unit of the myofibril with contractile ability is the sarcomere.
The sarcomere is made up of a number of proteins. the main ones are actin, myosin, troponin and tropomyosin. Actin and myosin are shaped like threads intertwined with each other. With the help of troponin, tropomyosin, calcium ions and ATP (adenosine triphosphate), actin and myosin filaments are brought together, as a result of which the sarcomere is shortened, and, accordingly, the entire muscle fiber.
The mechanism of muscle contraction
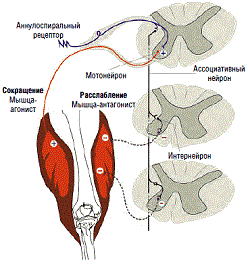
There are many monographs describing the mechanism of muscle fiber contraction, in which each author presents his own staging of this process. Therefore, the most correct solution would be to single out the general stages of the formation of muscle contraction and describe this process from the moment the impulse is transmitted by the brain to the moment of complete muscle contraction.
The contraction of the muscle fiber occurs in the following order:
- The nerve impulse originates in the precentral gyrus of the brain and is transmitted along the nerve to the muscle fiber.
- Through the mediator acetylcholine, an electrical impulse is transferred from the nerve to the surface of the muscle fiber.
- The spread of the impulse throughout the muscle fiber and its penetration deep into the special T-shaped tubules.
- The transition of excitation from the T-shaped tubules to the cisterns. Tanks are called special cellular formations containing large amounts of calcium ions. As a result, the opening of calcium channels and the release of calcium into the intracellular space.
- Calcium triggers the process of mutual convergence of actin and myosin filaments by activating and rearranging the active centers of troponin and tropomyosin.
- ATP is an essential component of the above process as it supports the process of bringing actin and myosin filaments closer together. ATP promotes the detachment of myosin heads and the release of its active centers. In other words, without ATP, the muscle is unable to contract because it cannot relax before doing so.
- As the actin and myosin filaments approach each other, the sarcomere shortens and the muscle fiber itself and the entire muscle contract.
Factors affecting muscle contractility
Violation at any of the above stages can lead to both the absence of muscle contraction and the state of constant contraction, that is, convulsions.
The following factors lead to prolonged tonic contraction of the muscle fiber:
- excessively frequent impulses of the brain;
- excess acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft;
- decrease in the threshold of myocyte excitability;
- decrease in ATP concentration;
- a genetic defect in one of the contractile proteins.
Causes of leg cramps
Causes imply diseases or certain conditions of the body in which favorable conditions are created for the occurrence of cramps in the lower extremities. There are a lot of diseases and various conditions that can lead to convulsions, therefore, in this case, one should not deviate from the chosen direction, but, on the contrary, it is necessary to classify diseases according to the factors listed above.
Excessive brain impulses
The brain, namely its special section - the cerebellum, is responsible for maintaining a constant tone of every muscle in the body. Even during sleep, the muscles do not stop receiving impulses from the brain. The fact is that they are generated much less frequently than in the waking state. Under certain circumstances, the brain begins to increase impulses, which the patient feels as a feeling of muscle stiffness. When a certain threshold is reached, the impulses become so frequent that they maintain the muscle in a state of constant contraction. This condition is called tonic convulsions.
Leg cramps due to increased brain impulses develop with the following diseases:
- epilepsy;
- acute psychosis;
- eclampsia;
- traumatic brain injury;
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- craniocerebral thromboembolism.
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a severe disease characterized by the appearance of foci of synchronous impulses in the brain. Normally, different parts of the brain emit waves of different frequencies and amplitudes. During an epileptic seizure, all the neurons of the brain begin to pulse synchronously. This leads to the fact that all the muscles of the body begin to contract and relax uncontrollably.
There are generalized and partial seizures. Generalized seizures are considered classic and live up to their name. In other words, they are manifested by contraction of the muscles of the whole body. Partial seizures are less common and are manifested by uncontrolled contraction of only one muscle group or one limb.
There is a special kind of convulsions, named after the author who described them. The name of these seizures is Jacksonian seizures or Jacksonian epilepsy. The difference between this type of convulsions is that they begin as a partial seizure, for example, from the arm, leg or face, and then spread to the whole body.
Acute psychosis
This mental illness is characterized by visual and auditory hallucinations. caused by many reasons. The pathophysiology of this disease is not well understood, but it is assumed that the substrate for the appearance of symptoms of distorted perception is abnormal brain activity. If medical assistance is not provided, the patient's condition deteriorates sharply. Rising body temperature above 40 degrees is a poor prognostic sign. Often, an increase in temperature is accompanied by generalized convulsions. Seizures of only the lower extremities are practically uncommon, but may be the beginning of a generalized seizure, as in the Jacksonian seizure mentioned above.
In addition, the patient may complain that his legs are cramping due to distorted perception. It is important to take this complaint seriously and check whether it is true. If the limb is in a state of convulsions, its muscles are tense. Forced extension of the limb leads to the rapid disappearance of painful symptoms. If there is no objective confirmation of lower limb cramps, the patient's complaints are explained by paresthesias (sensory hallucinations) caused by acute psychosis.
This pathological condition can occur during pregnancy and poses a serious threat to the life of the pregnant woman and the fetus. In non-pregnant women and men, this disease cannot occur, since the triggering factor for its development is the incompatibility of certain cellular components of the mother and fetus. Eclampsia is preceded by preeclampsia, in which the pregnant woman's blood pressure rises. edema appears and general well-being worsens. With high blood pressure figures (average of 140 mm Hg and above), the risk of placental abruption increases due to narrowing of the blood vessels that feed it. Eclampsia is marked by the appearance of generalized or partial seizures. Leg cramps, as in the previous case, may be the beginning of a partial Jacksonian seizure. During convulsions, sharp contractions and relaxation of the uterine muscles occur, leading to detachment of the fetal site and cessation of fetal nutrition. In this situation, there is an urgent need for emergency delivery by caesarean section in order to save the life of the fetus and stop uterine bleeding in a pregnant woman.
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injuries can lead to leg cramps, but it should be recognized that this happens quite rarely. There is a pattern according to which the magnitude of the lesion corresponds to the severity of seizures and the duration of their manifestation. In other words, a brain contusion with a subdural hematoma is more likely to cause seizures than a normal concussion. The mechanism of seizures in this case is associated with the destruction of brain cells. In the lesion, the ionic composition changes, which leads to a change in the excitability threshold of surrounding cells and an increase in the electrical activity of the affected area of the brain. So-called foci of epileptic activity of the brain are formed, which are periodically discharged by convulsions, and then again accumulate a charge. As the area affected by the injury heals, the ionic composition of the brain cells also normalizes, which inevitably leads to the disappearance of the focus of high convulsive activity and the patient's recovery.
intracranial hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage is more often a complication of hypertension. in which aneurysms (areas of a thinned vascular wall) form in the vessels of the brain over time. Almost always intracranial hemorrhage is accompanied by loss of consciousness. With the next rise in blood pressure, the aneurysm ruptures and blood flows into the substance of the brain. Firstly, blood presses on the nervous tissue, thus violating its integrity. Secondly, a torn vessel loses its ability to supply blood to a certain part of the brain for some time, leading to oxygen starvation. In both cases, the brain tissue is damaged either directly or indirectly by a change in the ionic composition of the intercellular and intracellular fluid. There is a decrease in the threshold of excitability in the focus of affected cells and the formation of a zone of high convulsive activity. The more massive the hemorrhage, the more likely it will lead to the development of seizures.
Cranial thromboembolism
The control of this disease is extremely relevant in modern society, since it is caused by a sedentary lifestyle, overweight, unhealthy diet, smoking and alcohol abuse. Through many mechanisms, blood clots (thrombi) form in any part of the body, which grow and can reach quite large sizes. Due to the anatomical features of the leg veins are the most common place for the formation of blood clots. Under certain circumstances, the thrombus breaks off and, reaching the brain, clogs the lumen of one of the vessels. After a short time (15 - 30 seconds), symptoms of hypoxia of the affected area of the brain appear. Most often, hypoxia of a certain part of the brain leads to the disappearance of the function that it provides, for example, to loss of speech, the disappearance of muscle tone, etc. However, sometimes the affected area of the brain becomes a focus of high convulsive activity, which was mentioned earlier. Leg cramps often occur when a thrombus clogs the vessels that feed the lateral part of the precentral gyrus, since it is this part of the brain that is responsible for voluntary leg movements. Restoration of the blood supply to the affected focus leads to its gradual resorption and the disappearance of seizures.
Excess acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft
Acetylcholine is the main mediator involved in the transmission of impulses from the nerve to the muscle cell. The structure that provides this transmission is called the electrochemical synapse. The mechanism of this transmission is the release of acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft, followed by its action on the muscle cell membrane and the generation of an action potential.
Under certain conditions, an excess of mediator can accumulate in the synaptic cleft, inevitably leading to more frequent and stronger muscle contraction, up to the development of seizures, including the lower extremities.
The following conditions cause seizures by increasing the amount of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft:
- overdose of drugs of the group of cholinesterase blockers;
- muscle relaxation with depolarizing drugs;
- magnesium deficiency in the body.
Overdose of drugs of the group of cholinesterase blockers
Cholinesterase is an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine. Thanks to cholinesterase, acetylcholine does not stay long in the synaptic cleft, which results in muscle relaxation and rest. Preparations of the group of cholinesterase blockers bind this enzyme, leading to an increase in the concentration of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft and an increase in muscle cell tone. According to the mechanism of action, cholinesterase blockers are divided into reversible and irreversible.
Reversible cholinesterase blockers are used primarily for medical purposes. Representatives of this group are prozerin, physostigmine, galantamine, etc. Their use is justified in the case of postoperative intestinal paresis. in the recovery period after a stroke of the brain, with atony of the bladder. An overdose of these drugs or their unreasonable use leads first to a feeling of painful muscle stiffness, and then to convulsions.
Irreversible cholinesterase blockers are otherwise called organophosphates and belong to the class of chemical weapons. The most famous representatives of this group are the chemical warfare agents sarin and soman, as well as the familiar insecticide, dichlorvos. Sarin and soman are banned in most countries of the world as inhumane weapons. Dichlorvos and other related compounds are often used on the farm and cause household poisoning. The mechanism of their action is the strong binding of cholinesterase without the possibility of its independent detachment. The bound cholinesterase loses its function and leads to accumulation of acetylcholine. Clinically, there is spastic paralysis of the entire musculature of the body. Death occurs from paralysis of the diaphragm and disruption of the process of voluntary breathing.
Muscle relaxation with depolarizing drugs
Muscle relaxation is used when performing anesthesia before surgery and leads to better anesthesia. There are two main types of muscle relaxants - depolarizing and non-depolarizing. Each type of muscle relaxant has strict indications for use.
The most famous representative of depolarizing muscle relaxants is suxamethonium chloride (dithylin). This drug is used for short operations (up to a maximum of 15 minutes). After exiting anesthesia with the parallel use of this muscle relaxant, the patient feels muscle stiffness for some time, as after hard and prolonged physical work. Together with other predisposing factors, the above sensation can turn into convulsions.
Magnesium deficiency in the body
Magnesium is one of the most important electrolytes in the body. One of its functions is to open the channels of the presynaptic membrane for the return entry of an unused mediator into the end of the axon (the central process of the nerve cell responsible for the transmission of the electrical impulse). With a lack of magnesium, these channels remain closed, which leads to the accumulation of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. As a result, even light physical activity after a short time provokes the appearance of seizures.
Magnesium deficiency often develops with malnutrition. This problem mainly affects girls who seek to limit themselves in food for the benefit of the figure. Some of them use adsorbents in addition to the diet, the most famous of which is activated carbon. This drug, of course, is extremely effective in many situations, but its side effect is the removal of useful ions from the body. With a single use of it, seizures do not occur, but with prolonged use, the risk of their occurrence increases.
Decreased myocyte excitability threshold
A muscle cell, like any other cell in the body, has a certain threshold of excitability. Although this threshold is strictly specific for each cell type, it is not constant. It depends on the difference in the concentration of certain ions inside and outside the cells and the successful operation of cellular pumping systems.
The main reasons for the development of seizures due to a decrease in the threshold of excitability of myocytes are:
- electrolyte imbalance;
- hypovitaminosis.
Electrolyte imbalance
The difference in the concentration of electrolytes creates a certain charge on the surface of the cell. In order for a cell to become excited, it is necessary that the impulse received by it be equal to or greater in strength than the charge of the cell membrane. In other words, the impulse must overcome a certain threshold value in order to bring the cell into a state of excitation. This threshold is not stable, but depends on the concentration of electrolytes in the space surrounding the cell. When the electrolyte balance in the body changes, the excitability threshold decreases, weaker impulses cause muscle contraction. The frequency of contractions also increases, which leads to a state of constant excitation of the muscle cell - convulsions. Disturbances that often lead to changes in electrolyte balance are vomiting. diarrhea. bleeding, shortness of breath and intoxication.
Hypovitaminosis
Vitamins play an extremely important role in the development of the body and maintaining its normal performance. They are part of enzymes and coenzymes that perform the function of maintaining the constancy of the internal environment of the body. The contractile function of the muscles is more affected by the deficiency of vitamins A, B, D and E. In this case, the integrity of cell membranes suffers and, as a result, there is a decrease in the threshold of excitability, leading to convulsions.
Decreased ATP concentration
ATP is the main chemical energy carrier in the body. This acid is synthesized in special organelles - mitochondria, present in every cell. Energy is released when ATP is broken down into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and phosphate. The released energy is spent on the operation of most systems that maintain the viability of the cell.
In a muscle cell, calcium ions normally lead to its contraction, and ATP is responsible for relaxation. If we take into account that a change in the calcium concentration in the blood rarely leads to convulsions, since calcium is not consumed and is not formed during muscle work, then a decrease in ATP concentration is the direct cause of convulsions, since this resource is consumed. It should be noted that convulsions develop only in the case of the ultimate depletion of ATP, which is responsible for muscle relaxation. Recovery of ATP concentration requires a certain time, which corresponds to rest after hard work. Until the normal concentration of ATP is restored, the muscle does not relax. It is for this reason that the overworked muscle is hard to the touch and rigid (poorly amenable to extension).
Diseases and conditions that lead to a decrease in the concentration of ATP and the appearance of seizures are:
Diabetes mellitus is a severe endocrine disease leading to a number of acute and delayed complications. Diabetes requires the patient to be highly disciplined, since only the right diet and timely intake of drugs in the required concentration can compensate for the lack of insulin in the body. However, no matter how much the patient makes efforts to control the level of glycemia, he will not be able to completely avoid jumps in blood glucose concentration. This is because this level depends on many factors that are not always controllable. These factors include stress. time of day, the composition of the food consumed, the type of work that the body performs, etc.
One of the terrible complications that develop in diabetes mellitus is diabetic angiopathy. As a rule, with good control of the disease, angiopathy develops no earlier than the fifth year. There are micro and macro angiopathy. The mechanism of the damaging action consists in the defeat, in one case, of the main main, and in the other - small vessels that feed the tissues of the body. Muscles, which normally consume most of the energy, begin to suffer from insufficient blood circulation. With a lack of blood circulation, less oxygen enters the tissues and less ATP is produced, in particular in muscle cells. According to the previously mentioned mechanism, the lack of ATP leads to muscle spasm.
inferior vena cava syndrome
This pathology is typical only for pregnant women and develops, on average, starting from the second half of pregnancy. By this time, the fetus reaches a size sufficient to begin to gradually displace the internal organs of the mother. Along with the organs, the large vessels of the abdominal cavity are also compressed - the abdominal aorta and the inferior vena cava. The abdominal aorta has a thick wall and also pulsates, which prevents the development of blood stasis at this level. The wall of the inferior vena cava is thinner, and the blood flow in it is laminar (constant, not pulsating). This makes the venous wall vulnerable to compression.
As the fetus grows, the compression of the inferior vena cava increases. At the same time, circulatory disorders in this segment also progress. There is stagnation of blood in the lower extremities and edema develops. Under such conditions, tissue nutrition and oxygen saturation gradually decrease. These factors together lead to a decrease in the amount of ATP in the cell and an increase in the likelihood of developing seizures.
Chronic heart failure
This disease is characterized by the inability of the heart to adequately perform a pumping function and maintain an optimal level of blood circulation. This leads to the development of edema, starting in the lower extremities and rising higher as the impairment of cardiac function progresses. In conditions of stagnation of blood in the lower extremities, a deficiency of oxygen and nutrients develops. Under such conditions, the performance of the muscles of the lower extremities is noticeably reduced, ATP deficiency sets in faster and the likelihood of seizures increases.
Phlebeurysm
A varicose vein is an area of thinned venous wall that protrudes beyond the normal contours of the vessel. It develops more often in people whose occupation is associated with many hours of standing on their feet, in patients with chronic heart failure, in obese patients. In the first case, the mechanism of their development is associated with a constantly increased load on the venous vessels and their expansion. In case of heart failure, stagnation of blood develops in the vessels of the lower extremities. With obesity, the load on the legs increases significantly, blood volume increases, and the diameter of the veins is forced to adapt to it.
The speed of blood flow in varicose veins decreases, the blood thickens, and blood clots form that clog those same veins. Under such conditions, the blood is looking for another way of outflow, but soon high pressure leads to the appearance of new varicose veins. Thus, a vicious circle is closed, the result of which is the progression of blood stasis in the lower extremities. Blood stasis leads to a decrease in ATP production and an increase in the likelihood of seizures.
Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is an inflammation of a venous vessel. As a rule, thrombophlebitis accompanies varicose veins, since the mechanisms of their formation intersect. In both cases, the triggering factor is circulatory stagnation. With varicose veins, it leads to varicose veins, and with thrombophlebitis, it leads to inflammation. The inflamed vein is compressed by edema and deformed, which causes its capacity to suffer, blood stasis aggravates and inflammation progresses again. Another vicious circle leads to the fact that it is almost impossible to completely cure thrombophlebitis and varicose veins in a conservative way. When using certain drugs, inflammation can be reduced, but not the disappearance of the factors that caused it. The mechanism of seizures, as in previous cases, is associated with stagnation of blood in the lower extremities.
Obliterating atherosclerosis
This disease is the scourge of countries with a high level of development, since its occurrence and severity increases along with the level of well-being of the population. It is in these countries that the percentage of obese people is highest. With excessive nutrition, smoking and a sedentary lifestyle, atherosclerotic plaques form on the walls of the arteries, which reduce the patency of the vessels. Their most common localization is the iliac, femoral and popliteal arteries. As a result of plaque formation, the capacity of the artery becomes limited. If, under normal load, muscle tissue receives enough oxygen and nutrients, then with an increase in load, their deficiency gradually forms. A muscle that does not receive oxygen produces less ATP, which after a certain time, provided that the intensity of work is maintained, will lead to the development of leg cramps.
Anemia is a decrease in the number of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and/or hemoglobin in the blood. Erythrocytes are cells containing up to 98% of hemoglobin protein, and he, in turn, is able to bind oxygen and transport it to peripheral tissues. Anemia can develop for many reasons, such as acute and chronic bleeding, impaired erythrocyte maturation, a genetic defect in hemoglobin, long-term use of certain medications (pyrazolone derivatives) and much more. Anemia leads to a decrease in gas exchange between air, blood and tissues. The amount of oxygen supplied to the periphery is not enough to meet the optimal needs of the muscles. As a result, fewer ATP molecules are formed in mitochondria, and its deficiency increases the risk of seizures.
Early postoperative period
This condition is not a disease, but deserves close attention when it comes to seizures. Operations of medium and high degrees of complexity, as a rule, are accompanied by a certain blood loss. In addition, blood pressure can be artificially lowered for a long time for special stages of the operation. These factors, combined with the complete immobility of the patient for several hours of surgery, create an increased risk of blood clots in the lower extremities. This risk is increased in patients with atherosclerosis or varicose veins.
The postoperative period, which in some cases takes quite a long time, requires the patient to comply with strict bed rest and little physical activity. Under these conditions, blood circulation in the lower extremities slows down significantly, and blood clots or blood clots form. Thrombi partially or completely block the blood flow in the vessel and cause hypoxia (low oxygen content in the tissues) of the surrounding muscles. As in previous diseases, a decrease in oxygen concentration in muscle tissue, especially under conditions of increased stress, leads to seizures.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a disease associated with increased production of thyroid hormones. Based on the cause and mechanism of development, primary, secondary and tertiary hyperthyroidism is distinguished. Primary hyperthyroidism is characterized by a violation at the level of the thyroid gland itself, secondary - at the level of the pituitary gland and tertiary - at the level of the hypothalamus. An increase in the concentration of the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine leads to tachypsychia (acceleration of thought processes), as well as restlessness and a state of constant anxiety. These patients are much more active than healthy people. The excitability threshold of their nerve cells decreases, which leads to an increase in cell excitability. All of the above factors lead to more intense muscle work. Together with other predisposing factors, hyperthyroidism may well cause seizures.
Excessive exercise
Unbearable and prolonged physical activity for an unprepared body is definitely harmful. Muscles are quickly depleted, the entire supply of ATP is consumed. If you do not give the muscles time to rest, during which a certain amount of these energy carriers is synthesized again, then with further muscle activity, the development of seizures is very likely. Their probability increases many times in a cold environment, for example, in cold water. This is due to the fact that the cooling of the muscle leads to a decrease in the metabolic rate in it. Accordingly, the consumption of ATP remains the same, and the processes of its replenishment slow down. That is why convulsions quite often occur in water.
flat feet
This pathology consists in the incorrect formation of the arch of the foot. As a result, the fulcrum of the foot is in places that are not physiologically adapted for them. The muscles of the foot, which are outside the arch, have to carry a load for which they are not designed. The result is their rapid fatigue. A tired muscle is deprived of ATP and at the same time loses the ability to relax.
In addition to the defeat of the foot itself, flat feet indirectly affect the condition of the knee and hip joints. Since the arch of the foot is not formed correctly, it does not perform a shock-absorbing function. As a result, the above joints are subjected to greater concussion and are more likely to fail, causing the development of arthrosis and arthritis.
Genetic defect in one of the contractile proteins
This category of diseases is incurable. It is comforting to know that the frequency of the disease in the population is low and the probability of the manifestation of the disease is 1:200 - 300 million. This group includes various fermentopathies and diseases of abnormal proteins.
One of the diseases of this group, manifested by convulsions, is Tourette's syndrome (Gilles de la Tourette). Due to the mutation of specific genes in the seventh and eleventh pairs of chromosomes, abnormal connections are formed in the brain, leading to the appearance of involuntary movements (tics) and cries (often obscene) in the patient. In the case when a tic affects the lower limb, it can manifest itself in the form of periodic convulsions.
First aid for convulsions
The main task of a person assisting with a spasm to himself or to someone else is to recognize the cause of the spasm. In other words, it is necessary to distinguish whether the spasm is a manifestation of a partial epileptic seizure or is caused by some other reasons. Depending on the mechanism of development of seizures, there are at least two algorithms for providing assistance, which are radically different from each other.
The first distinguishing feature of epileptic seizures is staging. The first stage is clonic, that is, it is manifested by alternating rhythmic contractions and muscle relaxation. The duration of the clonic stage, on average, is 15 - 20 seconds. The second stage of epileptic seizures is tonic. With it, a long spasm of the muscle occurs, on average, up to 10 seconds, after which the muscle relaxes, and the attack ends.
The second feature of epileptic convulsions is the dependence of their occurrence on certain, strictly individual trigger factors for each patient. The most common of these are bright flickering lights, loud noises, and a certain taste and smell.
The third feature is manifested only in the case of the transition of partial convulsions to generalized ones and consists in the loss of consciousness of the patient at the end of the attack. Loss of consciousness is often accompanied by involuntary urination and passing of stools. After coming to oneself, the phenomenon of retrograde amnesia is observed. in which the patient does not remember that he had an attack.
If, according to the above criteria, the patient has a partial seizure of epileptic convulsions, he, first of all, must be put on a chair, bench or ground in order to avoid injury in case of a possible fall. Then you should wait for the end of the attack, without taking any action.
In the case of the spread of convulsions and their transition to a generalized form, it is necessary to lay the patient on his side and put a blanket, shirt under his head or wrap his arms around it to avoid damage during an attack. It is important not to fix the head, but to protect it from blows, since with strong fixation there is a risk of folding of the cervical vertebrae, which inevitably leads to the death of the patient. If the patient has a generalized seizure, it is equally important to call an ambulance as soon as possible, since without the introduction of certain medications, the likelihood of repeated seizures is high. At the end of the attack, it is necessary to try to find out which factor could provoke the attack and try to eliminate it.
When the cause of seizures is not related to epilepsy, the following measures should be taken. First, you need to give the limbs an elevated position. This provides an improved outflow of blood and eliminates congestion. Secondly, you should take hold of your toes and perform dorsal flexion of the foot (toward the knee) in two stages - first, half-bend and release, and then again slowly bend as much as possible and hold in this position until the spasms stop. This manipulation leads to a violent stretching of the muscle, which, like a sponge, draws in oxygen-rich blood. In parallel, it is useful to perform a light massage of the limb, as it improves microcirculation and speeds up the recovery process. Pinching and pricking have a distracting effect and interrupt the reflex circuit that closes with pain from muscle spasm.
Seizure treatment
Treatment of convulsions should obey the following rule. An attack of seizures should be stopped first of all, since it is a stressful condition for the body. The causes that caused it are treated secondarily. If it is impossible to eliminate the causes, the patient should receive constant pathogenetic and symptomatic treatment aimed at reducing the likelihood and severity of seizures.
Medical treatment of frequent seizures
Drug treatment of seizures is conditionally divided into interruption of seizures and treatment aimed at preventing them.
Medicinal intervention is performed only if the patient has a partial or generalized epileptic seizure. With convulsions of a different origin, they are interrupted using the manipulations indicated in the section "First Aid for Convulsions".
Drugs used to relieve an attack of epileptic seizures
Health, life, hobbies, relationships
seizures after a stroke
Seizures are a complex response to internal or external stimuli. The reason is different in each case. In fact, convulsions are involuntary contractions of skeletal muscles that are paroxysmal in nature. They may vary in prevalence, intensity and duration. Seizures are regular and episodic. Depending on the duration of the contraction, tonic and clonic are distinguished.
Clonic is a short-term contraction and relaxation of individual muscles. They look like fast movements. For example, tick half of the face or eyelid.
Tonic - rather long contractions (up to three minutes or more). They feel like hardening of the muscles. At such a moment, it is not possible to control the contracted muscles.
Reasons why seizures may occur.
One of the causes of seizures may be a focus of irritation that appears in the motor area of the brain. It happens during the onset of a stroke or at the time of recovery after an attack. Localization of seizures in specific muscles depends on how the brain area is irritated. If there is a suspicion of such a mechanism of muscle contractions, then you should immediately seek help from specialists.
How to identify the cause of the seizures.
At the beginning, you can immediately discard or establish obvious reasons: long hard physical work, stuffiness or overheating. Or some kind of viral infection.
What to do during seizures.
You need to stand on the cold floor and walk around a bit.
Lie down and stretch your leg.
Painful muscles need to be rubbed.
You should also mix one teaspoon of olive oil and two teaspoons of mustard and spread this gruel on the place where the cramp occurred.
It is also necessary to take an anesthetic, aspirin, it will additionally improve microcirculation in the vessels of the legs.
Treatment outside the attack
A person must make adjustments to his lifestyle.
It is necessary to exclude the use of strong tea and coffee, as well as quit smoking - so these factors can provoke convulsions. If a person takes steroid hormones and diuretics, the frequency and dose of their intake should be reduced.
You need to drink plenty of fluids. But not sweet carbonated drinks, but water, mineral water is best.
The menu should be adjusted: eat more vegetables and leafy greens, they supply minerals to the human body.
Women during menopause should take additional calcium supplements with magnesium.
In order to normalize calcium metabolism, vitamin D should be used.
Live healthy!: Convulsions 09/27/2013
Seizures after a stroke most often appear if the patient has a seizure with a focus in the frontal lobe of the brain. This problem can occur in acute circulatory disorders in the brain and a few months after an attack during an exacerbation of the disease.
The resumption of symptoms does not indicate incorrect therapy, but the development of a second attack, a large area of necrosis, or the formation of a cystic cavity in place of dead tissues.
What causes seizures
Seizures may occur after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. They are the result of the death of neurons in the brain. When foci of necrosis begin to form, the body tries to stop the lesion and restore normal blood circulation in the brain. This task is performed by distributing dead neurons between brain cells.
Such self-defense leads to the formation of cavities with liquid in place of dead tissues. This formation does not cause discomfort, but sometimes it irritates neurons, which is accompanied by convulsive seizures.
Seizures after a stroke can be triggered by:
- Emotional surges.
- Physical or psychological fatigue.
- As a side effect after taking certain medications.
The main reasons for the development of seizures are the occurrence of cysts, adhesions and other neoplasms in areas of dead tissue.
The main symptoms of seizures
During seizures, certain muscle groups contract or twitch. The duration of this phenomenon ranges from a few seconds to ten minutes.
After an attack of acute circulatory disorders in the brain, the patient most often suffers from short-term convulsions throughout the body. They can occur in the arms, legs, face, or neck. After an attack of convulsions, the patient loses consciousness, or he falls asleep as a result of the brain being in a state of shock.
Seizures can manifest themselves in different ways. Some patients experience a slight tremor, while others suffer from severe convulsive seizures.
Seizures during and after a stroke can manifest as follows:
- facial muscles contract for a short time. In this case, one half of the face may be distorted, a mask-like face may appear;
- the muscles of the limbs become numb, and the person completely loses control over them. There is a feeling of a wooden arm or leg;
- contraction of the muscles of the face may be accompanied by numbness of the limbs.
In the event of an attack, you must urgently call an ambulance.
How to renderfirst aid
Everyone should know what to do if a seizure occurs. If a loved one or a stranger has an attack, you must:
- Give him oxygen. If this happened indoors, then you need to open the windows, otherwise you should remove tight clothing from the patient.
- Place a cushion or pillow under the patient's head.
- In the presence of prostheses in the mouth, or if the attack occurred during a meal, it is necessary to clean the oral cavity from foreign objects.
- If the victim began to breathe hoarsely, he should be laid on his side and checked that nothing made it difficult for him to breathe.
- With the development of painful sensations in the muscle tissue, you need to massage and warm up the muscles well. It is advisable to lubricate the skin with olive oil mixed with mustard before the massage.
- The patient should take aspirin, which will help him get rid of heat and tension and improve the process of blood circulation in the vessels.
- Even if the attack has stopped, it is necessary to call a specialist.
Seizures are treated in eight percent of cases. If they grow, it means that the treatment of the stroke did not work, and the focus of necrosis increases.
Treatment of post-stroke seizures is the use of one or more drugs. Most often, the patient's condition is facilitated with the help of Finlepsin or Carbamazeline. Most doctors prefer to treat with Finlepsin. It most often gives a positive result and can almost completely relieve seizures.
At the beginning of therapy, the patient should consume no more than two hundred milligrams of the drug per day. But it is not advisable to carry out treatment with this drug without consulting a doctor, since the drug may cause some adverse reactions. In most cases, they appear:
- decrease in intellectual activity. This side effect develops if the patient takes the medicine for a long time;
- impotence, apathy, complete calmness;
- osteoporosis or increased bone fragility. You can compensate for this problem with calcium supplements;
- increased risk of bleeding. This problem may occur if Finlepsin is combined with anticoagulants.
Treatment with this remedy is only suitable for people under 65 years of age. A maximum of 400 mg of the drug can be consumed per day. There are analogues of the remedy that have a more gentle effect. These drugs can be addictive, so you need to change the medicine periodically. Any therapy should be carried out only under the supervision of the attending physician. He will be able to notice the development of a repeated attack of stroke in time and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Until now, we have hardly discussed motor disorders in our loved ones, since there is no direct connection with them, and we did not want to blur the main topic of our site. However, a recent discussion of the problems that develop after a stroke - and in Russia stroke remains a very common cause of development - has shown that this topic is important.
I was asked to tell about it without much zaum, in simple words. I promised to try.
I read in a serious scientific journal that after a stroke, movement disorders manifest themselves in one way or another in more than 80% of patients. Due to the death of cells that previously regulated the work of the muscles, they weaken (paresis) or turn off completely (paralysis). There may also be a disorder of body position and coordination of movements. This is fraught with falls and - at best - a developing fear of independent walking, and at worst - a fracture. The "problems with the head" that appear along with this only increase the risks.
Fortunately, even in old age, the plasticity of the brain allows it to rebuild and gradually restore lost motor functions. And here the task of doctors (and after overcoming an acute violation - and those around them) is to create the necessary conditions for the speedy rehabilitation: the main method is physiotherapy exercises in combination with physio- and occupational therapy.
However, in about every third case, the so-called spasticity begins to develop in the post-stroke period - an increased tone in the muscle, which prevents it from stretching and forcibly returns the limb to a certain position, which limits overall mobility. Spasm is quite difficult to physiotherapy and interferes with normal recovery. As it turned out, visitors to our site also encountered this phenomenon.
Due to the constant tone, which does not decrease even at rest, changes begin to occur in muscles, tendons and joints (fibrosis, atrophy), painful deformities (contractures) and pathological postures develop, which aggravate the problem and seriously complicate the patient's life.
Spasticity does not develop immediately, usually a few months after a stroke. However, the specialist can notice the first signals in 2-3 weeks. Initially, flaccid muscles come into tone, which increases and becomes more pronounced in response to external stimuli (for example, an attempt to bend or straighten a limb). After six months, a maximum of a year, spasticity turns into a problem that significantly affects the patient's quality of life. It hurts.
In the upper torso, the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and fingers are often affected. In the lower body, spasticity may affect the hip, knee, ankle, or toes. In the arm area, the flexor muscles are usually affected, and on the leg, the extensor muscles.
Look at the pictures from our newspaper "Memini". 
You have probably seen something similar in patients with cerebral palsy.
Needless to say, this problem has a bad effect on the ability of a person to dress himself, eat (simply not able to hold a spoon), write with a pen, hygiene suffers, etc.
If spasticity is not treated, then after 3-4 years, contractures are formed - joint deformities. Bones are also deformed. There are forced painful postures.
About who is to blame, I will not write. I immediately turn to the question "What to do?".
The answer is simple: heal.
Treatments for spasticity may include:
prescribing drugs (central and local action),
physiotherapy,
occupational therapy.
(In rare cases, surgery may be considered.)
The basis of therapy is the effect on the muscle, which allows to reduce its tone. Below we consider in more detail the role of each of these methods.
PRESCRIPTION OF MEDICINES
The oral (taken by mouth) medications most commonly used to reduce spasticity include:
centrally acting muscle relaxants- baclofen, tizanidine, etc.
anticonvulsants clonazepam, diazepam.
Both groups of drugs help reduce muscle contraction and improve range of motion. Their intake relieves painful muscle spasms, enhances the effect of physiotherapy exercises and, as a result, prevents the development of contractures. Unfortunately, a feature of these drugs is that they act not only on spastic muscles, but on the whole organism as a whole. For the treatment of spasticity, these drugs are prescribed in large dosages, which leads to the appearance of side effects in the form of general weakness, dizziness, changes in mood and lethargy. This is especially unpleasant if a patient after a stroke and without it begins to develop cognitive impairment.
For this reason, more and more specialists are inclined to replace the above-mentioned drugs with injections of botulinum toxin type A. In terms of the strength of its effect on the muscle, botulinum toxin significantly exceeds all existing drugs taken in the form of tablets, and is comparable to surgical intervention. At the same time, denervation of the muscle with the help of a toxin is an extremely simple and safe procedure that can be performed by a doctor who has undergone appropriate training. Botulinum toxin preparations are well tolerated, and the likelihood of drug-drug interactions with their use is minimal. The recommendation from the American Academy of Neurology explicitly states the need to offer patients botulinum neurotoxin as one of the methods to reduce muscle tone and improve passive function in adult patients suffering from spasticity.
In our country, three botulinum toxin preparations are widely used for the treatment of spasticity: Botox (USA), Dysport (England), Xeomin (Germany). The latter is positioned by the manufacturer as a drug of a new generation, free from complexing proteins. In addition, the Chinese drug Lantox is registered in Russia, but, as far as I know, it is used mainly in cosmetology.
PHYSIOTHERAPY
Physical therapy has traditionally played an important role in the treatment of spasticity. The main components of the method include rehabilitation exercises, massage, acupuncture, thermal and electrical effects on spastic muscles, and the use of orthopedic devices.
Standard rehabilitation involves daily stretching to help restore strength to affected muscles, maintain joint range of motion, and prevent contractures. Regular stretching can ease muscle contraction and reduce stiffness for a period of several hours.
An important place in the process of restoration of motor functions and in the prevention of pathological conditions is occupied by massage. It allows you to relieve pain, helps restore muscle performance, improves their blood supply. However, only a specialist can be entrusted with performing a massage, since spastic and hypotonic muscles need different effects.
In Russia, acupuncture is often used in complex therapy, but controlled studies conducted abroad do not show a significant effectiveness of this treatment method.
Electrical stimulation is widely used to restore balance between the tone of the flexor and extensor muscles. The effect usually lasts about 10 minutes when the stimulation is first applied, but after several months of such treatments, the effect may be longer. Alternatively, the spastic muscle may also be stimulated directly to cause fatigue.
In the treatment of spasticity, bandages, bandages, tourniquets, splints, orthoses can be used to fix the limb. They allow you to support and align the spastic limb, as well as correct its deformity and improve function. Today, medical engineering has developed many orthopedic devices that provide not only immobilization and fixation in the correct position, but also deep pressure and heat maintenance in the tissues. Modern devices include a setting mechanism that controls the necessary function: from fixing with a lock to providing the necessary movements with assistance.
ERGO THERAPY, OR WORK THERAPY
Occupational therapy is a practice specially selected by a doctor that allows the patient to restore self-care skills after a stroke. It can be considered a special type of physical therapy, in which the exercise becomes practical: fasten a button, use cutlery... With the help of occupational therapy - by regularly repeating the same movements - patients restore the lost skills of everyday life, whenever possible. Otherwise, when it is not possible to restore some important actions, occupational therapy allows you to choose devices that compensate for the loss of a useful skill, or to form new motor models that are alternative to those used before the disease.
In other words, functional therapy is aimed at maintaining all the functions of the limb through the restoration of old movement patterns and/or the creation of new dynamic stereotypes based on a new muscle arrangement that allows normal movement. An important role here is played not only by the diligence of the patient, but also by the help of the person caring for him.
SURGICAL INTERVENTION
The two main categories of surgery for spasticity are at the level of the nervous system (neurosurgery) or the bones, tendons, and muscles (orthopedic surgery). The most significant indication for surgical treatment is the development of contracture. In this case, orthopedic surgery is often the only treatment for spasticity. With the help of surgery, muscles can be denervated, tendons and muscles can be freed from contractures, lengthened or moved, thereby reducing spasticity. Muscles can be denervated by cutting off certain nerves where they exit the spinal cord (dorsal rhizotomy). This operation is mainly used to treat severe spasticity of the leg muscles that interferes with the patient's movement.
To summarize briefly, the ideal option is to relax with botulinum toxin (lasts approximately 3-4 months) and develop. Here are the prices...
Although I read two studies. In one, the authors argued that if you count the costs that can be avoided due to botulinum therapy (nurse, aids), then in general it turns out to be even profitable. In another scientific language, something like this is said: it is better to spend money and get a result than to drink pills in large doses (by the way, they are also not free in our country), without much success.
True, both studies were conducted abroad.
I am often asked to talk about spasticity after a stroke and how to deal with it. There is still no 100% universal answer to this question. Today I will try to answer the questions: how spasticity occurs after a stroke and how to treat it with medication.
What is spasticity after a stroke?
Post-stroke spasticity (muscle spasticity) is hyperexcitation of the stretch reflex that occurs due to upper motor neuron syndrome.
Where does spasticity come from after a stroke?
The muscles of a person who does not suffer from spasticity after a stroke, during any action (movement, maintaining a posture) work in concert - some stretch (agonists), others contract (antagonists). Moreover, most of the movements are carried out unconsciously. A person does not need to think about how to change muscle tone in order to take a step. These processes occur automatically at the level of the spinal cord. One of the reflexes that allows you to unconsciously carry out movements is the stretch reflex.
To make it clear, remember the appointment with a neurologist.
The doctor knocks with a hammer on the hands and feet, during exposure, the hands and feet move spontaneously. This process is usually especially liked by patients. But what is happening? The doctor knocks on the muscle tendon, at the moment of impact of the hammer it is stretched.
Hyperextension of the tendon gives a signal that the antagonist muscles need to be activated in order to return the stretched muscle to its previous state. This is an instantaneous reaction, which is expressed in the movement of the arms and legs in response to the impact of the hammer. This reflex arc closes at the level of the spinal cord, it does not involve the brain. But in everyday life, during movement, the brain always controls this reflex.
If a person does not suffer from spasticity after a stroke, during movement (especially during sharp, fast actions), the muscles are constantly stretched, but the reaction, as when exposed to a hammer, does not occur. The brain sends special inhibitory impulses that prevent the reflex from being hyperexcited. During a vascular accident, the cells that send these impulses die and the reflex gets out of control. There is spasticity after a stroke.
The mechanism of spasticity after a stroke
The reflex is constantly excited, any stretching causes an increase in muscle tone and spasticity after a stroke. Muscles prone to lethargy - stretch (extensors of the arm, flexors of the leg), muscles prone to tension - tense (flexors of the arm, extensors of the leg). This tension, increased muscle tone and spasticity after a stroke. Muscles just can't relax, tk. they are constantly affected by the stretch reflex.
How to deal with spasticity after a stroke?
Spasticity after a stroke must be treated with medication.
Drug treatment of spasticity after a stroke.
The selection of drugs that affect spasticity after a stroke requires patience. You need to gradually increase the dose, see how it affects muscle tone. If it doesn’t work, change it, increase the dose again and see.
There are 2 groups of drugs that can affect spasticity after a stroke:
Centrally acting drugs- provide inhibition of the reflex through the central nervous system.
- non-benzodiazepine tranquilizers (diazepam, clonazepam),
- anticonvulsants (Finlepsin, Gabapentin, Pregabalin),
- alpha-agonists (Clonidine).
These drugs have one drawback - their use can cause sedation, decreased memory, attention, intelligence, dizziness. This can negatively affect rehabilitation. Gradually increasing the dose will help reduce the chance of these side effects.
Peripherally acting drugs- “extinguish” the stretch reflex at the level of the spinal cord. These include well-known muscle relaxants (Mydocalm, Sirdalud, Baclofen). The downside of drugs is a general decrease in muscle tone. Those. they reduce the tone in both spasmodic and stretched muscles. Therefore, their reception must necessarily be combined with gymnastics.
Treatment of spasticity with botulinum toxin injections.
The next step in influencing spasticity after a stroke is the use of botulinum toxin injections (Botox, Dysport, Xeomin). This is indicated when the tone is very large and other methods do not help. Botulinum toxin acts at the muscle level by blocking the impulses of the stretch reflex.
A very important point - after the injection of botulinum toxin for 3 months, you need to actively engage in gymnastics, otherwise the effect will not be persistent.
The owners of the patent RU 2428964:
The invention relates to restorative medicine. The doctor performs passive stretching of the spasmodic muscle of the limb, combined with rotation of the hand or foot alternately in both directions, for 20-30 minutes at the forced maximum expiration of the patient, and holds the stretching phase until the end of the exhalation. Exercises are carried out for 3 weeks. EFFECT: method provides reduction of muscle spasm, normalization of muscle tone.
The invention relates to medicine, namely to restorative medicine.
Strokes remain an important medical and social problem, being one of the main causes of long-term disability in people of working age. In Russia, among stroke patients, no more than 3-23% return to work, 85% of patients require constant medical and social support. Due to the lack of timely and adequate restorative treatment, leading to the occurrence of irreversible anatomical and functional changes, almost a third remain disabled (Kovalchuk V.V. Principles of organization and effectiveness of various methods of rehabilitation of patients after a stroke: abstract of thesis ... Ph.D. - St. Petersburg, 2008. - P.3.).
During the first three months after a stroke, there is an increase in muscle tone in the paretic limbs, and although at the first stage, mild or moderate spasticity, for example, in the extensors of the lower extremities, will only help restore walking function, in most cases this progressive increase in tone will lead to the development of muscle contractures, which are combined with periodic painful bouts of muscle spasms. Subsequently, trophic changes occur in the joints of the paretic limbs and articular contractures develop. The spastic state of the muscles is a significant obstacle in the restoration of motor functions, leads to disability, self-service skills and dramatically reduces the quality of life of patients who have had a stroke (Kadykov A.S., Chernikova L.A., Shakhparonova N.V. Rehabilitation after a stroke // Atmosphere, Nervous Diseases, 2004, No. 1, pp. 21-23).
The fight against muscle spasticity, the restoration of normal muscle tone is an important and necessary component of the motor rehabilitation of patients who have had a stroke.
Known methods of restorative medicine aimed at reducing muscle spasticity:
A method for reducing muscle spasm with the help of position treatment by laying arms and / or legs for 2-3 hours in a special position opposite to the Wernicke-Mann position (Kadykov A.S., Chernikova L.A., Shakhparonova N.V. Rehabilitation after a stroke // Atmosphere Nervous diseases - 2004. - No. 1. - P. 23.);
A method for reducing muscle spasm using physiotherapy, including heat treatment with paraffin or ozocerite applications and / or cold treatment (Kadykov A.S., Chernikova L.A., Shakhparonova N.V. Rehabilitation after a stroke // Atmosphere. Nervous diseases. - 2004. - No. 1. - P. 23);
A method for treating post-stroke conditions, including daily therapeutic massage of the spine with elements of acupressure and manual therapy of the cervicothoracic spine, pre-cooling the spine with compresses, therapeutic massage of the limbs with elements of acupressure from the knee along the back of the thigh and cooling the limbs with compresses, after which they perform lymphatic drainage from the knee up to the pelvis and from the foot to the knee (Pat. No. 2289380 of the Russian Federation, IPC A61N 1/00. Method for the treatment of cerebral ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke and post-stroke conditions. Badaev B.B. / Badaev Boris Borisovich, publ. 20.12. 2006);
A method for preventing stroke patients by daily exposure for 8 days to an electric field with a voltage U determined according to the law: U = -1.5 kV + 0.5 kV sin 78.5t, with a frequency of 12.5 Hz, supplementing it with evening relaxation exercises (Pat. No. 2308984 of the Russian Federation, IPC A61N 1/20. A method for preventing patients who have had a stroke, performed in a home hospital. Romanov A.I., Khatkova S.E., Panteleev S.N., Savitskaya N.N., Doroshenko G.P., Shamin V.V., Matveeva E.V. / Limited Liability Company “Epidaurus”, published 27.10.2007);
A method for reducing increased muscle tone in cerebral palsy as a result of combined transspinal micropolarization and magnetic pulse stimulation (Pat. No. 2262357 of the Russian Federation, IPC A61N 1/20. A method for reducing increased muscle tone in cerebral palsy. Sirbiladze K.T., Pinchuk D. .Yu., Petrov Yu.A., Iozenas N.O., Yurieva R.G. / State educational institution of higher professional education St. Petersburg State Academy named after I.I. Mechnikov. Published 20.10.2005.);
A method for normalizing muscle tone in children with spastic forms of cerebral palsy by relaxing the child on an incompletely inflated ball, laying him face down, while one methodologist fixes his shoulders on the surface of the ball, his arms - symmetrically along the body, another methodologist fixes the lower limbs on the surface ball and, as relaxation is achieved, spreads them, performing slow rocking back and forth, right-left and in a circle, then perform exercises to stretch the limbs and torso of the child symmetrically, with the same effort, in the same horizontal plane, sequentially, starting from the upper limbs and of the shoulder girdle (Pat. No. 2289381 of the Russian Federation, IPC A61N 1/00. A method for normalizing muscle tone in children with spastic forms of cerebral palsy. Kozhevnikova V.T., Sologubov E.G., Polyakov S.D., Smirnov I.E. / State Institution Scientific Center for Children's Health of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences (GU SCCH RAMS), State Institution Children's Psychoneurological Hospital No. 18 Department and health care in Moscow. Published December 20, 2006);
A method for reducing muscle spasticity as a result of being in positions: lying on your back, on a roller and on your stomach, propping your lower jaw with your palms (Kachesov V.A. Fundamentals of intensive rehabilitation. - M., 1999. - P. 76);
A method of relaxing the spastic muscle by performing a massage in the form of stroking, rubbing, shaking, kneading segmental zones (Belova A.N. Neurorehabilitation. - M .: Antidor, 2000. - P. 163);
A method for relaxing a spastic muscle with the help of therapeutic exercises with exercises aimed at relaxing muscles, by using the weight of a limb for shaking or free lowering, and suppressing pathological synkinesis by eliminating vicious friendly movements (Belova A.N. Neurorehabilitation. - M .: Antidor, 2000. - P. 107);
A method for reducing the spasticity of the limb by fixing the limb and performing by the doctor movement towards the spasticity of the contracting muscle, with flexion and rotation of the contracting muscles (Kachesov V.A. Fundamentals of intensive rehabilitation. - M., 1999. - P. 76);
A known method of treating muscle spasm using postisometric relaxation, consisting of two phases, alternating 5-6 times, first perform isometric contraction of the muscle on inspiration for 8-10 s, with the help of light resistance provided by the doctor in the direction opposite to muscle contraction, then passive stretching of the muscle on exhalation for 10-20 s (Belova A.N. Neurorehabilitation. - M .: Antidor, 2000. - P. 115). This method is chosen for the prototype.
However, this method cannot be used to treat severe muscle spasticity, since it is carried out when the muscle is performing the contraction phase, which is possible only with unexpressed spasm; muscle contraction and retention of this phase for 8-10 s through the resistance created by the doctor causes persistent pain in the patient and provokes the subsequent progression of spasticity; with concomitant osteoporosis, with the development of muscle or joint contracture, with the application of greater force by the doctor to stretch the muscle, a limb fracture may occur during the passive stretching phase.
The objective of the invention is to increase the effectiveness of the treatment of muscle spasticity after a stroke.
The technical result is to reduce muscle spasm, normalize muscle tone.
This is achieved due to the fact that within 20-30 minutes the doctor performs passive stretching of the spasmodic muscle of the limb, combined with rotation of the hand or foot alternately in both directions, at the forced maximum exhalation of the patient, and holds the stretching phase until the end of the exhalation, the exercises are carried out for 3 weeks.
After placing the patient's limb in a comfortable position that helps to relax spasmodic muscles, the doctor performs a passive exercise, since the patient cannot perform active movements on his own; given that the length of the spasmodic muscle is sharply shortened, a stretching exercise is performed that increases the length of the muscle and provides reflex relaxation; turns of the hand or foot during the exercise create the direction of the physiological movement of the spasmodic muscle according to the biomechanics of movement, contributing to its uniform extensibility and restoration of the physiological tone; performing the exercise on exhalation creates conditions for reflex relaxation of the muscle, forced expiration will allow the patient to exhale as much as possible, which will lengthen the stretching time and allow you to work out the muscle more effectively; holding the phase of passive stretching of the muscle on exhalation contributes to its deeper relaxation and the muscle getting used to being in a “healthy” state, preventing its subsequent persistent spasm; exercises are performed until a feeling of stretching occurs, relieving the patient of persistent pain and limb injury; the duration of one lesson of 20-30 minutes allows you to repeat the exercise many times, increasing the angle of extension in the joint of the spasmodic limb, due to a gradual increase in the length of the muscle and its relaxation; a course of 3 weeks, as practice has shown, will reduce muscle spasm, restore muscle tone, and achieve full movement.
A method for treating muscle spasticity after a stroke is carried out as follows.
The spasmodic limb is placed in a comfortable position that provides muscle relaxation, after which, for 20-30 minutes, the doctor performs passive stretching of the spasmodic muscle of the limb, combined with rotation of the hand or foot alternately in both directions, at the forced maximum expiration of the patient, and holds the stretching phase until the end exhalation, exercises are carried out for 3 weeks.
Clinical example.
Patient Zh., C/C No. 22547. Diagnosis: Condition after acute circulatory disorders in the basin of the right anterior cerebral artery, dated March 22, 2009. Complaints about the lack of movement in the left arm, its constant bent position, periodic pain in the left shoulder.
The patient underwent rehabilitation treatment, in which the left arm was placed on a hard roller without abduction to the side, providing support from the shoulder joint to the elbow inclusive, which ensured muscle relaxation, after which the doctor performed passive stretching of the spasmodic muscle of the limb, combined with rotation of the hand alternately in both side, on a forced maximum expiration of the patient with retention of the stretching phase until the end of the exhalation. The exercise was performed daily for 20-30 minutes. The course of treatment was 3 weeks.
As a result of the treatment, the patient experienced a persistent decrease in spasticity of the muscles of the left upper limb, movement in her elbow joint was restored, and at rest she acquired her normal “straightened” position.
A method for treating a spastic state of muscles after a stroke by passive stretching of the muscle on exhalation, characterized in that for 20-30 minutes the doctor performs passive stretching of the spasmodic muscle of the limb, combined with rotation of the hand or foot alternately in both directions, at the forced maximum exhalation of the patient, and holds the stretching phase until the end of the exhalation, exercises are carried out for 3 weeks.
Similar patents:
The invention relates to medicine, namely to cardiology and angiology, and can be used to correct vascular wall dysfunctions in patients with stage III arterial hypertension (AH) with metabolic syndrome (MS) who have had ocular vascular thrombosis.
The invention relates to restorative medicine, physiotherapy exercises (exercise therapy) in the rehabilitation of children who have suffered a severe traumatic brain injury. .
The invention relates to medicine, namely to cardiac surgery, and can be used in the treatment of patients after cardiac surgery and who are on artificial lung ventilation (ALV).